Adding and Editing Metadata
Minimum Required Role: Metadata Administrator (also provided by Full Administrator)
- Custom metadata - Display name, description, tags, and key-value pairs. You can add and edit custom metadata using the Navigator UI, MapReduce service and job properties, HDFS metadata files, and the Cloudera Navigator Data Management API. Custom metadata is typically implemented by end users who want to be able to classify and organize information for their own uses or to collaborate with other users.
- Managed metadata. You can add and edit managed metadata using the Navigator UI and the API. Managed metadata is typically implemented for centralized curation of data sets.
Continue reading:
- Adding and Editing Metadata Using the Navigator UI
- Custom Metadata Example
- Managed Metadata Example
- Editing MapReduce Custom Metadata
- Example: Setting Properties Dynamically
- Editing HDFS Custom Metadata Using Metadata Files
- Editing HDFS and Hive Metadata Using the Navigator Metadata API
- HDFS PUT Custom Metadata Example for /user/admin/input_dir Directory
- HDFS POST Custom Metadata Example for /user/admin/input_dir Directory
- Hive POST Custom Metadata Example for total_emp Column
- HDFS PUT Managed Metadata Example
- Accessing and Editing Metadata with the Navigator SDK
Adding and Editing Metadata Using the Navigator UI
- Run a search in the Navigator UI.
- Click an entity link returned in the search. The Details tab displays.
- To the left of the Details tab, click . The Edit Metadata dialog box drops down.
- Add metadata fields:
- In the Name field, type a new display name.
- In the Description field, type a description.
- Managed Metadata
- Click the
 and select a property.
and select a property. - Click the value field after the : to display type-specific selection controls such as integer spinners and date selection controls. Either type the value or use the controls to select a value.
 to add another managed property key-value pair or another value for a
given key.
to add another managed property key-value pair or another value for a
given key. - Click the
- Custom Metadata: In the Tags field, type a tag and press Enter or Tab to create new tag entries.
- Key-Value Pairs
- Click
 to add a key-value pair.
to add a key-value pair. - Type a key and a value. You can specify special characters (for example, ".", " ") in the name, but it makes searching for the entity more difficult because some characters collide with special characters in the search syntax.
