Using Spark SQL
This section provides information about using Spark SQL.
Using SQLContext, Apache Spark SQL can read data directly from the file system. This is useful when the data you are trying to analyze does not reside in Apache Hive (for example, JSON files stored in HDFS).
Using HiveContext, Spark SQL can also read data by interacting with the Hive MetaStore. If you already use Hive, you should use HiveContext; it supports all Hive data formats and user-defined functions (UDFs), and it enables you to have full access to the Hive parser. HiveContext extends SQLContext, so HiveContext supports all SQLContext functionality.
There are two ways to interact with Spark SQL:
-
Interactive access using the Spark shell (see "Accessing Spark SQL through the Spark Shell" in this guide).
-
From an application, operating through one of the following two APIs and the Spark Thrift server:
-
JDBC, using your own Java code or the Beeline JDBC client
-
ODBC, through the Simba ODBC driver
For more information about JDBC and ODBC access, see "Accessing Spark SQL through JDBC: Prerequisites" and "Accessing Spark SQL through JDBC and ODBC" in this guide.
-
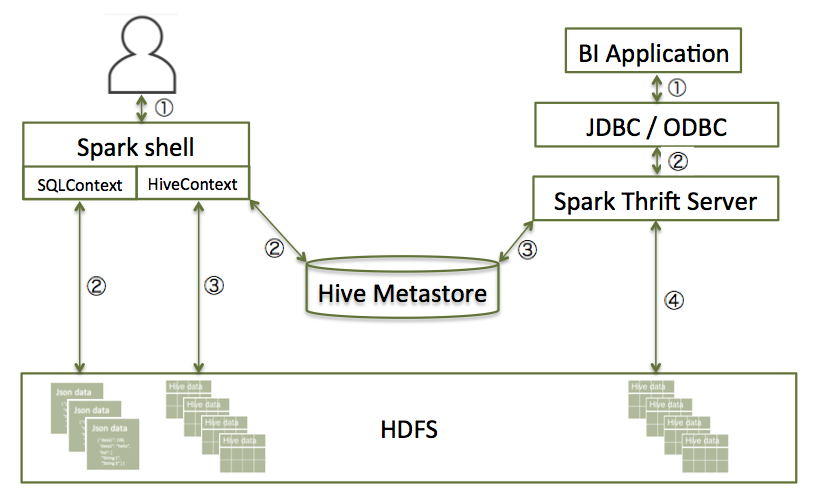
The following diagram illustrates the access process, depending on whether you are using the Spark shell or business intelligence (BI) application:
The following diagram illustrates the access process, depending on whether you are using the Spark shell or business intelligence (BI) application:
The following subsections describe how to access Spark SQL through the Spark shell, and through JDBC and ODBC.


