Deployment options
The following section describes general options for deploying Cloudbreak and Cloudbreak-managed clusters.
Cloudbreak deployment options
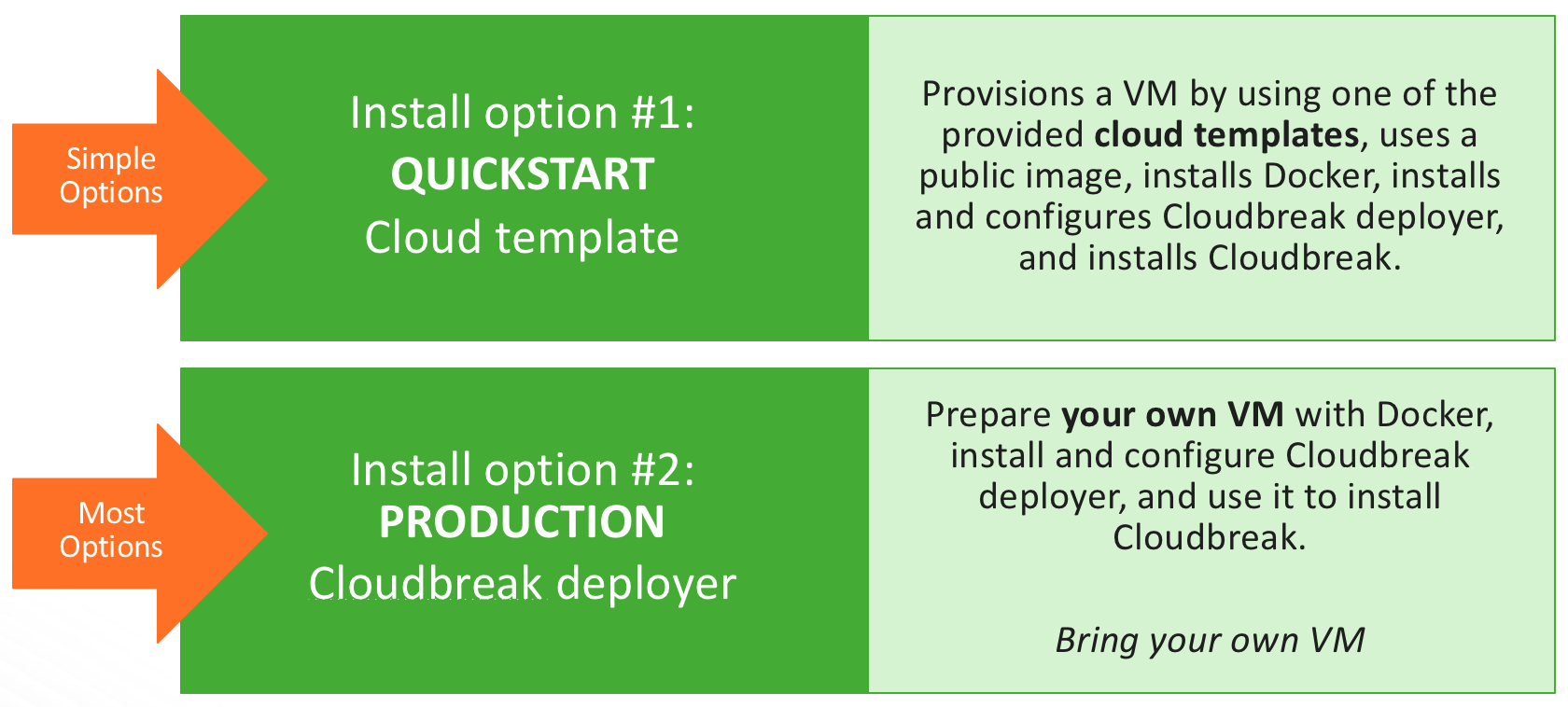
In general, Cloudbreak offers a quickstart option, as well as a production deployment option:
- The quickstart option allows you to get started with Cloudbreak quickly, but offers limited flexibility. Use this option for getting started with Cloudbreak. This option is not suitable a production.
- The production option is less automated, but offers more configurability. This option is recommended when your production environments.
