Launching Cloudbreak on Azure
These steps describe how to launch Cloudbreak on Azure for production. Before launching Cloudbreak on Azure, review and meet the prerequisites. Next, follow the steps below.
VM requirements
To launch the Cloudbreak deployer and install the Cloudbreak application, you must have an existing VM.
System requirements
Your system must meet the following requirements:
- Minimum VM requirements: 16GB RAM, 40GB disk, 4 cores
- Supported operating systems: RHEL, CentOS, and Oracle Linux 7 (64-bit)
You can install Cloudbreak on Mac OS X for evaluation purposes only. Mac OS X is not supported for a production deployment of Cloudbreak.
Root access
Every command must be executed as root. In order to get root privileges execute:
sudo -i
System updates
Ensure that your system is up-to-date by executing:
yum -y update
Reboot it if necessary.
Install iptables
Perform these steps to install and configure iptables.
Steps
-
Install iptables-services:
yum -y install net-tools ntp wget lsof unzip tar iptables-services systemctl enable ntpd && systemctl start ntpd systemctl disable firewalld && systemctl stop firewalld
Without iptables-services installed the
iptables savecommand will not be available. -
Configure permissive iptables on your machine:
iptables --flush INPUT && \ iptables --flush FORWARD && \ service iptables save
Disable SELINUX
Perform these steps to disable SELINUX.
Steps
-
Disable SELINUX:
setenforce 0 sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
-
Run the following command to ensure that SELinux is not turned on afterwards:
getenforce
-
The command should return "Disabled".
Install Docker
Perform these steps to install Docker. The minimum Docker version is 1.13.1. If you are using an older image that comes with an older Docker version, upgrade Docker to 1.13.1 or newer.
Steps
-
Install Docker service:
yum install -y docker systemctl start docker systemctl enable docker
-
Check the Docker Logging Driver configuration:
docker info | grep "Logging Driver"
-
If it is set to
Logging Driver: journald, you must set it to "json-file" instead. To do that:-
Open the
dockerfile for editing:vi /etc/sysconfig/docker
-
Edit the following part of the file so that it looks like below (showing
log-driver=json-file):# Modify these options if you want to change the way the docker daemon runs OPTIONS='--selinux-enabled --log-driver=json-file --signature-verification=false'
-
Restart Docker:
systemctl restart docker systemctl status docker
-
Install Cloudbreak on a VM
Install Cloudbreak using the following steps.
Steps
-
Install the Cloudbreak deployer and unzip the platform-specific single binary to your PATH. For example:
yum -y install unzip tar curl -Ls public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/cloudbreak/cloudbreak-deployer_2.7.0_$(uname)_x86_64.tgz | sudo tar -xz -C /bin cbd cbd --version
Once the Cloudbreak deployer is installed, you can set up the Cloudbreak application.
-
Create a Cloudbreak deployment directory and navigate to it:
mkdir cloudbreak-deployment cd cloudbreak-deployment
-
In the directory, create a file called
Profilewith the following content:export UAA_DEFAULT_SECRET=MY-SECRET export UAA_DEFAULT_USER_PW=MY-PASSWORD export UAA_DEFAULT_USER_EMAIL=MY-EMAIL export PUBLIC_IP=MY_VM_IP
For example:
export UAA_DEFAULT_SECRET=MySecret123 export UAA_DEFAULT_USER_PW=MySecurePassword123 export UAA_DEFAULT_USER_EMAIL=dbialek@hortonworks.com export PUBLIC_IP=172.26.231.100
You will need to provide the email and password when logging in to the Cloudbreak web UI and when using the Cloudbreak CLI. The secret will be used by Cloudbreak for authentication.
You should set the CLOUDBREAK_SMTP_SENDER_USERNAME variable to the username you use to authenticate to your SMTP server. You should set the CLOUDBREAK_SMTP_SENDER_PASSWORD variable to the password you use to authenticate to your SMTP server.
-
Generate configurations by executing:
rm *.yml cbd generate
The cbd start command includes the cbd generate command which applies the following steps:
- Creates the
docker-compose.ymlfile, which describes the configuration of all the Docker containers required for the Cloudbreak deployment. - Creates the
uaa.ymlfile, which holds the configuration of the identity server used to authenticate users with Cloudbreak.
- Creates the
-
Start the Cloudbreak application by using the following commands:
cbd pull-parallel cbd start
This will start the Docker containers and initialize the application. The first time you start the Cloudbreak app, the process will take longer than usual due to the download of all the necessary docker images.
If you encounter errors during
cbd start, refer to Toubleshooting. -
Next, check Cloudbreak application logs:
cbd logs cloudbreak
You should see a message like this in the log:
Started CloudbreakApplication in 36.823 seconds.Cloudbreak normally takes less than a minute to start.
