Blueprints
Ambari blueprints are your declarative definition of your HDP or HDF cluster, defining the host groups and which components to install on which host group. Ambari uses them as a base for your clusters.
You have two options concerning using blueprints with Cloudbreak:
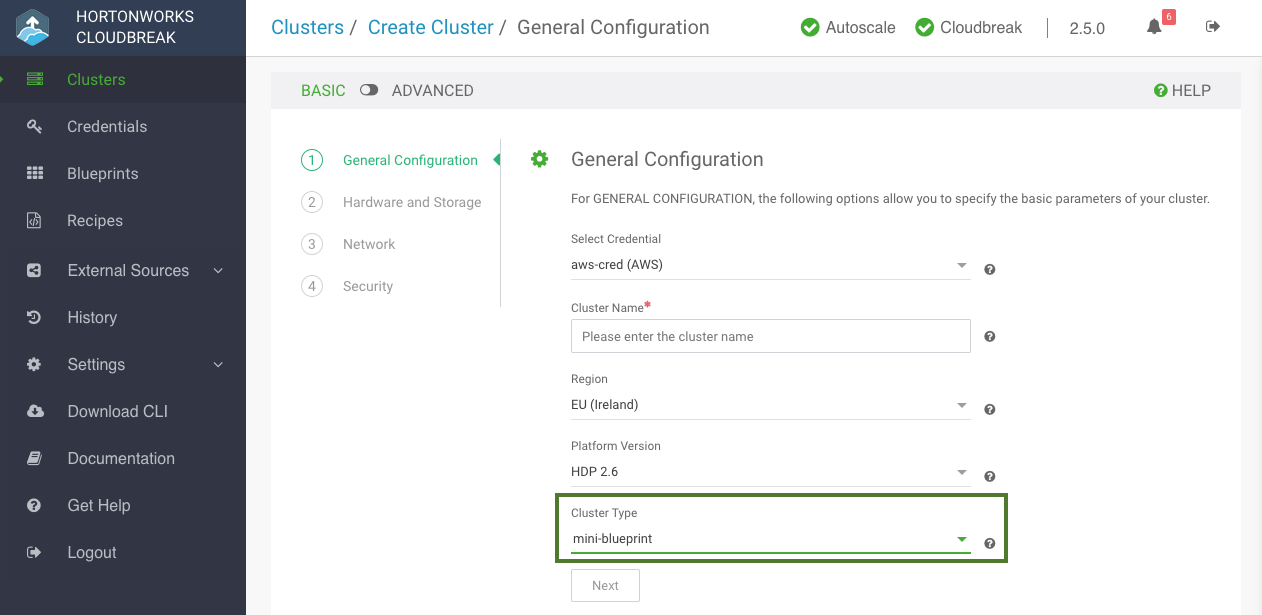
- Use one of the pre-defined blueprints: To use one of the default blueprints, simply select them when creating a cluster. The option is available on the General Configuration page. First select the Stack Version and then select your chosen blueprint under Cluster Type. For the list of default blueprints, refer to Default Cluster Configurations.
- Add your custom blueprint by uploading a JSON file or pasting the JSON text.
We recommend that you review the default blueprints to check if they meet your requirements. You can do this by selecting Blueprints from the navigation pane in the Cloudbreak web UI or by reading the documentation below.
Using Custom Blueprints
This option allows you to create and save your custom blueprints.
Creating a Blueprint
Ambari blueprints are specified in the JSON format. A blueprint can be exported from a running Ambari cluster and can be reused in Cloudbreak after slight modifications. When a blueprint is exported, it includes some hardcoded configurations such as domain names, memory configurations, and so on, that are not applicable to the Cloudbreak cluster. There is no automatic way to modify an exported blueprint and make it instantly usable in Cloudbreak, the modifications have to be done manually.