- Click
- Click Save. The new metadata appears in the Managed Metadata or Custom Metadata pane.
Custom Metadata Example
In the following example, the tag archive_personal and the property year with value 2015 have been added to the file 2015_11_20: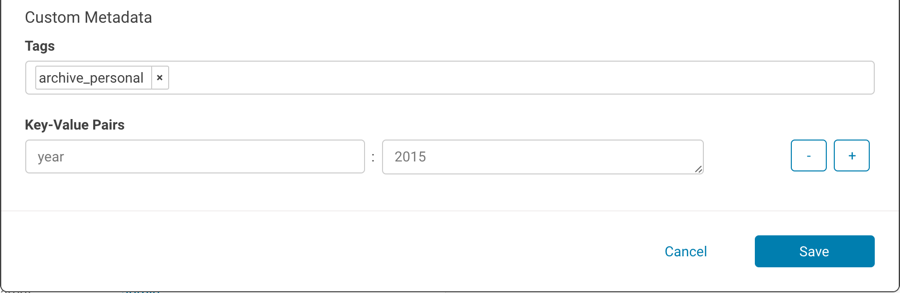
After you save, the metadata appears in the Tags and Custom Metadata panes:
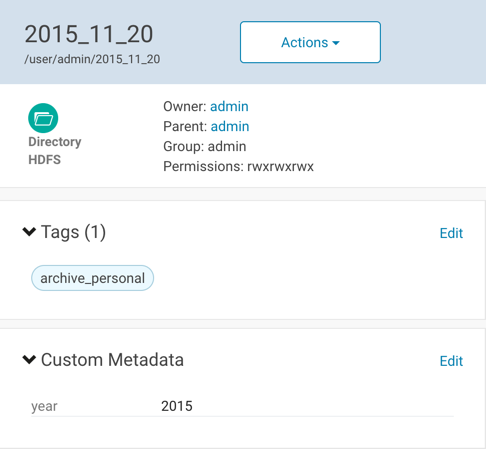
Managed Metadata Example
The following example shows the Department and RetainUntil managed properties for the customers entity: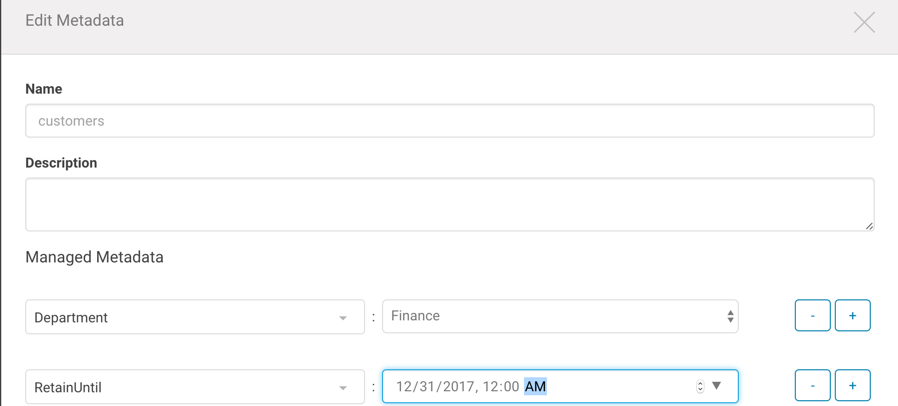
After you specify the values and save, the properties display in the Managed Metadata pane:
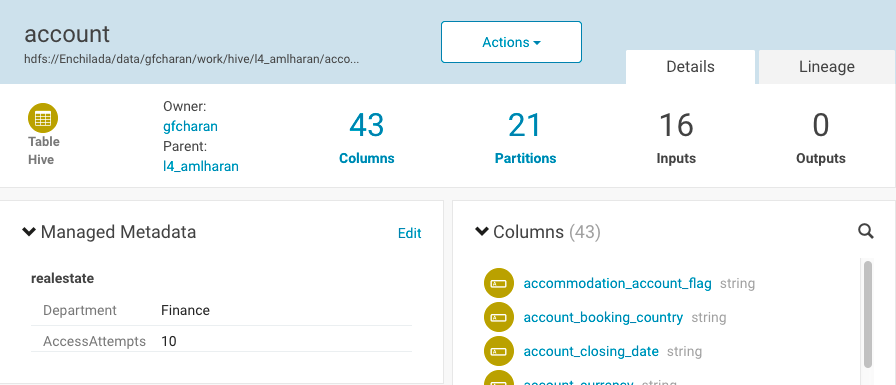
Editing MapReduce Custom Metadata
You can associate custom metadata with arbitrary configuration parameters to MapReduce jobs and job executions. The configuration parameters to be extracted by Navigator can be specified statically or dynamically.
- Do one of the following:
- Select .
- On the tab, in Cloudera Management Service table, click the Cloudera Management Service link.
- Click the Configuration tab.
- Select .
- Select .
- Click Navigator Metadata Server Advanced Configuration Snippet for cloudera-navigator.properties.
- Specify values for the following properties:
- nav.user_defined_properties - A comma-separated list of user-defined property names.
- nav.tags - A comma-separated list of property names that serve as tags. The property nav.tags can point to multiple property names that serve as tags, but each of those property names can only specify a single tag.
- Click Save Changes to commit the changes.
- Click the Instances tab.
- Restart the role.
- In the MapReduce job configuration, set the value of the property names you specified in step 6.
- Specify one or more of the following properties in a job configuration:
- Job properties (type:OPERATION)
- nav.job.user_defined_properties - A comma-separated list of user-defined property names
- nav.job.tags - A comma-separated list of property names that serve as tags
- Job execution properties (type:OPERATION_EXECUTION)
- nav.jobexec.user_defined_properties - A comma-separated list of user-defined property names
- nav.jobexec.tags - A comma-separated list of property names that serve as tags
- Job properties (type:OPERATION)
- In the MapReduce job configuration, set the value of the property names you specified in step 1.