Related links
Toubleshooting
Access Cloudbreak web UI
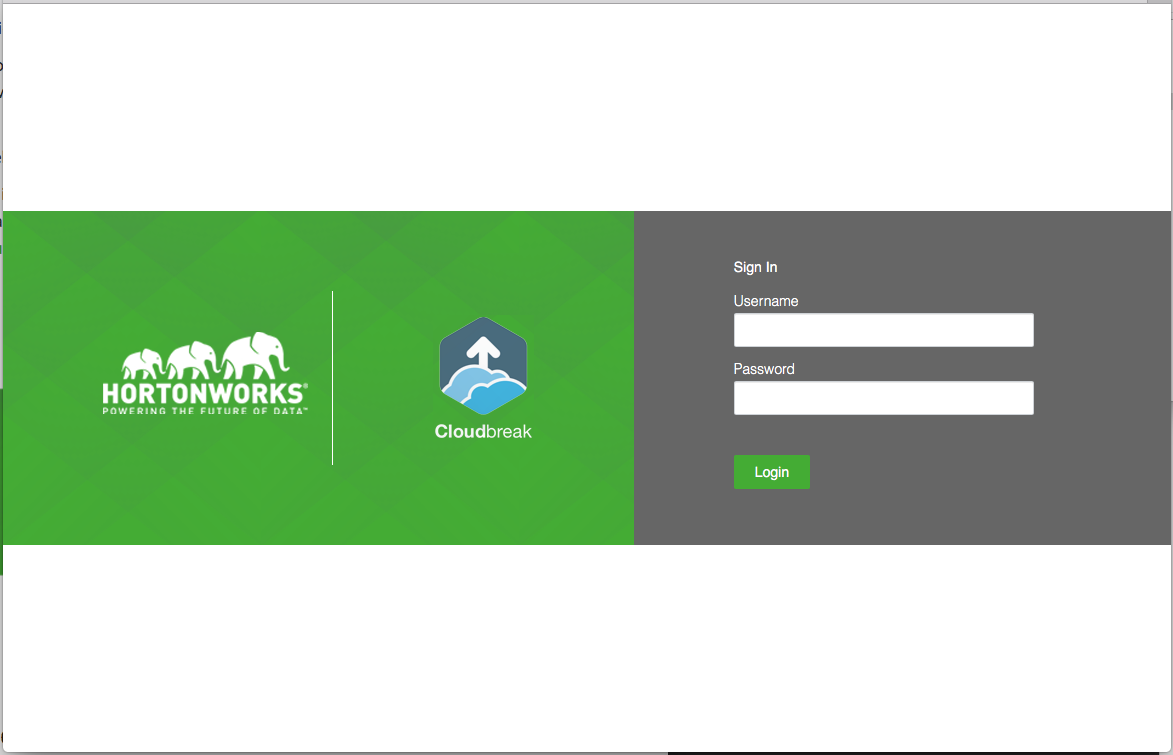
Log in to the Cloudbreak UI using the following steps.
Steps
-
You can log into the Cloudbreak application at
https://IP_Address. For examplehttps://34.212.141.253. You may usecbd startto obtain the login information. Alternatively, you can obtain the VM's IP address from your cloud provider console. -
Confirm the security exception to proceed to the Cloudbreak web UI.
The first time you access Cloudbreak UI, Cloudbreak will automatically generate a self-signed certificate, due to which your browser will warn you about an untrusted connection and will ask you to confirm a security exception.
Browser Steps Firefox Click Advanced > Click Add Exception... > Click Confirm Security Exception Safari Click Continue Chrome Click Advanced > Click Proceed... -
The login page is displayed:
-
Log in to the Cloudbreak web UI using the credentials that you configured in your
Profilefile:- The username is the
UAA_DEFAULT_USER_EMAIL - The password is the
UAA_DEFAULT_USER_PW
- The username is the
-
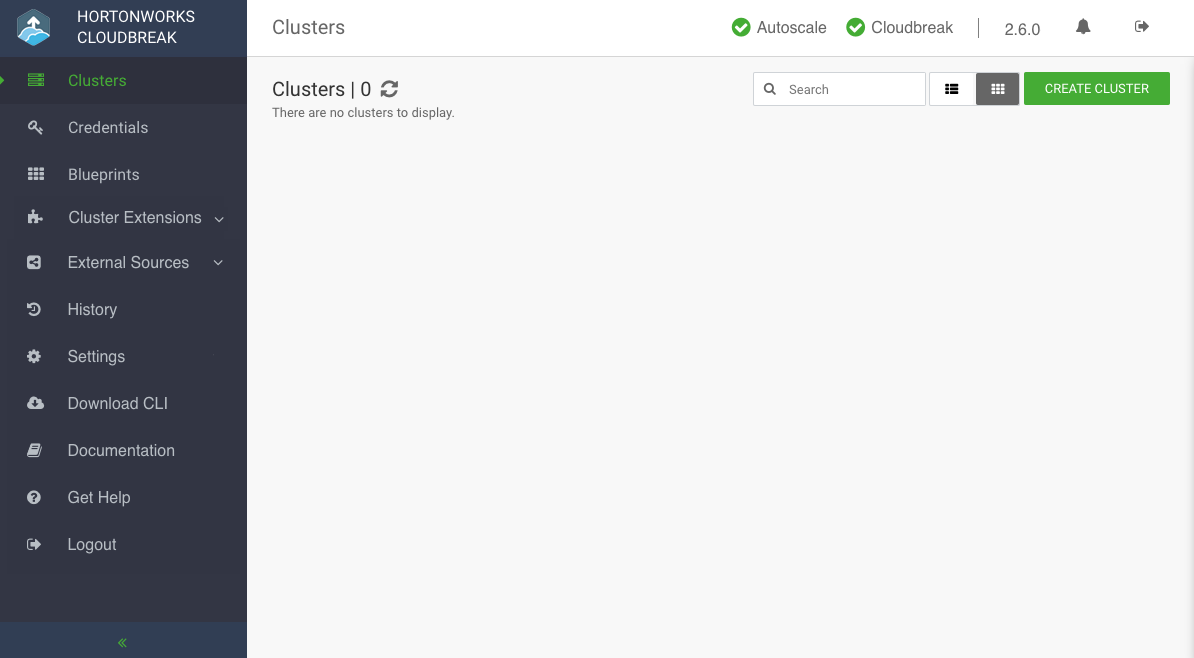
Upon a successful login, you are redirected to the dashboard:
Configure external Cloudbreak database
By default, Cloudbreak uses an embedded PostgreSQL database to persist data related to Cloudbreak configuration, setup, and so on. For a production Cloudbreak deployment, you must configure an external database.
