ZooKeeper Authentication
As of Cloudera Manager 5.11, ZooKeeper supports mutual server-to-server (quorum peer) authentication using SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer), which provides a layer around Kerberos authentication. Server to server authentication among ZooKeeper servers in an ensemble mitigates the risk of spoofing by a rogue server on an unsecured network. For more information about quorum peer authentication and how the feature leverages ZooKeeper's SASL support, see the Cloudera Engineering Blog post, Hardening Apache ZooKeeper Security.
Client-to-server SASL-based authentication has been supported since Cloudera Manager/CDH 5.2 (ZooKeeper 3.4.0+). Follow the steps in Configuring ZooKeeper Server for Kerberos Authentication and Configuring ZooKeeper Client Shell for Kerberos Authentication to configure ZooKeeper to use this mechanism.
To configure client-server or server-server authentication for ZooKeeper, follow the appropriate steps below:
Requirements
Configuring ZooKeeper to use Kerberos for client-server or server-server authentication requires that your organization's Kerberos instance (MIT Kerberos, Microsoft Active Directory) be up and running, and reachable by the ZooKeeper server or client during the configuration processes detailed below. See Configuring Hadoop Security in CDH 5 for details.
Before enabling mutual authentication, the ZooKeeper servers in the cluster must be configured to authenticate using Kerberos.
Configuring ZooKeeper Server for Kerberos Authentication
You can configure the ZooKeeper server for Kerberos authentication in Cloudera Manager or through the command line.
Using Cloudera Manager to Configure ZooKeeper Server for Kerberos Authentication
To set up the ZooKeeper server for Kerberos authentication in Cloudera Manager, complete the following steps:
- In Cloudera Manager, open the ZooKeeper service.
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Enter Kerberos in the in the Search bar.
- Find the Enable Kerberos Authentication property and select the check-box next to the ZooKeeper services that you want to configure for Kerberos authentication.
Using the Command Line to Configure ZooKeeper Server for Kerberos Authentication
Follow the steps below for each ZooKeeper server in the ensemble. To maintain consistency across ZooKeeper servers in the ensemble, use the same name for the keytab file you deploy to each server, for example, zookeeper.keytab. Each keytab file will contain its respective host's fully-qualified domain name (FQDN).
- Create a service principal for the ZooKeeper server using the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the host on which ZooKeeper server is running and the name of your Kerberos realm
using the pattern zookeeper/fqdn.example.com@ YOUR-REALM. This principal will be used to
authenticate the ZooKeeper server with the Hadoop cluster. Create this service principal as follows:
kadmin: addprinc -randkey zookeeper/fqdn.example.com@YOUR-REALM
- Create a keytab file for the ZooKeeper server:
$ kadmin kadmin: xst -k zookeeper.keytab zookeeper/fqdn.example.com@YOUR-REALM
- Copy the zookeeper.keytab file to the ZooKeeper configuration directory on the ZooKeeper server host, using the appropriate ZooKeeper configuration directory: /etc/zookeeper/conf/. The zookeeper.keytab file should be owned by the zookeeper user, with owner-only read permissions.
- Add the following lines to the ZooKeeper configuration file zoo.cfg:
authProvider.1=org.apache.zookeeper.server.auth.SASLAuthenticationProvider jaasLoginRenew=3600000
- Set up the Java Authentication and
Authorization Service (JAAS) by creating a jaas.conf file in the ZooKeeper configuration directory with the settings shown below, replacing fqdn.example.com with the ZooKeeper server's hostname.
Server { com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required useKeyTab=true keyTab="/etc/zookeeper/conf/zookeeper.keytab" storeKey=true useTicketCache=false principal="zookeeper/fqdn.example.com @YOUR-REALM"; }; - Add the following setting to the java.env file located in the ZooKeeper configuration directory, creating the file if necessary:
export JVMFLAGS="-Djava.security.auth.login.config=/etc/zookeeper/conf/jaas.conf"
- Repeat these steps for each ZooKeeper server in the ensemble.
