Cloudera SDX for Altus: Best Practices and Supported Configuration
Cloudera Shared Data Experience (SDX) for Altus is a centralized framework for data management and governance for CDH clusters in the cloud. While cluster data is stored in cloud storage such as Amazon S3 or Azure Data Lake Store (ADLS), Cloudera SDX externalizes cluster metadata into a shared database available to all workloads and clusters running in the cloud. Workloads in multiple clusters share access to the same consistent data and metadata with no need for replication.
You can set up Cloudera SDX for clusters that you create using Altus Director or Cloudera Manager and share data with Altus services clusters. The Altus SDX service provides configured SDX namespaces that enable you to share Hive metastore (HMS) and Sentry data between Altus Data Warehouse and Altus Data Engineering clusters and clusters that you create with Altus Director or Cloudera Manager.
The following image shows the components in Cloudera SDX and how they interact:
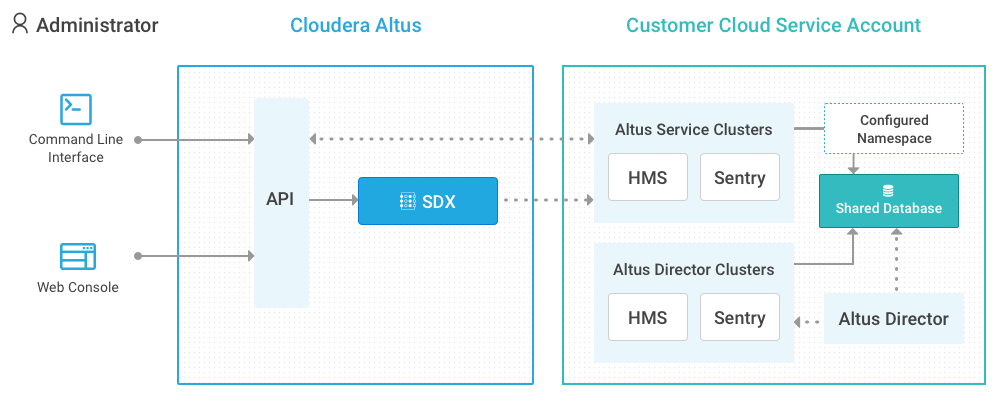
- CDH clusters created with Cloudera Manager or Altus Director
- You can configure Cloudera SDX for CDH clusters created with Altus Director or Cloudera Manager to share data with other CDH clusters. Set up external databases for Hive metastore (HMS) and Sentry to be shared between CDH clusters created using Altus Director, Cloudera Manager, or Altus cloud services.
- Altus Data Engineering or Altus Data Warehouse clusters
- Altus services clusters use an Altus SDX namespace to point to databases for shared data and metadata. To share data with clusters created using Altus Director or Cloudera Manager, set up a configured SDX namespace in Altus services to point to the same databases used for the clusters in Altus Director and Cloudera Manager.
Setting Up Cloudera SDX
To share data between CDH clusters, set up the Hive metastore and Sentry databases for the clusters created with Cloudera Manager or Altus Director. Then, in Altus services, create a configured SDX namespace that uses the same Hive metastore and Sentry databases. Altus Data Warehouse or Altus Data Engineering clusters that use the configured SDX namespace can share metadata and access policies with clusters created with Altus Director or Cloudera Manager that use the Hive metastore and Sentry databases.
On AWS, you can manually set up or use Altus Director to set up a database for the Hive metastore and Sentry data. On Azure, manually set up a database for the Hive metastore and Sentry data.
- Set up the Hive metastore and Sentry databases and create a cluster using Altus Director or Cloudera Manager.
- Set up a configured SDX namespace and cluster in Altus.
Setting up the Databases and Clusters with Altus Director or Cloudera Manager
You can use Altus Director to deploy CDH clusters on the cloud. You can also use Cloudera Manager to create and manage clusters.
-
Set up external databases for the Hive metastore and Sentry databases.
On AWS, configure Altus Director to create an Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) instance and set up databases for the Hive metastore and Sentry data. When you configure the RDS, set the configuration parameters according to the number of clusters that will share the RDS. For example, scale up the maximum number of connections to accommodate the number of clusters sharing the database. For more information about setting up a Hive metastore database using RDS, see the blog post, How To Set Up a Shared Amazon RDS as Your Hive Metastore.