Related links
Configure an external database
Create Cloudbreak credential
Before you can start creating clusters, you must first create a Cloudbreak credential. Without this credential, you will not be able to create clusters via Cloudbreak. Cloudbreak works by connecting your Azure account through this credential, and then uses it to create resources on your behalf.
There are two methods for creating a Cloudbreak credential:
| Method | Description | Prerequisite | Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interactive | The advantage of using this method is that the app and service principal creation and role assignment are fully automated, so the only input that you need to provide is the Subscription ID and Directory ID. During the interactive credential creation, you are required to log in to your Azure account. | (1) Your account must have the "Owner" role (or its equivalent) in the subscription. (2) You must be able log in to your Azure account. | To configure an interactive credential, refer to Create an interactive credential. |
| App-based | The advantage of the app-based credential creation is that it allows you to create a credential without logging in to the Azure account, as long as you have been given all the information. In addition to providing your Subscription ID and Directory ID, you must provide information for your previously created Azure AD application (its ID and key which allows access to it). | (1) Your account must have the "Contributor" role (or equivalent) in the subscription. (2) You or your Azure administrator must perform prerequisite steps of registering an Azure application and assigning the "Contributor" role to it. This step typically requires admin permissions so you may have to contact your Azure administrator. | To configure an app based credential, refer to Create an app-based credential. |
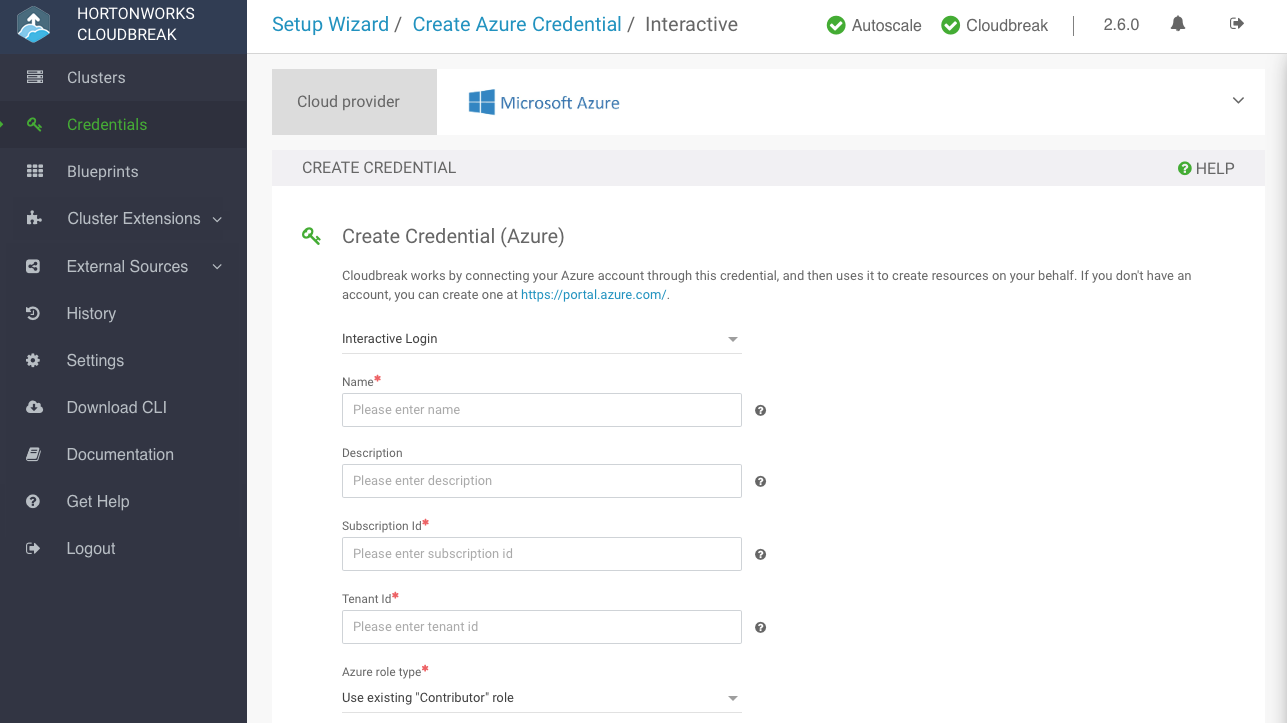
Create interactive credential
Follow these steps to create an interactive Cloudbreak credential.
Prerequisites
Your account must have have an Owner role in order for the interactive credential creation to work.
If your account does not have an Owner role, you must you the app-based credential option instead of the interactive option. To review the requirements for both options. refer to Azure roles.
Steps
-
In the Cloudbreak web UI, select Credentials from the navigation pane.
-
Click Create Credential.
-
Under Cloud provider, select "Microsoft Azure".
