Overview of Data Management Mechanisms for an Enterprise Data Hub
-
First, auditing is part of a system’s security regime and can explain what happened, when, and to whom or what in case of a breach or other malicious intent. For example, if a rogue administrator deletes a user’s data set, auditing provides the details of this action, and the correct data may be retrieved from backup.
-
The second activity is compliance, and auditing participates in satisfying the core requirements of regulations associated with sensitive or personally identifiable data (PII), such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) or the Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard. Auditing provides the touchpoints necessary to construct the trail of who, how, when, and how often data is produced, viewed, and manipulated.
-
Lastly, auditing provides the historical data and context for data forensics. Audit information leads to the understanding of how various populations use different data sets and can help establish the access patterns of these data sets. This examination, such as trend analysis, is broader in scope than compliance and can assist content and system owners in their data optimization efforts.
The risks facing auditing are the reliable, timely, and tamper-proof capture of all activity, including administrative actions. Until recently, the native Hadoop ecosystem has relied primarily on using log files. Log files are unacceptable for most audit use cases in the enterprise as real-time monitoring is impossible, and log mechanics can be unreliable - a system crash before or during a write commit can compromise integrity and lead to data loss.
Cloudera Navigator is a fully integrated data management and security tool for the Hadoop platform. Data management and security capabilities are critical for enterprise customers that are in highly regulated industries and have stringent compliance requirements. This topic only provides an overview of some of the auditing and metadata management capabilities that Cloudera Navigator offers. For complete details, see Cloudera Data Management.
Cloudera Navigator
The following sections describe some of the categories of functionalities Cloudera Navigator provides for auditing, metadata management and lineage.
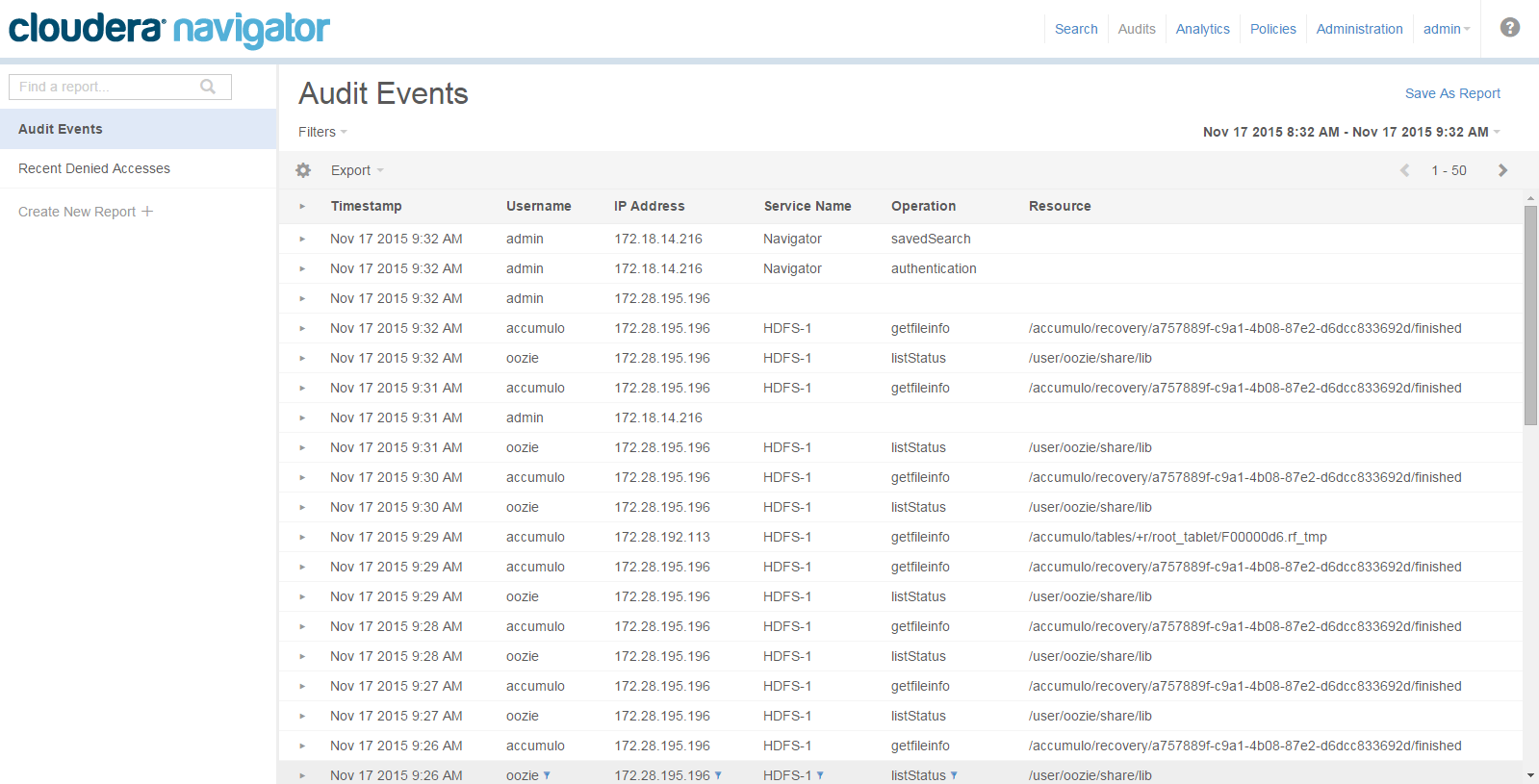
Auditing
- HDFS entities accessed by HDFS, Hive, HBase, Impala, and Solr services
- HBase and Impala
- Hive metadata
- Sentry
- Solr
- Cloudera Navigator Metadata Server
Metadata Management