In general, the blueprint should include the following elements:
"Blueprints": {
"blueprint_name": "hdp-small-default",
"stack_name": "HDP",
"stack_version": "2.6"
},
"settings": [],
"configurations": [],
"host_groups": [
{
"name": "master",
"configurations": [],
"components": []
},
{
"name": "worker",
"configurations": [],
"components": [ ]
},
{
"name": "compute",
"configurations": [],
"components": []
}
]
}
For correct blueprint layout and other information about Ambari blueprints, refer to the Ambari cwiki page.
Creating Blueprints for Ambari 2.6.1+
Ambari 2.6.1 or newer does not install the mysqlconnector; therefore, when creating a blueprint for Ambari 2.6.1 or newer you should not include the MYSQL_SERVER component for Hive Metastore in your blueprint. Instead, you have two options:
- Configure an external RDBMS instance for Hive Metastore and include the JDBC connection information in your blueprint. If you choose to use an external database that is not PostgreSQL (such as Oracle, mysql) you must also set up Ambari with the appropriate connector; to do this, create a pre-ambari-start recipe and pass it when creating a cluster.
- If a remote Hive RDBMS is not provided, Cloudbreak installs a Postgres instance and configures it for Hive Metastore during the cluster launch.
Cloudbreak requires you to define an additional element in the blueprint called "blueprint_name". This should be a unique name within Cloudbreak list of blueprints. For example:
"Blueprints": {
"blueprint_name": "hdp-small-default",
"stack_name": "HDP",
"stack_version": "2.6"
},
"settings": [],
"configurations": [],
"host_groups": [
...
The "blueprint_name" is not included in the Ambari export.
After you provide the blueprint to Cloudbreak, the host groups in the JSON will be mapped to a set of instances when starting the cluster, and the specified services and components will be installed on the corresponding nodes. It is not necessary to define a complete configuration in the blueprint. If a configuration is missing, Ambari will use a default value.
Here are a few blueprint examples. You can also refer to the default blueprints provided in the Cloudbreak UI.
Related Links
Blueprint Examples (Hortonworks)
Ambari cwiki (External)
Creating a Template Blueprint
Cloudbreak allows you to create special blueprints which include templating: the values of the variables specified in the blueprint will be dynamically generated & replaced in the cluster creation phase, picking up the parameter values that you provided in the Cloudbreak UI or CLI. Cloudbreak supports mustache kind of templating with {{{variable}}} syntax. You cannot use functions in the blueprint file; only variable injection is supported.
External Authentication Source (LDAP/AD)
When using External Authentication Sources, the following variables can be specified in your Blueprint for replacement:
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ldap.connectionURL | the URL of the LDAP (host:port) | ldap://10.1.1.1:389 |
| ldap.bindDn | The root Distinguished Name to search in the directory for users | CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=ad,DC=hdc,DC=com |
| ldap.bindPassword | The root Distinguished Name password | Password1234! |
| ldap.directoryType | The directory of type | LDAP or ACTIVE_DIRECTORY |
| ldap.userSearchBase | User search base | CN=Users,DC=ad,DC=hdc,DC=com |
| ldap.userNameAttribute | Username attribute | cn |
| ldap.userObjectClass | Object class for users | person |
| ldap.groupSearchBase | Group search base | OU=Groups,DC=ad,DC=hdc,DC=com |
| ldap.groupNameAttribute | Group attribute | cb |
| ldap.groupObjectClass | Group object class | group |
| ldap.groupMemberAttribute | Attribute for membershio | member |
| ldap.domain | Your domain | example.com |
External Database (RDBMS)
When using External Databases, the following variables can be specified in your Blueprint for replacement:
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| rds.[type].connectionURL | The jdbc url to the RDBMS | jdbc:postgresql://db.test:5432/test |
| rds.[type].connectionDriver | The connection driver | org.postgresql.Driver |
| rds.[type].connectionUserName | The user name to the database | admin |
| rds.[type].connectionPassword | The password for the connection | Password1234! |
| rds.[type].databaseName | The name of the database | hive |
| rds.[type].host | The host of the database | 10.1.1.1 |
| rds.[type].hostWithPort | Database host + port | 10.1.1.1:1234 |
| rds.[type].subprotocol | Parsed from jdbc url | postgres |
| rds.[type].databaseEngine | Capital database name | POSTGRES |
Upload a Blueprint
Once you have your blueprint ready, perform these steps.