-
Select Interactive Login:
-
Provide the following information:
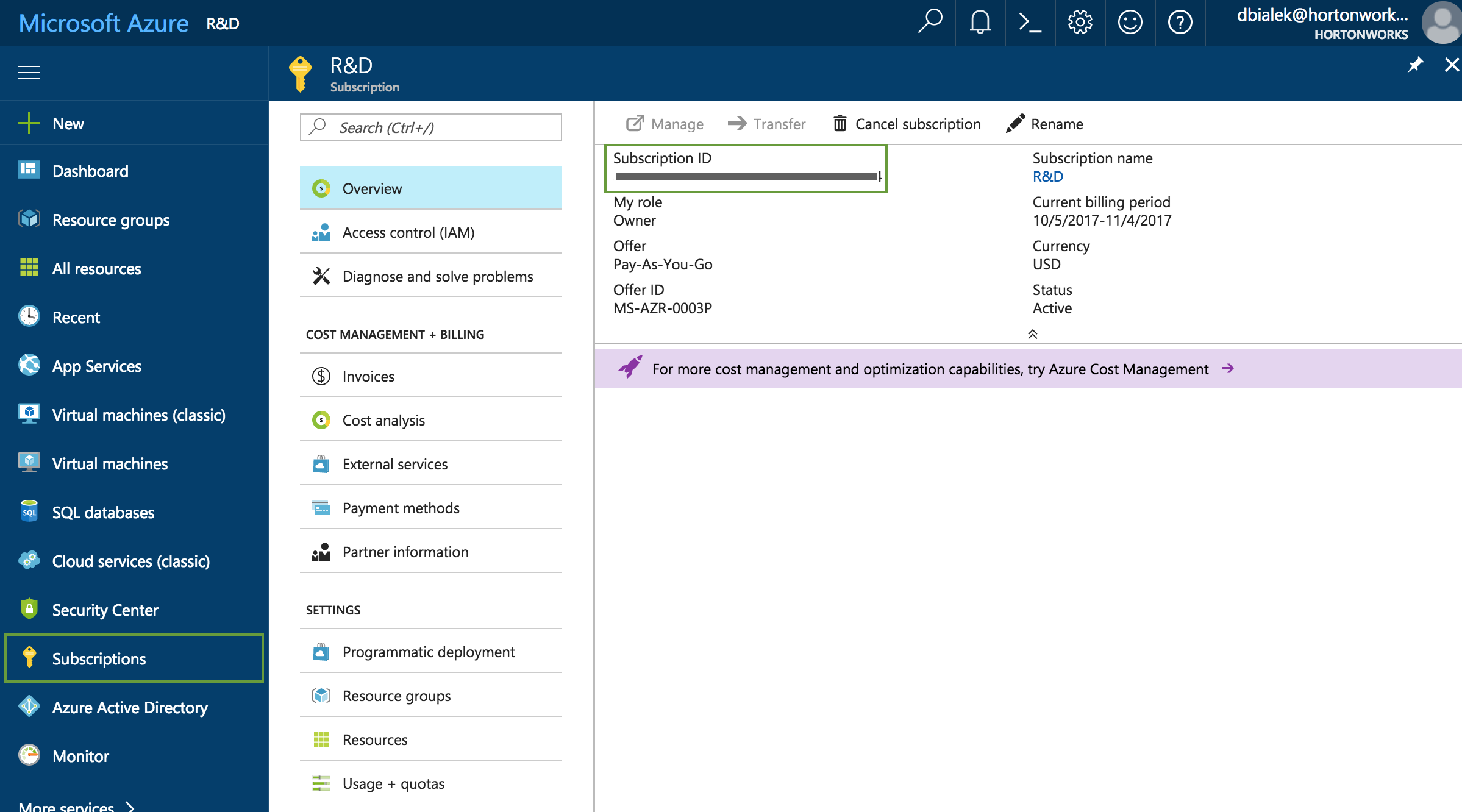
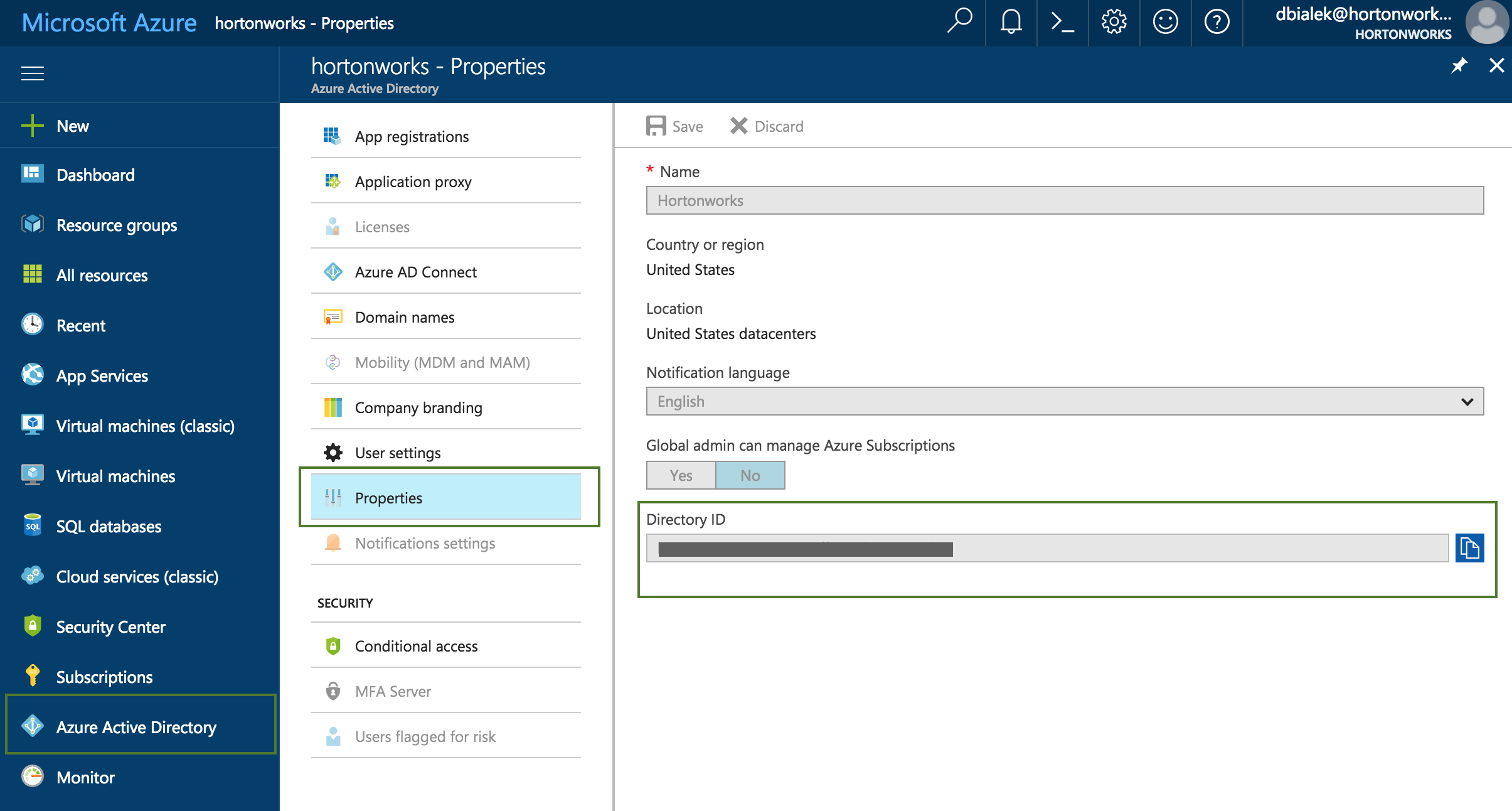
Parameter Description Name Enter a name for your credential. Description (Optional) Enter a description. Subscription Id Copy and paste the Subscription ID from your Subscriptions. Tenant Id Copy and paste your Directory ID from your Active Directory > Properties. Azure role type You have the following options:
- "Use existing Contributor role" (default): If you select this option, Cloudbreak will use the "Contributor" role to create resources. This requires no further input.