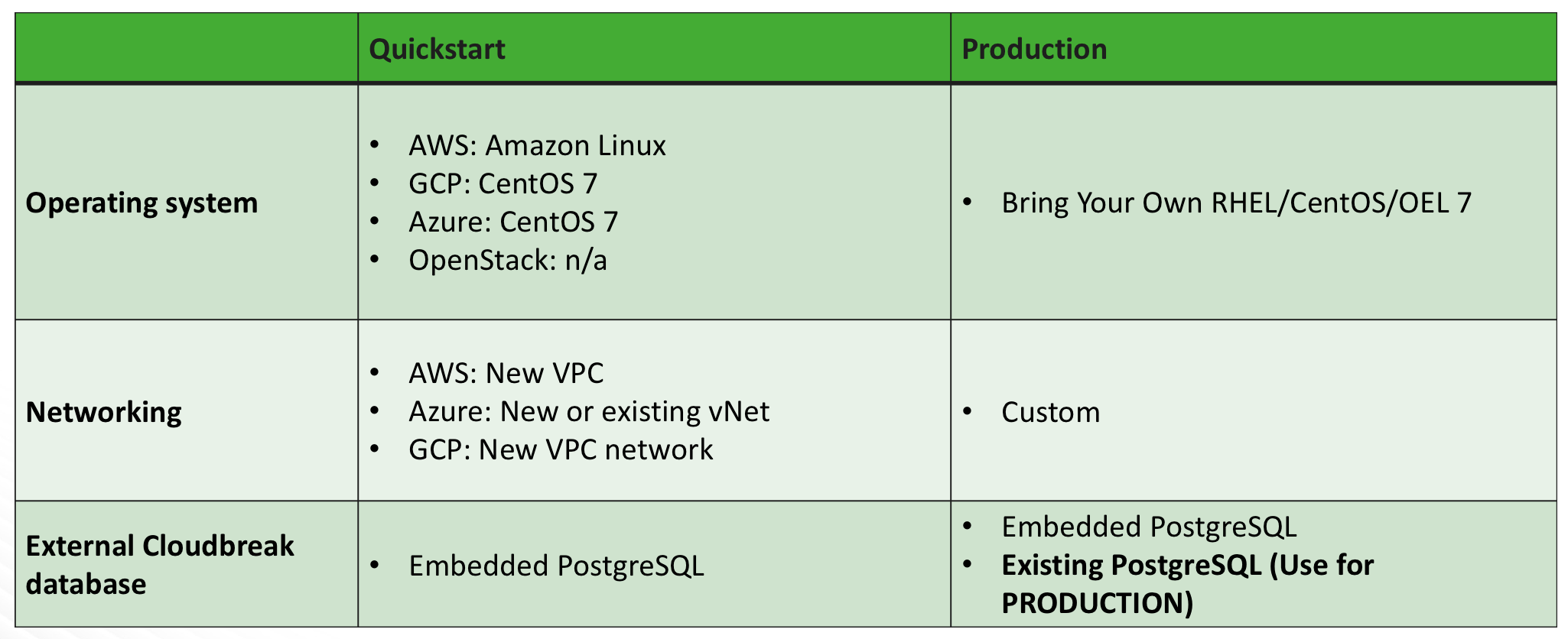
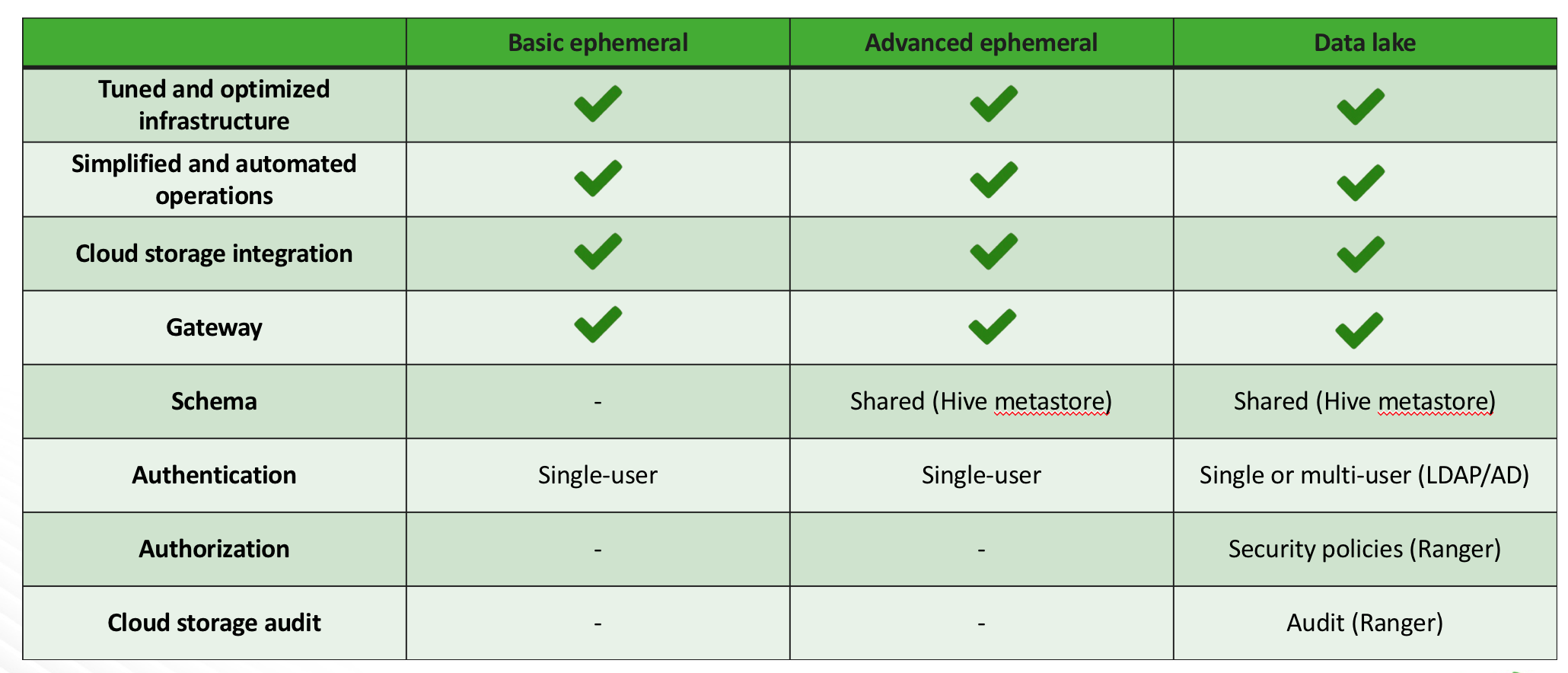
Deployment option cheatsheet
The following table summarizes the available Cloudbreak deployment options:
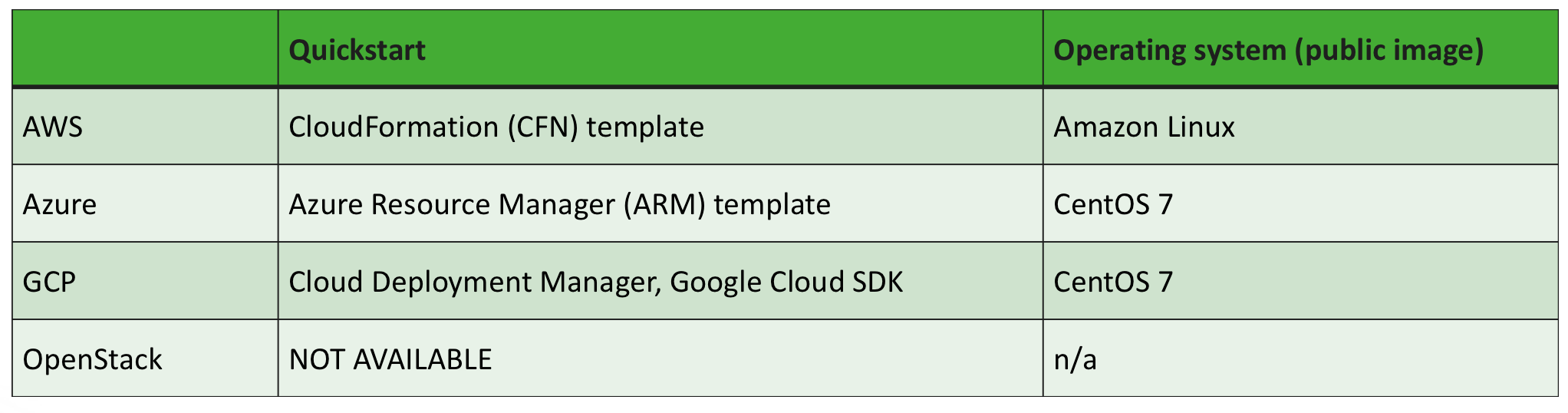
The following operating systems are used when launching by using the quickstart option:
