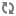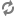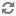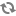DB Settings
Under DB Settings on the Customize Services page, select the "DB Flavor" (installed database type) that you are using with Ranger. The "Location of SQL Connector Jar" box contains the path to the JDBC driver .jar file.
A message box reminds you to make sure you have set the
jdbc/driver/pathbased on the location of the JDBC driver .jar file for the installed Ranger database. If you have not already done so, set the JDBC driver path as described in the installation prerequisites.
Table 3.1. Ranger DB Host
Database Type Host Example MySQL <HOST[:PORT]> c6401.ambari.apache.org
or
c6401.ambari.apache.org:3306
Oracle <HOST:PORT:SID> c6401.ambari.apache.org:1521:ORCL <HOST:PORT/Service> c6401.ambari.apache.org:1521/XE PostgreSQL <HOST[:PORT]> c6401.ambari.apache.org
or
c6401.ambari.apache.org:5432
MS SQL <HOST[:PORT]> c6401.ambari.apache.org
or
c6401.ambari.apache.org:1433
Next, enter the user names and passwords for your Ranger database server. The following table describes these settings in more detail. You can use a MySQL, Oracle, or PostgreSQL database.
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png)
Note The Ranger installation script requires DBA account credentials with privileges to create database (DB) users, and can assign privileges to DB users for READ/WRITE operations in Ranger Policy/Audit DB. However, if Ranger DB users are created before the Ranger installation, you do not need to provide the DB root user and password (you still need to enter some values due to Ambari UI validation, but they do not need to be the admin user details). See Pre-creating Ranger DB Users with the DBA Setup Script for information about pre-creating the users and DB using a separate step involving DB Admin. If users are pre-created, you should clear the “Setup DB and DB user” check box under “Advanced ranger-env” before proceeding with the installation.
Table 3.2. Ranger Database Settings
Configuration Property Name Description Default Value Example Value DB is automatically created by the Ranger installation? DB host The fully qualified domain name of the Ranger database server. For Oracle, Port/SID/Service are added here as well. See the Ranger DB Host table above. c6401.ambari.apache.org Yes Ranger DB root user The Ranger database user that has administrative privileges to create database schemas and users. root root Yes, if DB setup is not done Ranger DB root password The root password for the Ranger database user. N/A root Yes, if DB setup is not done Ranger DB name The name of the Ranger Policy database. For Oracle the tablespace name should be given here. ranger ranger Yes Ranger DB username The username for the Policy database. rangeradmin rangeradmin Yes Ranger DB password The password for the Ranger Policy database user PassWORd
Yes Ranger Audit DB name The name of the Ranger Audit database. This can be a different database in the same database. For Oracle the tablespace name should be given here. ranger_audit ranger_audit Yes Ranger Audit DB username The username for the Ranger Audit database. This username performs all audit logging operations. rangerlogger rangerlogger Yes Ranger Audit DB password The password for the Ranger Audit database. rangerlogger Yes ![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png)
Note For Oracle 11g Release 2 and Oracle 12c, the following format must be used for the Ranger DB host and the JDBC connect string:
Ranger DB host
Format:
If using a SID:
//hostname:port:SIDExample:
c6401.ambari.apache.org:1521:ORCLIf using a service:
//hostname:port/SIDExample:
c6401.ambari.apache.org:1521/ORCL
JDBC connect string
If using a SID:
jdbc:oracle:thin@hostname:port:SIDExample:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@c6401.ambari.apache.org:1521:ORCLIf using a service:
jdbc:oracle:thin@//hostname:port/ServiceExample:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//c6401.ambari.apache.org:1521/XE
Note that the Ambari UI will generate the string based on the value provided in the Ranger DB host. But currently it is generating the wrong connection string in certain cases (especially for Oracle DB). Hence you may need to replace the JDBC connection string as described above.
In an Oracle DB environment, if the JDBC connect string has been overridden to complete the ranger installation, the audit JDBC URLs must also be manually updated in order for DB auditing to work properly.
ranger.jpa.audit.jdbc.urlunder "Advanced ranger-admin-site" (ranger admin setting)xasecure.audit.destination.db.jdbc.urlunder "Advanced ranger-<component>-audit" (ranger plugin setting)
The following images show examples of the DB Settings for each Ranger database type:
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png)
Note To test the DB settings, click Test Connection. If a Ranger database has not been pre-installed, Test Connection will fail even for a valid configuration.
MySQL:

Oracle -- if the Oracle instance is running with a service name:
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png)
Important Note that the Ambari UI will generate the string based on the value provided in the Ranger DB host. But currently it is generating the wrong connection string for Oracle. Therefore you must replace the JDBC connection string as described above.
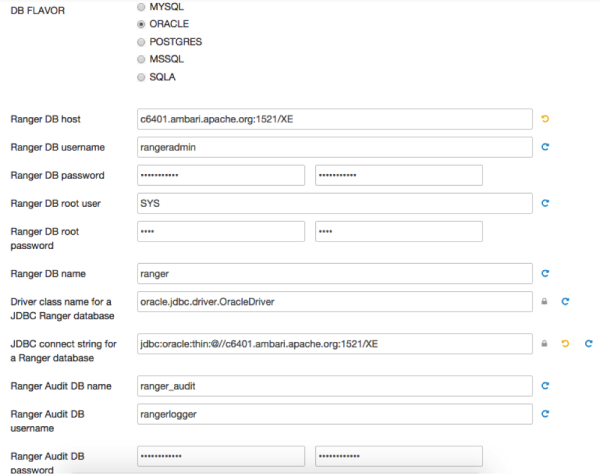
Oracle -- if the Oracle instance is running with a SID:
![[Important]](../common/images/admon/important.png)
Important Note that the Ambari UI will generate the string based on the value provided in the Ranger DB host. But currently it is generating the wrong connection string for Oracle. Therefore you must replace the JDBC connection string as described above.

PostgreSQL:

MS SQL: