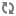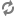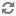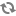Configuring PostgreSQL for Ranger
On the PostgreSQL host, install the applicable PostgreSQL connector.
RHEL/CentOS/Oracle Linux
yum install postgresql-jdbc*
SLES
zypper install -y postgresql-jdbc
Confirm that the .jar file is in the Java share directory.
ls /usr/share/java/postgresql-jdbc.jar
Change the access mode of the .jar file to 644.
chmod 644 /usr/share/java/postgresql-jdbc.jar
You can use the PostgreSQL root user to create the Ranger databases.
Optionally, you can also create a non-root user to use to create the Ranger databases. For example, you would use the following series of commands to create the
rangerdbauser and grant it adequate privileges.Log in as the root user and enter:
echo "CREATE DATABASE $dbname;" | sudo -u $postgres psql -U postgres echo "CREATE USER $rangerdba WITH PASSWORD '$passwd';" | sudo -u $postgres psql -U postgres echo "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE $dbname TO $rangerdba;" | sudo -u postgres psql -U $postgres
Where:
$postgresis the postgres user$dbnameis the name of your PostgreSQL database
Use the following command format to set the
jdbc/driver/pathbased on the location of the PostgreSQL JDBC driver .jar file. This command must be run on the server where Ambari server is installed.ambari-server setup --jdbc-db={database-type} --jdbc-driver={/jdbc/driver/path}For example:
ambari-server setup --jdbc-db=postgres --jdbc-driver=/usr/share/java/postgresql.jar
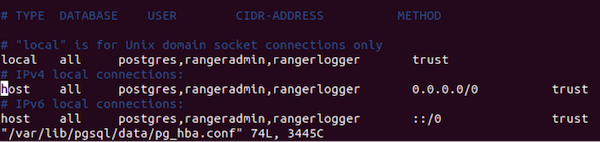
Add allow access details for Ranger users:
change
listen_addresses='localhost'tolisten_addresses='*' ('*' = any)to listen from all IPs inpostgresql.conf.Make the following changes to the Ranger db user and Ranger audit db user in
pg_hba.conf.