For metadata and data discovery, Cloudera Navigator features complete metadata storage. First, it consolidates the technical metadata for all data inside Hadoop into a single, searchable interface and allows for automatic tagging of data based on the external sources entering the cluster. For example, if there is an external ETL process, data can be automatically tagged as such when it enters Hadoop. Second, it supports user-based tagging to augment files, tables, and individual columns with custom business context, tags, and key/value pairs. Combined, this allows data to be easily discovered, classified, and located to not only support governance and compliance, but also user discovery within Hadoop.
Cloudera Navigator also includes metadata policy management that can trigger actions (such as the autoclassification of metadata) for specific datasets based on arrival or scheduled intervals. This allows users to easily set, monitor, and enforce data management policies, while also integrating with common third-party tools.
For details on how Cloudera Navigator handles metadata, see Cloudera Navigator Metadata Architecture.
Lineage
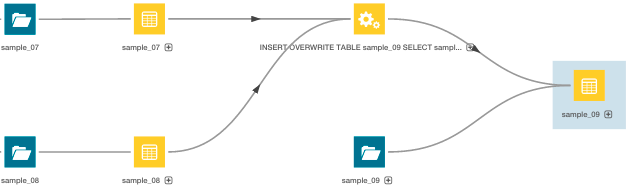
Cloudera Navigator provides an automatic collection and easy visualization of upstream and downstream data lineage to verify reliability. For each data source, it shows, down to the column-level within that data source, what the precise upstream data sources were, the transforms performed to produce it, and the impact that data has on downstream artifacts. Cloudera Navigator supports tracking the lineage of HDFS files, datasets, and directories, Hive tables and columns, MapReduce and YARN jobs, Hive queries, Impala queries, Pig scripts, Oozie workflows, Spark jobs, and Sqoop jobs. For details, see Cloudera Navigator Lineage Diagrams.
Integration within an EDH
- Using syslog, thus acting as a mediator between the raw event streams in Hadoop and the SIEM tools.
- Using a REST API for custom enterprise tools.
- You can also simply export the data to a file, such as a comma-delimited text file.
Auditing in Hadoop Projects
This section describes the CDH and managed service versions supported by the Cloudera Navigator auditing and metadata features.
Cloudera Navigator Auditing
| Component | Operations (For details, see Cloudera Navigator Auditing). | Minimum Supported Service Version |
|---|---|---|
| HDFS |
|
CDH 4.0.0 |
| HBase |
|
CDH 4.0.0 |
| Hive |
|
CDH 4.2.0, CDH 4.4.0 for operations denied due to lack of privileges. |
| Hue |
|
CDH 4.4.0 |
|
CDH 5.5.0 | |
| Impala |
|
Impala 1.2.1 with CDH 4.4.0 |
| Navigator Metadata Server |
|
Cloudera Navigator 2.3 |
| Sentry |
|
CDH 5.1.0 |
| Solr |
|
CDH 5.4.0 |
Cloudera Navigator Metadata
This section describes the CDH and managed service versions supported by the Cloudera Navigator metadata feature.| Component | Minimum Supported Version |
|---|---|
| HDFS. However, federated HDFS is not supported. | CDH 4.4.0 |
| Hive | CDH 4.4.0 |
| Impala | CDH 5.4.0 |
| MapReduce | CDH 4.4.0 |
Oozie. Supported actions:
|
CDH 4.4.0 |
| Pig | CDH 4.6.0 |
| Spark | CDH 5.4.0 |
| Sqoop 1. All Cloudera connectors are supported. | CDH 4.4.0 |
| YARN | CDH 5.0.0 |