- "Reuse existing custom role": If you select this option and enter the name of an existing role, Cloudbreak will use this role to create resources.
- "Let Cloudbreak create a custom role": If you select this option and enter a name for the new role, the role will be created. When choosing role name, make sure that there is no existing role with the name chosen. For information on creating custom roles, refer to Azure documentation.
If using a custom role, use the following role definition, which includes the minimum necessary Action set for Cloudbreak to be able to manage clusters.
To obtain the Subscription Id:
To obtain the Tenant ID (actually Directory Id):
-
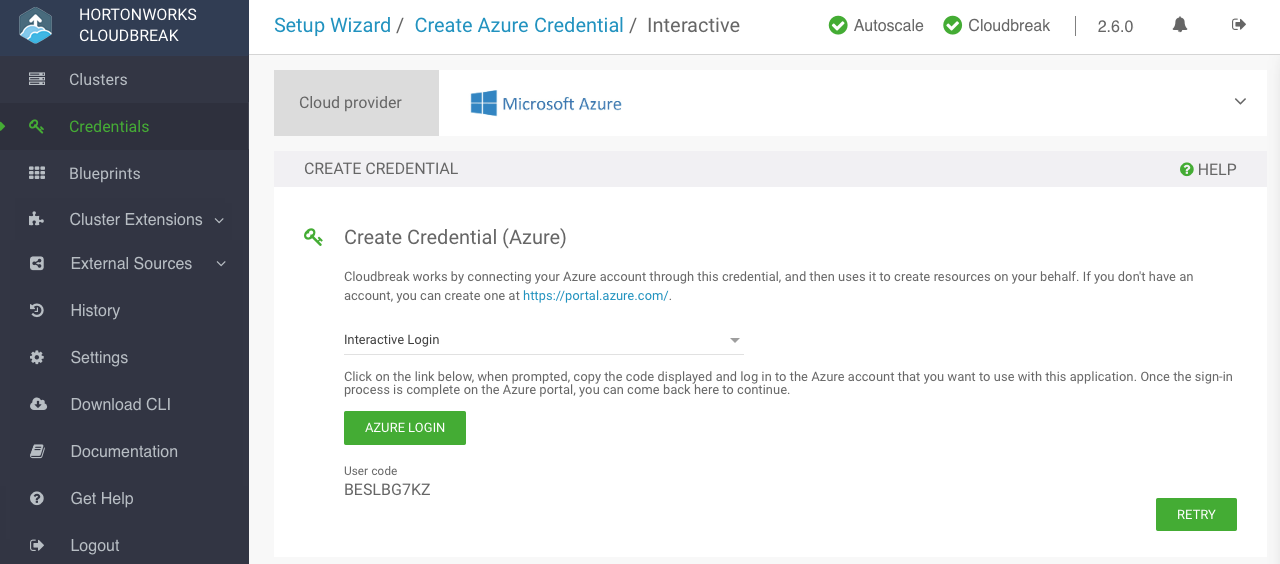
After providing the parameters, click Interactive Login.