Example: Setting Properties Dynamically
Add the tags onetag and twotag to a job:- Dynamically add the job_tag1 and job_tag2 properties:
conf.set("nav.job.tags", "job_tag1, job_tag2"); - Set the job_tag1 property to onetag:
conf.set("job_tag1", "onetag"); - Set the job_tag2 property to twotag:
conf.set("job_tag2", "twotag");
- Dynamically add the job_tag property:
conf.set("nav.jobexec.tags","job_exec_tag"); - Set the job_exec_tag property to atag:
conf.set("job_exec_tag", "atag");
- Dynamically add the user-defined key bar:
conf.set("nav.job.user_defined_properties", "key"); - Set the value of the user-defined key key to value:
conf.set("key", "value")
Editing HDFS Custom Metadata Using Metadata Files
You can add tags and properties to HDFS entities using metadata files. With metadata files, you can assign metadata to entities in bulk and create metadata before it is extracted. A metadata file is a JSON file with the following structure:
{
"name" : "aName",
"description" : "a description",
"properties" : {
"prop1" : "value1", "prop2" : "value2"
},
"tags" : [ "tag1" ]
}
- File - The path of the metadata file must be .filename.navigator. For example, to apply properties to the file /user/test/file1.txt, the metadata file path is /user/test/.file1.txt.navigator.
- Directory - The path of the metadata file must be dirpath/.navigator. For example, to apply properties to the directory /user, the metadata path must be /user/.navigator.
Editing HDFS and Hive Metadata Using the Navigator Metadata API
You can use the Cloudera Navigator Data Management API to modify the custom metadata of HDFS or Hive entities, whether the entities have been extracted or not. If an entity has been extracted when the API is called, the metadata is applied immediately. If the entity has not been extracted, you can preregister metadata, which is then applied once the entity is extracted. Metadata is saved regardless of whether or not a matching entity is extracted, and Navigator does not perform any cleanup of unused metadata.
- Identity
- Source ID
- Metadata fields (name, description, tags, properties)
- Fields relevant to the identifier
curl http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/api/v9/entities/?query=-internalType:* -u username:password -X GET
Custom metadata provided through the API overwrites existing metadata. For example, if you call the API with an empty name and description, empty array for tags, and empty dictionary for properties, the call removes this metadata. If you omit the tags or properties fields, the existing values remain unchanged.
Modifying custom metadata using HDFS metadata files and the metadata API at the same time is not supported. You must use one or the other, because the two methods work differently. Metadata specified in files is merged with existing metadata, whereas the API overwrites metadata. Also, the updates provided by metadata files wait in a queue before being merged, but API changes are committed immediately. Some inconsistency can occur if a metadata file is merged when the API is in use.
You modify metadata using either the PUT or POST method. Use the PUT method if the entity has been extracted, and the POST method to preregister metadata. Use the following syntax:- PUT
curl http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/api/v9/entities/identity -u username:password -X PUT -H\ "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{properties}'where identity is an entity ID and properties are:- name - Name metadata.
- description - Description metadata.
- tags - Tag metadata.
- properties - Custom metadata properties. The format is {key: value}.
- customProperties - Managed metadata properties. The format is {namespace: {key: value}}. If a property is assigned a value that does not conform to type constraints, an error is returned.
- POST
curl http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/api/v9/entities/ -u username:password -X POST -H\ "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{properties}'where properties are:- sourceId (required) - An existing source ID. After the first extraction,
you can retrieve source IDs using the call:
curl http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/api/v9/entities/?query=type:SOURCE -u username:password -X GET
For example:[ ... { { "identity": "61cfefd303d4284b7f5014b701f2c76d", "originalName": "source.listing", "originalDescription": null, "sourceId": "012437f9eeb3c23dc69e679ac94a7fa2", "firstClassParentId": null, "parentPath": "/user/hdfs/.cm/distcp/2016-02-03_487", ... "properties": { "__cloudera_internal__hueLink": "http://vc0142.halxg.cloudera.com:8888/filebrowser/#/user/hdfs/.cm/distcp/2016-02-03_487/source.listing" }, "technicalProperties": null, "fileSystemPath": "/user/hdfs/.cm/distcp/2016-02-03_487/source.listing", "type": "FILE", "size": 92682, "created": "2016-02-03T21:12:16.587Z", "lastModified": "2016-02-03T21:12:16.587Z", "lastAccessed": "2016-02-03T21:12:16.587Z", "permissions": "rw-r--r--", "owner": "hdfs", "group": "supergroup", "blockSize": 134217728, "mimeType": "application/octet-stream", "replication": 3, "userEntity": false, "deleted": false, "sourceType": "HDFS", "metaClassName": "fselement", "packageName": "nav", "internalType": "fselement" }, ...If you have multiple services of a given type, you must specify the source ID that contains the entity you expect it to match. - parentPath - The path of the parent entity, defined as:
- HDFS file or directory - fileSystemPath of the parent directory. (Do not provide this field if the entity affected is the root directory.) Example parentPath for /user/admin/input_dir: /user/admin. If you add metadata to a directory, the metadata does not propagate to any files or folders in that directory.