On Azure, install a database server and create databases for the Hive metastore and Sentry.
Make note of the following details for each database that you create:- Host name and port number
- Database name
- User name and password for the database administrator
-
Create the cluster using Altus Director or Cloudera Manager.
If you use Altus Director to create a cluster, follow the SDX Director template. The Kerberos configuration settings in the template are required for SDX. Update the parameters that show a value of REPLACE-ME with values appropriate for your setup.
If you use Cloudera Manager to create a cluster, enable Kerberos so that the clusters can share Sentry access policies.
On AWS, create the cluster in the same Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) where you set up the database servers. You can use Altus Director to create the schema in the Hive metastore and Sentry database.
On Azure, install Altus Director and create the cluster on the same virtual network where you set up the database server.
When you create the cluster, complete the following tasks:-
Configure it to use the Hive metastore and Sentry external databases.
Set the database hostname, port number, and login credentials for the Hive metastore and Sentry databases that you set up in Step 1. The Hive services in all the clusters must share the same Server Name for Sentry Authorization property.
Restart the Hive and Sentry services.
-
Set up access from the clusters to your data in object storage.
The cluster must have read and write privileges to the object storage so that workloads can create and update data and metadata in the Hive metastore and Sentry databases.
On AWS, you can enable access to Amazon S3 for the hosts in your cluster in one of the following two ways:- Configure the Amazon S3 connector in your cluster.
Define AWS credentials in Cloudera Manager and then add and configure the S3 Connector Service to use the AWS credentials. For more information about configuring secure access to Amazon S3 through the S3 connector, see Configuring the Amazon S3 Connector
- Configure all hosts with IAM role-based authentication that allows access to S3.
If you configure role-based authentication, you do not need to add the Amazon S3 connector service or use S3Guard.
On Azure, enable access to ADLS for the hosts in your cluster in one of the following ways:- Configure the ADLS Connector in your cluster.
Configure ADLS credentials and add the ADLS Connector service to your cluster. The ADLS connector service provides a secure connection between the cluster and ADLS. For more information about configuring secure access to ADLS through the ADLS connector, see Configuring ADLS Access Using Cloudera Manager.
- Set up a connection from cluster to ADLS through properties in configuration files.
For more information about configuring connectivity to ADLS through configuration files, see Configuring ADLS Connectivity for CDH.
Note that using configuration files to provide access to ADLS for jobs running in a cluster can compromise security. Cloudera recommends that you use this method only to access ADLS in development environments or other environments where security is not a concern.
- Configure the Amazon S3 connector in your cluster.
-
-
Note the URI and administrator credentials for the Hive metastore and Sentry databases.
You can find the database URI on the Altus Director web UI. On the Cluster Details page go to the Database Servers section. Click Learn More to display the JDBC URLs for the Hive metastore and Sentry databases.
For each database, make note of the following details:- Connection URI
- User name and password for the database administrator
-
Grant administrator privileges to the Sentry administrator group.
You can use Hue, Beeline, or impala-shell to set permissions for the Sentry groups that access the Hive metastore. All clusters that use the same Sentry groups have the same access permissions to data and metadata in the Hive metastore.
Sentry permissions are not granted per cluster: all clusters use the same permissions data. Every Hive service must share the same value in the Server Name for Sentry Authorization property.
You can set up Cloudera Navigator to display lineage data from Altus Data Engineering clusters on AWS. For more information, see Cluster Lineage for CDH Clusters.
Setting up an Altus SDX Namespace and Cluster
Altus SDX is an Altus cloud service that externalizes cluster metadata to provide a consistent view of data for multiple clusters and workloads running on the cloud. You can set up a configured SDX namespace in Altus services that points to an existing Hive metastore and Sentry databases for CDH clusters on the cloud. With a configured SDX namespace, you can share data between clusters created with Altus Director or Cloudera Manager and Altus Data Engineering and Altus Data Warehouse clusters.
-
Identify the Hive metastore and Sentry databases that you want to use for the configured SDX namespace.
Get the connection URI and administrator credentials for the Hive metastore and Sentry databases that you set up for the cluster in Altus Director.