- Restart the ZooKeeper server to have the configuration changes take effect. See ZooKeeper Installation for details.
Configuring ZooKeeper Client Shell for Kerberos Authentication
In addition to configuring ZooKeeper Server hosts to use Kerberos for authentication, you should also configure the ZooKeeper client shell (the ZooKeeper CLI) to authenticate to the ZooKeeper service using Kerberos credentials. As with the ZooKeeper Server, you must create a Kerberos principal for the client, as detailed below:
- Create a Kerberos principal for the zookeeper-client, zkcli@YOUR-REALM, replacing
YOUR-REALM with the name of your organization's Kerberos realm:
kadmin: addprinc -randkey zkcli@YOUR-REALM
- Create a keytab file for the ZooKeeper client shell using the -norandkey option.
$ kadmin kadmin: xst -norandkey -k zkcli.keytab zkcli@YOUR-REALM
- On the host running the ZooKeeper client shell, set up JAAS (Java Authentication and Authorization Service) in the configuration directory appropriate for your installation type:
- Package installation: /etc/zookeeper/conf/
- Tarball installation: EXPANDED_DIR/conf
- Create a jaas.conf file containing the following settings:
Client { com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required useKeyTab=true keyTab="/path/to/zkcli.keytab" storeKey=true useTicketCache=false principal="zkcli@YOUR-REALM"; }; - In this same configuration directory, add the following setting to the java.env file, creating the file if necessary.
export JVMFLAGS="-Djava.security.auth.login.config=/etc/zookeeper/conf/jaas.conf"
Verifying the Configuration
- Start the ZooKeeper client, passing to it the name of a ZooKeeper server:
zookeeper-client -server fqdn.example.com:port
- From the ZooKeeper CLI, create a protected znode using your ZooKeeper client principal:
create /znode1 znode1data sasl:zkcli@{{YOUR-REALM}}:cdwra - Verify the znode is created and the ACL is set correctly:
getAcl /znode1
Enabling Server-Server Mutual Authentication
As of Cloudera Manager 5.11, support for mutual authentication between ZooKeeper Servers can be enabled through the Cloudera Manager Admin Console. For secured networks, server-to-server
authentication is considered an optional security enhancement, so the capability is disabled by default:
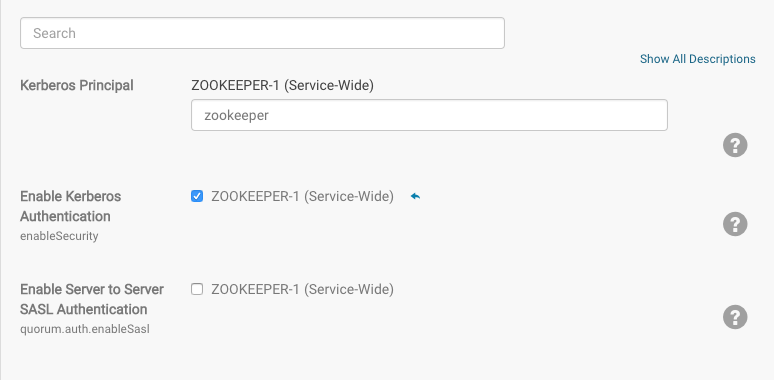
Server-to-server SASL authentication requires all servers in the ZooKeeper ensemble to authenticate using Kerberos, as detailed in Configuring ZooKeeper Server for Kerberos Authentication.
- Log into the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- Select .
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Select under the Filters menu to display the security properties.
- Click the Enable Server to Server SASL Authentication box to select it.
- Click Save.
- Select Restart from the Actions drop-down to restart the cluster with this setting.
To disable server-to-server SASL authentication, simply return to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console page shown above, de-select Enable Server to Server SASL Authentication (by clicking the checked box), and restart the cluster.