- Hive database - If you are updating database metadata, do not specify this field.
- Hive table or view - The name of database containing the table or view. Example for a table in the default database: default.
- Hive column - database name/table name/view name. Example for a column in the sample_07 table: default/sample_07.
- originalName (required) - The name as defined by the source system.
- HDFS file or directory- Name of file or directory (ROOT if the entity is the root directory). Example originalName for /user/admin/input_dir: input_dir.
- Hive database, table, view, or column - The name of the database, table, view, or column.
- Example for default database: default
- Example for sample_07 table: sample_07
- name - Name metadata.
- description - Description metadata.
- tags - Tag metadata.
- properties - Custom metadata properties. The format is {key: value}.
- sourceId (required) - An existing source ID. After the first extraction,
you can retrieve source IDs using the call:
HDFS PUT Custom Metadata Example for /user/admin/input_dir Directory
curl http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/api/v9/entities/e461de8de38511a3ac6740dd7d51b8d0 -u username:password -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json"\
-d '{"name":"my_name","description":"My description", "tags":["tag1","tag2"],"properties":{"property1":"value1","property2":"value2"}}'HDFS POST Custom Metadata Example for /user/admin/input_dir Directory
curl http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/api/v9/entities/ -u username:password -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json"\
-d '{"sourceId":"a09b0233cc58ff7d601eaa68673a20c6", "parentPath":"/user/admin","originalName":"input_dir", "name":"my_name","description":"My description",\
"tags":["tag1","tag2"],"properties":{"property1":"value1","property2":"value2"}}'Hive POST Custom Metadata Example for total_emp Column
curl http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/api/v9/entities/ -u username:password -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json"\
-d '{"sourceId":"4fbdadc6899638782fc8cb626176dc7b", "parentPath":"default/sample_07","originalName":"total_emp",\
"name":"my_name","description":"My description", "tags":["tag1","tag2"],"properties":{"property1":"value1","property2":"value2"}}'HDFS PUT Managed Metadata Example
The following example demonstrates how to set two properties in the MailAnnotation namespace: a multivalued property emailTo and a single-valued property emailFrom:curl http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/api/v9/entities/87afcb92d5de856c7e8292e2e12cf1ea -u admin:admin -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{"customProperties":{"MailAnnotation":{"emailTo":["lee@example.com","dana@example.com"],"emailFrom":"terry@email.com"}}}'
The response is:
{
"identity" : "87afcb92d5de856c7e8292e2e12cf1ea",
"originalName" : "years",
"originalDescription" : null,
"sourceId" : "012437f9eeb3c23dc69e679ac94a7fa2",
"firstClassParentId" : null,
"parentPath" : "/user/admin",
"extractorRunId" : "012437f9eeb3c23dc69e679ac94a7fa2##1",
"customProperties" : {
"MailAnnotation" : {
"emailTo" : [ "lee@example.com", "dana@example.com" ],
"emailFrom" : "terry@email.com"
}
},
"name" : null,
"description" : null,
"tags" : null,
"properties" : {
"__cloudera_internal__hueLink" : "Hue_Server_host:8888/filebrowser/#/user/admin/years"
},
"technicalProperties" : null,
"fileSystemPath" : "/user/admin/years",
"type" : "DIRECTORY",
"size" : null,
"created" : "2016-03-22T17:55:31.902Z",
"lastModified" : "2016-03-22T17:59:14.065Z",
"lastAccessed" : null,
"permissions" : "rwxr-xr-x",
"owner" : "hdfs",
"group" : "admin",
"blockSize" : null,
"mimeType" : null,
"replication" : null,
"sourceType" : "HDFS",
"metaClassName" : "fselement",
"userEntity" : false,
"deleted" : false,
"packageName" : "nav",
"internalType" : "fselement"
}Accessing and Editing Metadata with the Navigator SDK
In addition to the metadata features provided by the Cloudera Navigator data management component UI, you can also access and edit metadata using the Navigator SDK. For information on the SDK, see the Navigator SDK documentation.