-
Create a configured SDX namespace in Altus.
To create a configured SDX namespace, you must be an Altus administrator or have the Altus SdxAdmin role.
When you create the configured SDX namespace, you must provide the connection URI and administrator credentials for the Hive metastore and Sentry databases. In the Hive Metastore Settings section, specify the JDBC URI and the database administrator credentials for the Hive metastore database. In the Sentry Settings section, specify the JDBC URI and the database administrator credentials for the Sentry database.
For more information about creating a configured SDX namespace, see Creating an SDX Namespace in the Altus documentation.
-
Create an Altus Data Engineering or Data Warehouse cluster and set up the cluster to use the configured SDX namespace.
Set the following parameters when you create the Altus cluster:- SDX Namespace. Specify the configured SDX namespace that uses the Hive metastore and Sentry databases for the clusters in Altus Director.
- Environment. Specify an environment with the Secure Clusters option enabled. The
environment must also be set up to allow access to the Hive metastore and Sentry databases.
If the environment you specify also has the Cloudera Navigator integration option enabled, you can view cluster lineage in Cloudera Navigator for Altus Data Engineering clusters on AWS. For more information, see Cluster Lineage for CDH Clusters.
Note that a cluster that has the MapReduce2 service cannot use a configured SDX namespace.
-
Grant all privileges to the Sentry administrator group.
When you create a configured SDX namespace, Altus creates an Altus group and sets it up as an administrator group in Sentry. You, as creator of the configured SDX namespace, are a member of the group by default. If you use the configured SDX namespace with an Altus Data Engineering cluster, Altus also adds the altus user account, which runs data engineering jobs, to the group. Members of the Sentry administrator group can create roles and grant privileges in Sentry.
You must create a role with all privileges and assign the role to the SDX Sentry administrator group so that members of the group can create and manage the databases as required.
To grant all privileges to the SDX Sentry administrator group, run the following commands:create role SentryAdminRoleForAltus; grant all on server server1 to role SentryAdminRoleForAltus; grant role SentryAdminRoleForAltus to group SDXSentryAdminGroup;
For Altus Data Engineering clusters, submit a Hive job to run the commands.
For Altus Data Warehouse clusters, use the Query Editor to run the commands.
- If you are working with Altus Data Warehouse clusters, set up the users and groups in Altus and synchronize them with the cluster.
For more information about setting up users and group for Altus Data Warehouse clusters, see Setting Up User Access to an Altus Data Warehouse Cluster.
Guidelines for Using Cloudera SDX
- When you create databases and tables, use the LOCATION attribute to write the data to cloud storage.
-
When you create a database or table that you want to make accessible to multiple clusters, you must create the database or table in cloud storage. On AWS, create the databases in Amazon S3. In Azure, create the databases in Azure Data Lake Store (ADLS).
Use the LOCATION attribute to indicate the location in cloud storage where you want to create the database or table. If you do not provide the location, the database or table is created in a default location in HDFS in the cluster. When the cluster is terminated, the HDFS databases and tables are lost.
The following examples show the CREATE DATABASE statement with the LOCATION attribute pointing to Amazon S3 and ADLS locations:CREATE DATABASE databasename LOCATION s3a://path-to-aws-s3/dir/db CREATE DATABASE databasename LOCATION adl://path-to-azure-adl/dir/db
For more information about creating a database using Impala SQL statements, see CREATE DATABASE Statement.
The following examples show the CREATE TABLE statement with the LOCATION attribute pointing to Amazon S3 and ADLS locations:CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE tablename LOCATION s3a://path-to-aws-s3/dir/table_data CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE tablename LOCATION adl://path-to-azure-adl/dir/table_data
For more information about creating a table using Impala SQL statements, see CREATE TABLE Statement.
To view the location attribute of a database, use the DESCRIBE DATABASE statement:DESCRIBE DATABASE databasename
- Avoid concurrent updates by multiple clusters to the same schema, table, or partitions in a table.
-
Cloudera SDX does not manage the metadata updates made by different clusters. It does not have a mechanism to lock the metadata to prevent simultaneous updates by multiple clusters. Data conflicts and errors can arise if multiple clusters sharing an SDX namespace access a dataset at the same time and perform conflicting updates.