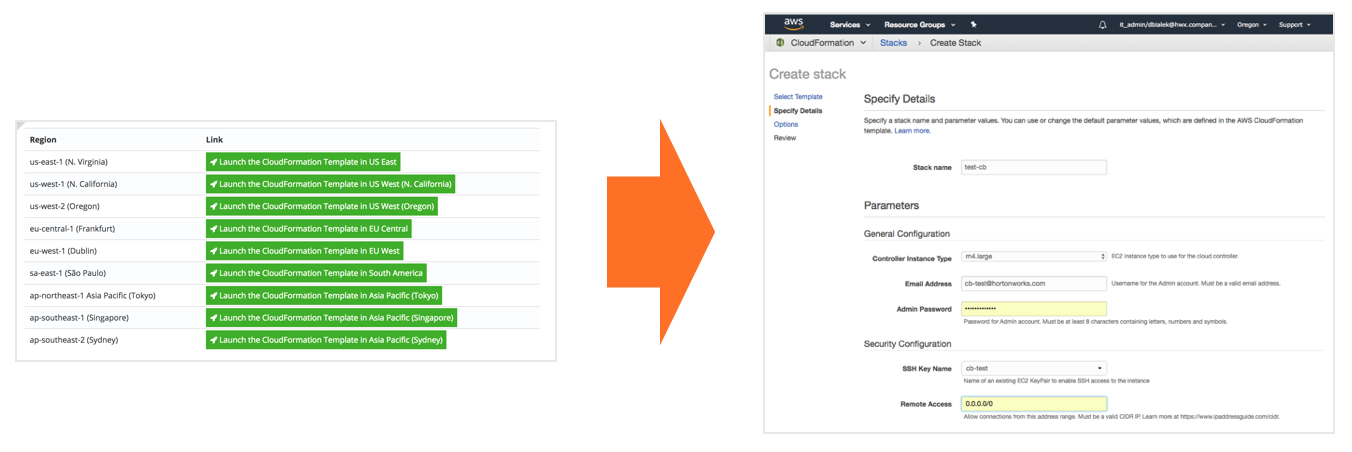
Quickstart option for AWS
The quickstart option allows you to instantiate Cloudbreak by using the CloudFormation template. This is the basic deployment option and the easiest to get started with.
