Setting Up Navigator Audit Server
The steps below show you how to add the Navigator Audit Server role to an existing Cloudera Manager cluster.
The Navigator Audit Server role runs on the Cloudera Management Service. By default, the installation process installs both Navigator Audit Server and Navigator Metadata Server roles on the same Cloudera Management Service instance, but that may not be optimal, especially for very large clusters.
Continue reading:
- Adding the Navigator Audit Server Role
- Starting, Stopping, and Restarting the Navigator Audit Server
- Configuring the Navigator Audit Server Data Expiration Period
- Review the Navigator Audit Server Filters
- Setting the Navigator Audit Server Java Heap Size
- Configuring the Navigator Audit Server Log Directory
Adding the Navigator Audit Server Role
Cloudera Manager Required Role: Navigator Administrator (or Full Administrator)
The steps below assume that an external database is running and available to be used with the Navigator Audit Server role. Before adding this role, gather the configuration details about the external database instance so you can enter them when needed during this process.
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- From the menu, select .
- Click theInstances tab.
- Click Add Role Instances. The Customize Role Assignments page displays and lists the nodes available to support additional roles, assuming the cluster has available resources. Reassign and customize role instances as needed.
- Select the Navigator Audit Server role and assign it to appropriate host for your cluster.
- When finished, click Continue. The Database Setup page displays.
- Click Use Custom Database.
- In the Navigator Audit Server section, enter the details of your database instance:
- Database host name
- Database type
- Database name
- Username
- Password
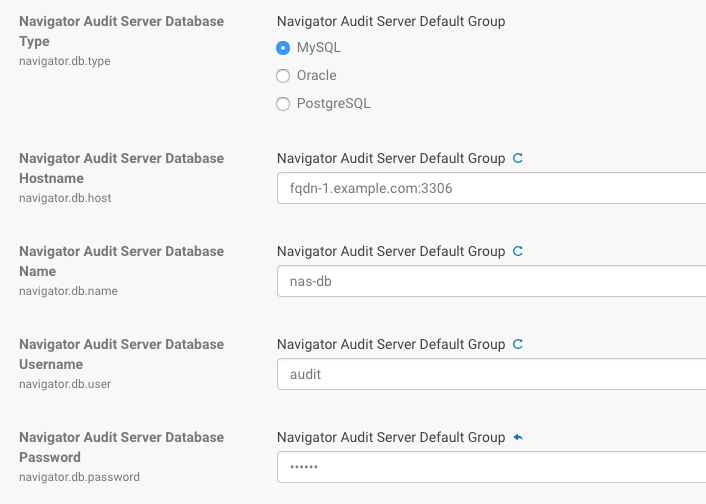
- Click Test Connection to verify the communication between the cluster and the external database. If the test fails, check the database settings and try again. If you selected embedded database, a message displays regarding database creation.
- Click Continue.
- The Cluster Setup Review Changes page displays.
- Click Finish.
Starting, Stopping, and Restarting the Navigator Audit Server
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- From the menu, select .
- Click the Instances tab.
- Click the link for the Navigator Audit Server from the Role Type list. The Actions for Selected button activates and displays (1) for the selected role.
- From the Actions for Selected (1) menu, select the Action you want to perform on
this role instance:
- Start
- Stop
- Restart
- Enter Maintenance Mode
- Exit Maintenance Mode
- Delete
- Click Cancel to abandon the process, or click Action to execute the action.
Configuring the Navigator Audit Server Data Expiration Period
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- From the menu, select .
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Select Navigator Audit Server from the Scope filter.
- For the Navigator Audit Server Data Expiration Period, enter the number of days or hours or audit events that should be retained in the database before purging and select either day(s) or hour(s) from the drop-down to label the value accordingly.
- Restart the Navigator Audit Server role.
Review the Navigator Audit Server Filters
Cloudera Manager Required Role: Navigator Administrator (or Full Administrator)
By far, HDFS produces the largest volume of audit events. Many of these events are caught and discarded by audit filters, particularly events that don't uniquely describe activity on the cluster or are produced only by controlled service users. Many of the default HDFS audit filters assume default service role names. To get value from the default filters, be sure to review them to make sure that the role names referenced match those used in your environment.