-
Copy the code provided in the UI:
-
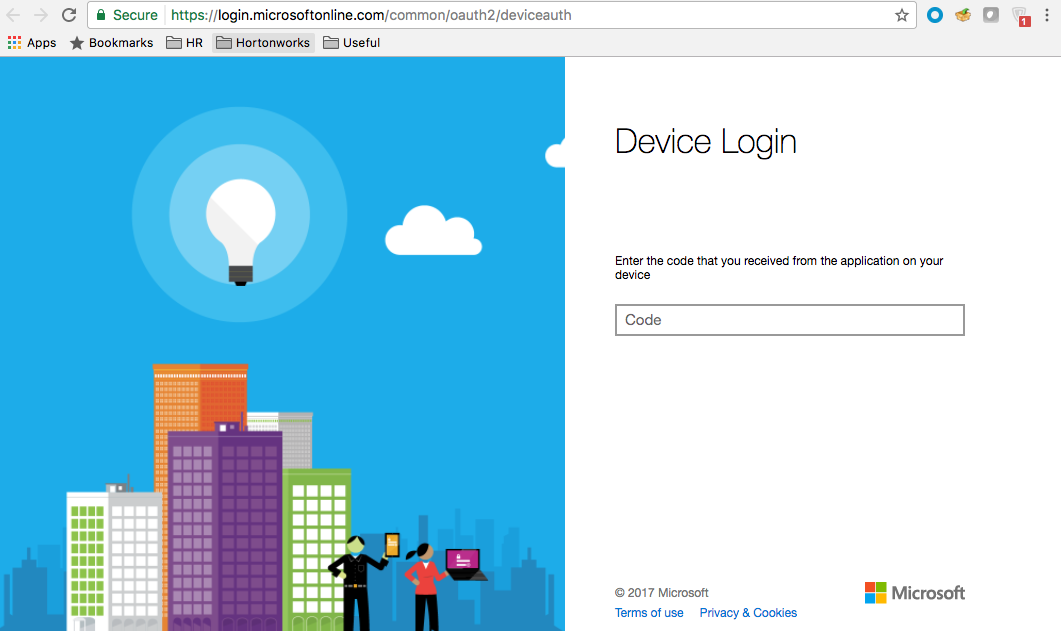
Click Azure login and a new Device login page will open in a new browser tab:
-
Next, paste the code in field on the Device login page and click Continue.
-
Confirm your account by selecting it:
-
A confirmation page will appear, confirming that you have signed in to the Microsoft Azure Cross-platform Command Line Interface application on your device. You may now close this window.
If you encounter errors, refer to Troubleshooting Azure.
Congratulations! You've successfully launched and configured Cloudbreak. Now you can use Cloudbreak to create clusters.
Related links
Create app-based credential
Azure roles
Troubleshooting Azure
Contributor (External)
Custom roles in Azure (External)
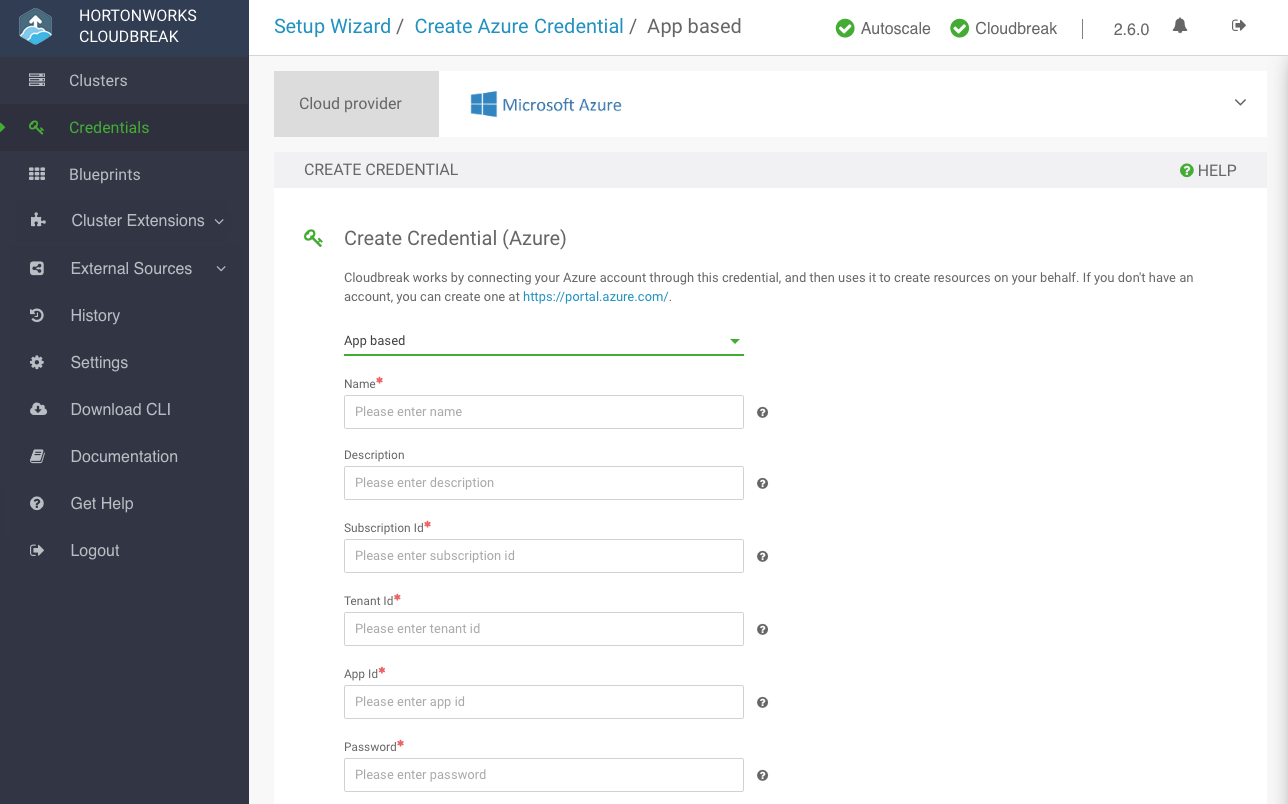
Create app-based credential
Follow these steps to create an app based Cloudbreak credential.