This option utilizes the following AWS services and provisions the following resources:
| Resource | Description | How it is used by Cloudbreak |
|---|---|---|
| AWS CloudFormation | AWS CloudFormation is used to create and manage a collection of related AWS resources. | Cloudbreak is launched by using a CloudFormation template. |
| Amazon EC2 | Amazon EC2 is used to launch a virtual machine for Cloudbreak. Security groups are used to control the inbound and outbound traffic to and from the Cloudbreak instance. | Cloudbreak automatically provisions a new VM that runs Amazon Linux, installs Docker, and launches Cloudbreak. |
| Amazon VPC | Amazon VPC is used to provision your own dedicated virtual network and launch resources into that network. As part of VPC infrastructure, an internet gateway and a route table are provisioned: An internet gateway is used to enable outbound access to the internet from the control plane and the clusters, and a route table is used to connect the subnet to the internet gateway. | Cloudbreak provisions a new VPC and subnet, and launches the Cloudbreak VM within it. |
| AWS IAM | AWS Identity & Access Management (IAM) is used to control access to AWS services and resources. | Cloudbreak provisions the CloudbreakQuickstartRole IAM role that is used during the quickstart deployment. |
| AWS Lambda | This is a utility service for running code in AWS. | Cloudbreak uses AWS Lambda is for running code when deploying Cloudbreak. |
Related links
Quickstart on AWS
Quickstart option for Azure
The quickstart option allows you to instantiate Cloudbreak by using Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template.
On Azure, resources are organized by using resource groups. When you launch Cloudbreak, you may either select to use an existing resource group or a new resource group is created. The following Azure resources are provisioned within the selected resource group:
- Virtual network (VNet) securely connects Azure resources to each other. You may either launch Cloudbreak into an existing VPC, or a new VPC is created and added to the resource group.
- Network security group (NSG) defines inbound and outbound security rules, which control network traffic flow.
- Virtual machine runs Cloudbreak. Based on the ARM template, Azure automatically provisions a new VM that runs CentOS 7, installs Docker, and launches Cloudbreak.
- Public IP address is assigned to your VM so that it can communicate with other Azure resources.
- Network interface (NIC) attached to the VM provides the interconnection between the VM and the underlying software network.
- Blob storage container is created to store Cloudbreak Deployer OS disk's data.
Related links
Quickstart on Azure
Quickstart option for GCP
Based on the Cloud Deployment Manager template, GCP automatically provisions a new VM that runs CentOS 7, installs Docker, and launches Cloudbreak.
The following basic resources are provisioned on you GCP account:
- Network
- Subnetwork (subnet)
- Route (routing table)
- Firewall
- VM instance
- Config
- Config waiter
The config and config waiter are scripts used for deploying Cloudbreak. The startup config script is watched by the waiter script and updated when the deployment in up and running or if it failed to start. The startup waiter script keeps the deployment "in-progress" until the startup script that's running on the created machine update the cbd-deployment-startup-config value to "success" or "failed".
Related links
Quickstart on GCP
Production deployment option
The option to install Cloudbreak deployer manually on your own VM is available for all cloud providers.
This option:
- Allows you to provide your own VM with CentOS 7, RHEL 7, or Oracle Linux 7
- Allows you to use your custom virtual network (On Azure this is also possible with the quickstart option)
- Requires you to install Docker
- Requires you to download the cbd tarball, extract it, and configure Cloudbreak deployer
Related links
Launch on AWS
Launch on Azure
Launch on GCP
Launch on OpenStack
Cluster deployment options
On a basic level, Cloudbreak offers three cluster deployment options:
- Basic cluster deployment with prescriptive options
- Advanced cluster deployment with customized options
- Enterprise HDP cluster deployment with a data lake and attached workload clusters:
The data lake deployment option is technical preview.
Related links
Setting up a data lake