Steps
- In the Cloudbreak UI, select Blueprints from the navigation pane.
-
To add your own blueprint, click Create Blueprint and enter the following parameters:
Parameter Value Name Enter a name for your blueprint. Description (Optional) Enter a description for your blueprint. Blueprint Source Select one of:
- Text: Paste blueprint in JSON format.
- File: Upload a file that contains the blueprint.
- URL: Specify the URL for your blueprint.
-
To use the uploaded blueprints, select it when creating a cluster. The option is available on the General Configuration page. First select the Platform Version and then select your chosen blueprint under Cluster Type.
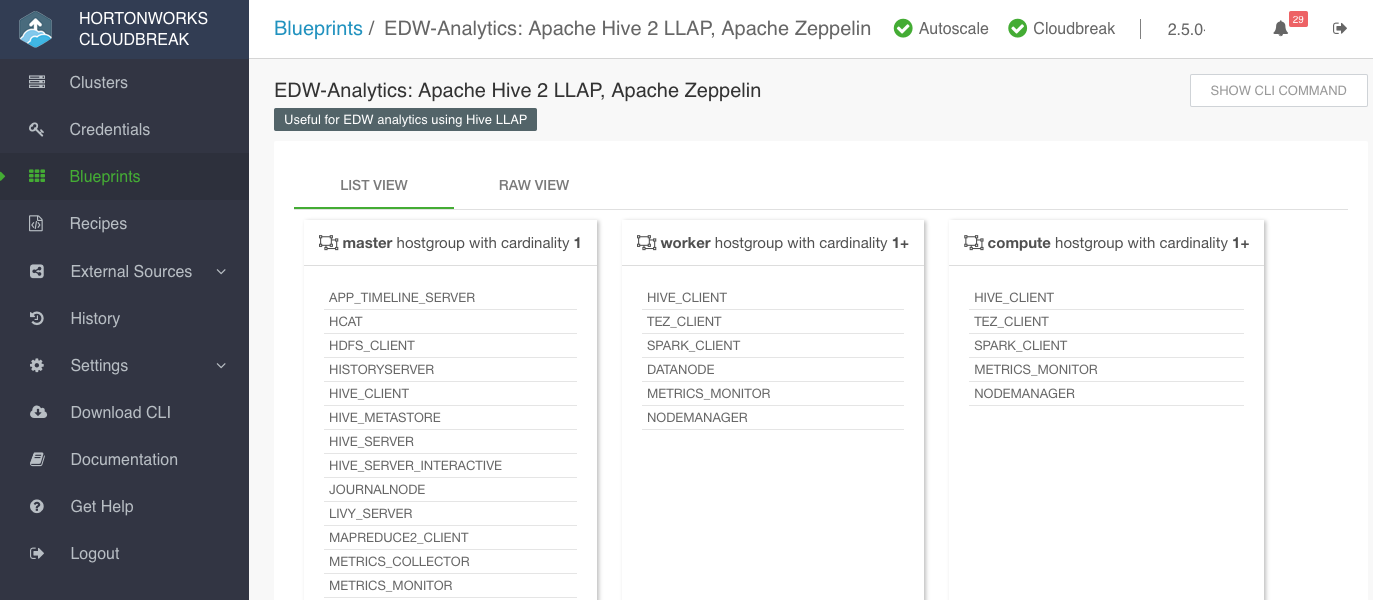
View Blueprint Details
Once a blueprint has been registered in Cloudbreak, you can access its details in the Cloudbreak UI.
Steps
-
In the Cloudbreak UI, select Blueprints from the navigation pane and click on an entry to navigate to details.
You can view blueprint details using the List View and Raw View:
Delete Blueprint
To delete a default or custom blueprint, perform these steps.
Steps
-
In the Cloudbreak UI, select Blueprints from the navigation pane.
-
Click on an entry to navigate to details.
-
Click Delete.
-
Confirm delete.