Prerequisites
-
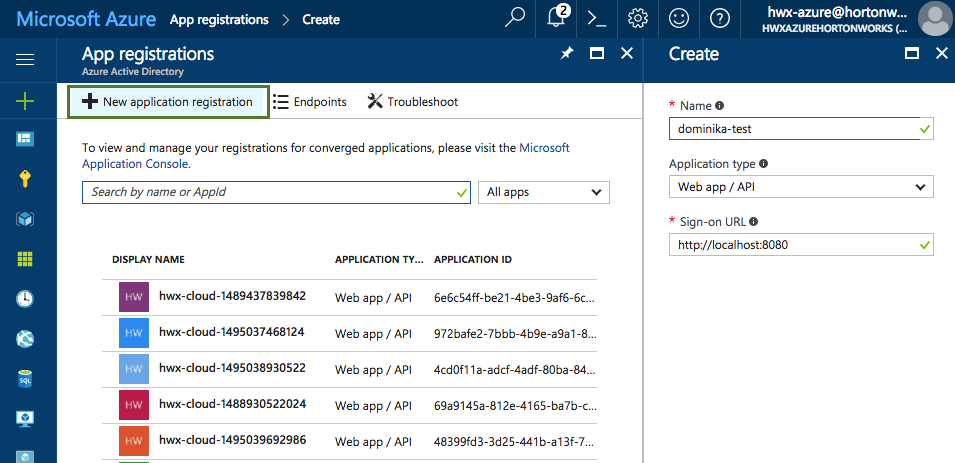
On Azure Portal, navigate to the Active Directory > App Registrations and register a new application. For more information, refer to Create an Azure AD application.
Aa an alternative to the steps listed below for creating an application registration, you use a utility called
azure-cli-tools. The utility supports app creation and role assignment. It is available at https://github.com/sequenceiq/azure-cli-tools/blob/master/cli_tools. -
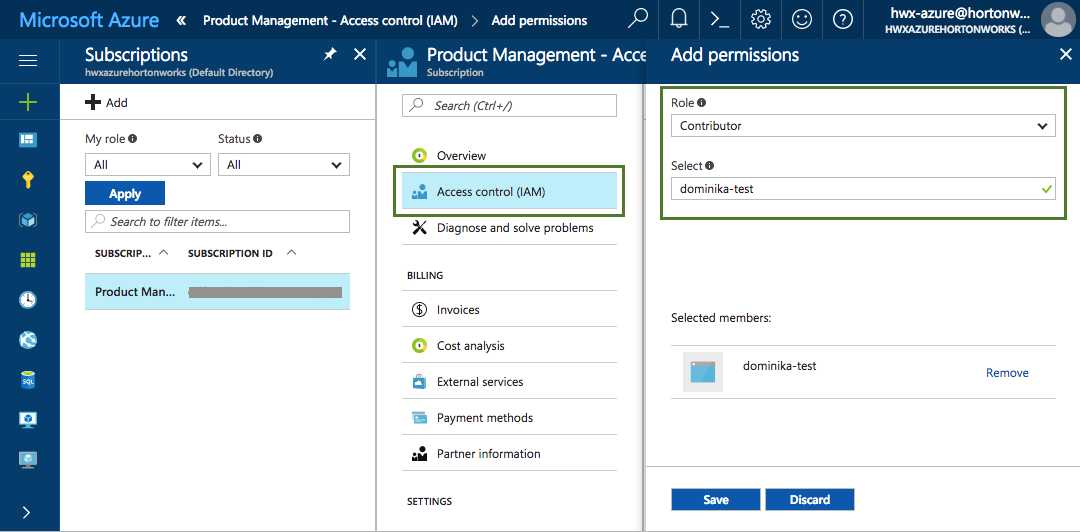
Navigate to the Subscriptions, choose Access control (IAM). Click Add and then assign the "Contributor" role to your newly created application by selecting "Contributor" under Role and typing your app name under Select (You must type your app name in order to find it):
This step typically requires admin permissions so you may have to contact your Azure administrator.
If you are unable to use the "Contributor" role, you can create a custom role by using the following role definition, which includes the minimum permissions required for creating clusters with Cloudbreak.
Steps
-
In the Cloudbreak web UI, select Credentials from the navigation pane.
-
Click Create Credential.
-
Under Cloud provider, select "Microsoft Azure".