For example, problems can arise if multiple clusters concurrently update the same table or partitions within a table or add or change the same schema or database.
Run your workloads in a way that ensures that multiple clusters do not make overlapping data or metadata changes.
- Avoid concurrent updates by multiple clusters to the same Sentry groups and roles.
-
Cloudera SDX does not manage the updates to the Sentry groups and roles made by different clusters. It does not have a mechanism to prevent clusters from concurrently setting or updating permissions on the same metadata. Errors can arise if multiple clusters perform conflicting updates to the same groups and roles at the same time.
- Ensure that interim local tables in HDFS are deleted before you terminate a cluster.
-
When you write interim data to a table stored in HDFS in a cluster, the metadata for the interim files is stored in the Hive metastore tables. If you terminate the cluster, Cloudera SDX does not delete the metadata for these tables from the Hive metastore.
The metadata remains in the Hive metastore tables and can cause data conflicts and errors for other clusters. For example, a job in another cluster that uses the same Hive metastore tables might try to read data in the tables and encounter errors because the HDFS locations do not exist or are not be valid.
To avoid errors with orphaned metadata in the Hive metastore tables, delete all tables created in HDFS before you terminate a cluster.
Cluster Lineage for CDH Clusters
Cloudera Navigator provides a unified view of cluster metadata and lineage across all clusters managed by a Cloudera Manager instance. In Altus Director, you can deploy multiple clusters to be managed by one Cloudera Manager instance. However, when you create clusters with Altus cloud services, each cluster is managed by a separate Cloudera Manager instance.
Altus services provide a Cloudera Navigator integration option that enables Altus Data Engineering clusters to send workload metadata to an Amazon S3 bucket configured as a metadata resource in Cloudera Navigator. On AWS, you can include Altus Data Engineering cluster metadata to the lineage information of clusters managed by another Cloudera Manager.
If you create an Altus Data Engineering cluster that uses an environment with the Cloudera Navigator integration option enabled, Cloudera Navigator can extract metadata from the S3 bucket to generate analytics and data lineage for the cluster. You can configure Altus to send cluster and workload metadata to an S3 bucket that is used by Cloudera Navigator for clusters managed by a Cloudera Manager instance. You can then configure Cloudera Navigator to extract metadata from the shared S3 bucket to display cluster lineage for clusters a Cloudera Manager instance and the Altus Data Engineering cluster.
-
In the Cloudera Manager instance that manages the clusters for which you want to display lineage data, enable the option to extract metadata and lineage data from Altus and specify the Amazon S3 bucket for metadata extraction.
Follow the instructions in Cloudera Navigator Configuration to set up the AWS credentials and connectivity and configure Cloudera Navigator to enable metadata and lineage extraction from Altus services clusters.
-
In Altus services, enable the Cloudera Navigator integration option in the Altus environment of the clusters from which Cloudera Navigator can extract lineage metadata. Specify the Amazon S3 bucket configured as a resource for metadata extraction in Cloudera Navigator.
The S3 bucket must be the same S3 bucket that is configured for metadata and data lineage for the CDH clusters with which you want to share data.
For more information about the Cloudera Navigator integration option, see Altus Environment Options in the Altus documentation.
For more information about creating an environment with the Cloudera Navigator integration option enabled, see Altus Environment Setup for AWS in the Altus documentation.
For more information about using Cloudera Navigator with Altus clusters, see Using Cloudera Navigator with Altus Clusters.
Supported Services and Components
You can set up Cloudera SDX to share data between clusters deployed with Altus Director or Cloudera Manager in AWS or Azure and secure Altus Data Warehouse and Altus Data Engineering clusters.
| Component | Cloudera Manager or Altus Director | Altus Services |
|---|---|---|
| Database |
|
Configured SDX namespace that uses databases deployed and initialized by Altus Director or Cloudera Manager. |
| Database server location |
|
Specify the URI that points to the Hive metastore and Sentry databases for clusters created with Altus Director. The Hive metastore and Sentry databases must be accessible from the Altus services clusters. |
| CDH version |
|
|
| Cloudera Navigator |
|
|
| File System |
|
|