See Default and Recommended Audit Filters for HDFS for more information about the provided filters and their use.
You can review and possibly change the filters as follows:
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- Select an HDFS service. Select
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Filter the properties on "audit".
- Review the list of filters in the property Audit Event Filter.
Show Me How
- Action: accept Fields: allowed: (?:false)
Collect events where the value of the audit event field "allowed" is false. This filter is first in the list to make sure that all events are tested against this filter.
- Action: discard Fields: src: (?:.*/\.hive‑staging($|.*)?|.*/\.staging($|/.*)?|.*/\.sparkStaging($|/.*)?
|.*/_impala_insert_staging($|/.*)?|/user/history/done_intermediate(?:/.*)? |/user/spark/spark2ApplicationHistory($|/.*)|/user/spark/applicationHistory($|/.*)
|/user/hue/\.cloudera_manager_hive_metastore_canary(?:/.*)? |/user/hue/\.Trash/Current/user/hue/\.cloudera_manager_hive_metastore_canary(?:/.*)? |/tmp(?:/.*)?)
Don't collect events that occur in these directories. Typically, HDFS operations in these directories represent background operations performed by service users. Consider modifying the paths to match how your environment is configured or removing directories from the list. Note that the regular expression entry ($|.*) indicates the directory itself and any subdirectories.
- Action: accept Fields: operation: delete|rename.*
Collect events that describe HDFS delete or rename operations. The regular expression entry .* indicates that add types of rename events are collected, such as rename options=1.
- Action: discard Fields: username: (?:cloudera-scm|dr.who|hbase|hive|impala|mapred|solr|spark)(?:/.+)?
Don't collect operations performed by this list of service users. Note that these are the default role names suggested by Cloudera Manager. If your environment uses other role names, consider replacing the names in the filter.
- Action: discard Fields: username: (?:hdfs)(?:/.+)?, operation:
(?:listStatus|listCachePools|listCacheDirectives|getfileinfo)
Don't collect these specific operations performed by the HDFS superuser. These operations describe metadata operations that do not reveal data access attempts. In addition, these operations tend to be background operations that are triggered when other services perform operations. Removing them from the audit log significantly reduces the volume of audit events without losing critical events. Note that this filter uses hdfs as the HDFS superuser account. Your environment may be configured with a different or more than one different user name with superuser privileges. To make this filter effective, change the name to that used in your system.
- Action: accept Fields: operation: (?:getfileinfo)
Added as a placeholder. Switch the action to discard to enable the filter. When set to discard, this filter does not collect any HDFS getfileinfo operation events. This is recommended for systems where this metadata event is not a meaningful audit event. Discarding it can make a significant reduction in the overall volume of the audit database as the getfileinfo event occurs along with every other action in HDFS directly or through services that access HDFS. Left as it is (accept), it has no effect.
- Action: accept Fields: allowed: (?:false)
- Make changes to the filters as appropriate.
- Restart the Navigator Audit Server role.
Setting the Navigator Audit Server Java Heap Size
Cloudera Manager Required Role: Navigator Administrator (or Full Administrator)
The Navigator Audit Server performance is typically bound by the performance of the database. With that in mind, consider increasing the Navigator Audit Server Java heap to as much as 4 GB; increasing heap beyond this point is unlikely to change the server performance. The default Java heap is set to 1.5 GiB.
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- Select .
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Select .
- For Filter Category, click Resource Management to display the Java Heap Size property.
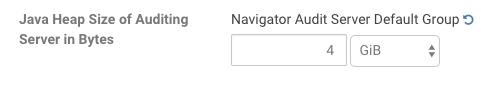
- Use the drop-down selector to change the unit scale to B (Bytes), KiB, MiB, or GiB and set your preferred heap size.
- Click Save Changes.
The setting takes effect only after restarting the role. Restart the Navigator Metadata Server role now or make other configuration changes and restart after you are finished with all changes.
- Restart the Navigator Audit Server role.
Configuring the Navigator Audit Server Log Directory
/var/log/cloudera-scm-navigator
- Log in to the Cloudera Manager Admin Console.
- From the menu, select .
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Select .
- Enter the path for the Navigator Audit Server Log Directory property.
- Restart the Navigator Audit Server role.