-
Select App based Login:
-
On the Configure credential page, provide the following parameters:
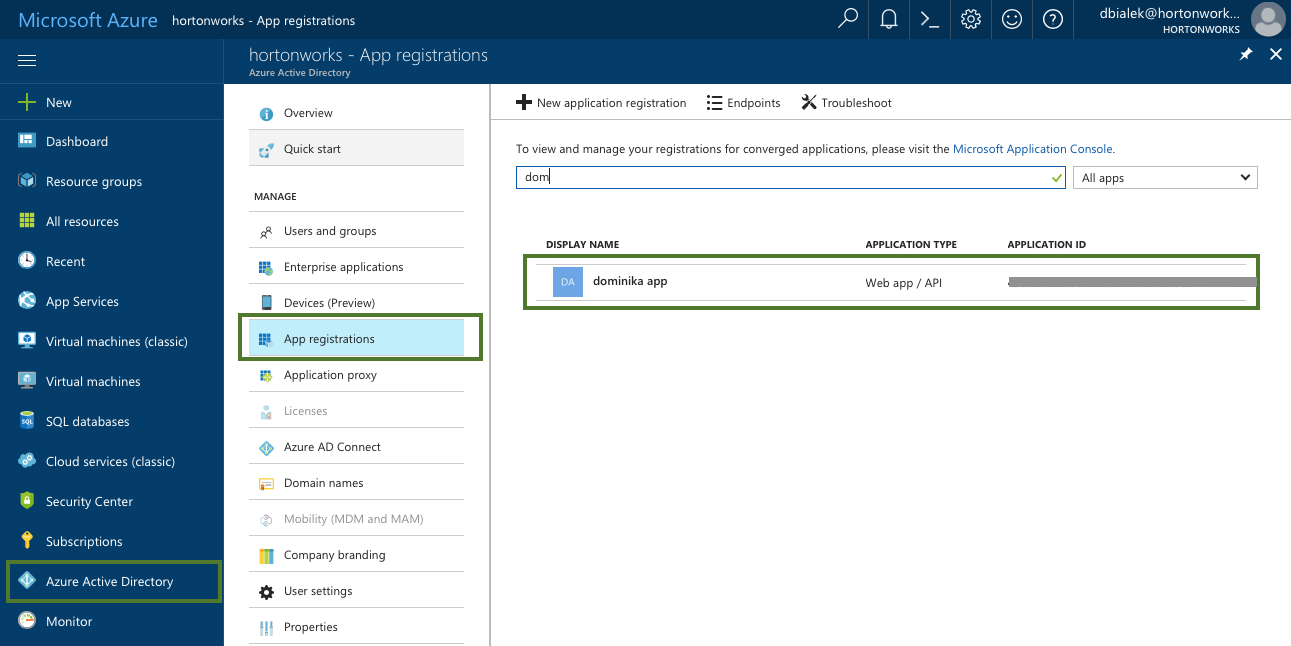
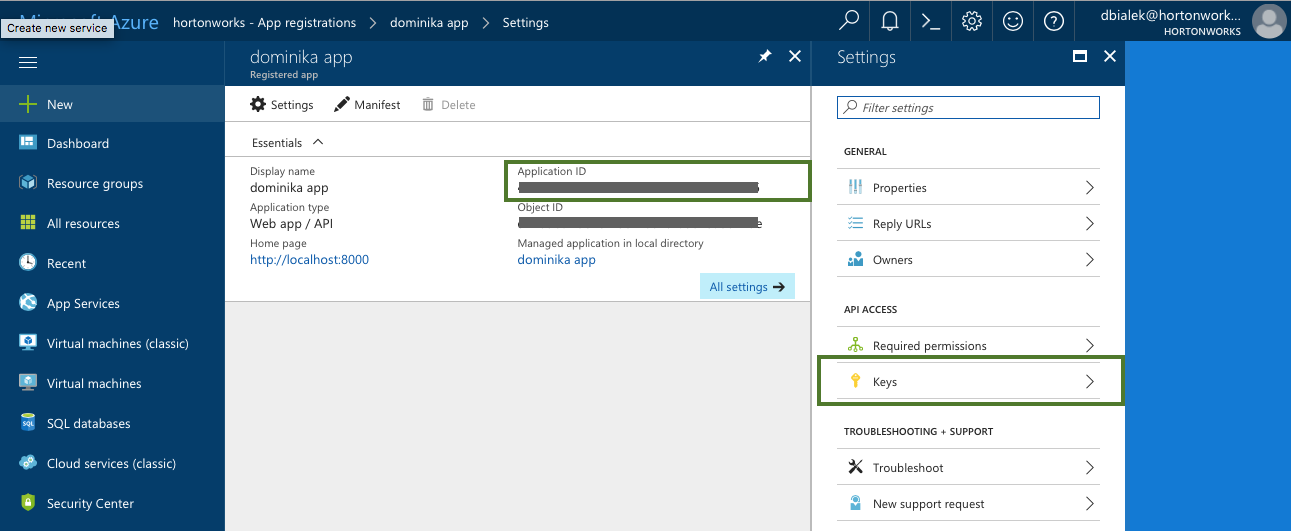
Parameter Description Select Credential Type Select App based. Name Enter a name for your credential. Description (Optional) Enter a description. Subscription Id Copy and paste the Subscription ID from your Subscriptions. Tenant Id Copy and paste your Directory ID from your Active Directory > Properties. App Id Copy and paste the Application ID from your Azure Active Directory > App Registrations > your app registration's Settings > Properties. Password This is your application key. You can generate it from your Azure Active Directory app registration's Settings > Keys. To obtain the Subscription Id from Subscriptions:
To obtain the App ID (actually Application ID) and an application key from Azure Active Directory:
To obtain the Tenant ID (actually Directory Id) from Azure Active Directory:
-
Click Create.
If you encounter errors, refer to Troubleshooting Cloudbreak on Azure.
Congratulations! You have successfully launched Cloudbreak and created a Cloudbreak credential. Now you can use Cloudbreak to create clusters.
Related links
CLI tools (Hortonworks)
Use portal to create an Azure Active Directory application (External)