Using EBS Volumes for Cloudera Manager and CDH
Cloudera Director 2.2 and higher supports the use of Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes with Cloudera Manager and CDH cluster instances. You can use EBS volumes to store HDFS data, stage data for processing, or install other applications. EBS can provide an efficient and cost-effective alternative to S3 or other storage mechanisms.
EBS volumes for a Cloudera Manager or CDH cluster instance have the same lifecycle as the instance. EBS volumes are terminated when the instance is terminated. Repair of an instance does not result in the remounting of an existing EBS volume; a new volume is used.
An advantage of using EBS volumes for cluster storage is that it allows you to pause your cluster and stop the associated EC2 instances during periods of inactivity. You will still be billed for your EBS volumes while the cluster is paused, but will not be billed for the stopped EC2 instances. For information on pausing a cluster, see Pausing a Cluster on AWS.
EBS Volume Types
| EBS volume type | Minimum and Maximum Size | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| gp2 | 1 GiB - 16 TiB | General-purpose SSD (solid state drive) volume that balances price and performance for a wide variety of transactional workloads. |
| io1 | 4 GiB - 16 TiB | Provisioned IOPS SSD (solid state drive) volume. Highest-performance SSD volume for mission-critical low-latency or high-throughput workloads. |
| st1 | 500 GiB - 16 TiB | Low-cost HDD (hard disk drive) volume designed for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads. |
| sc1 | 500 GiB - 16 TiB | Lowest-cost HDD (hard disk drive) volume designed for less frequently accessed workloads. |
For more information, see Amazon EBS Volume Types.
Amazon EC2 Instance Stores
If an instance type has instance store volumes and you do not specify EBS volumes, Cloudera Director automatically mounts all the instance store volumes that are available. If you do specify EBS volumes, Cloudera Director does not mount instance store volumes.
For more information on EC2 instance stores, see Amazon EC2 Instance Stores in the AWS documentation.
Configuring EBS Volumes
You configure EBS volumes in the instance template in the web UI or in the instance section of the configuration file for clusters launched with the CLI and bootstrap-remote.
Configuring an EBS Volume with the Web UI
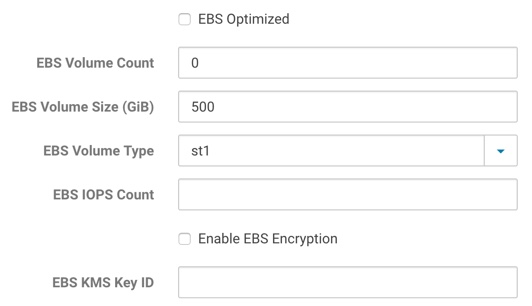
- EBS Optimized: Specify whether to enable EBS Optimized I/O. This optimization isn't available with all instance types. Some instance types are EBS optimized by default regardless of this flag. Additional usage charges may apply when using an EBS-optimized instance.
- EBS Volume Count: The number of EBS volumes to mount. Cloudera Director will create and attach these volumes to the provisioned instance. These added volumes will be deleted when the instance is terminated from Cloudera Director.
- EBS Volume Size (GiB): The size of the additional EBS volumes to mount. Specifying a size outside the ranges defined in the table above causes cluster deployment to fail.
- EBS Volume Type: The EBS volume type for the additional EBS volumes. Supported volumes are Throughput Optimized HDD (st1), Cold HDD (dc1), General Purpose SSD (gp2), and Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1). All EBS volumes for an instance must be of the same type.
- EBS IOPS Count: The number of I/O operations per second (IOPS) to provision for the volume. Only valid and required for Provisioned IOPS (io1) SSD volumes.
- Enable EBS Encryption: Whether to enable encryption for the additional EBS volumes. Note that the encryption does not apply to the root volume.
- EBS Key ID: The full ARN of the KMS Custom Master Key (CMK) to use when encrypting volumes. If encryption is enabled and this is blank, the default CMK will be used. Note that encryption does not apply to the root volume.
Configuring EBS Volumes with the Configuration File
# # EBS Volumes # # Director can create and attach additional EBS volumes to the instance. These volumes # will be automatically deleted when the associated instance is terminated. These # properties don't apply to the root volume. # # See http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/EBSVolumes.html # # ebsVolumeCount : 0 # ebsVolumeType: st1 # Specify either st1, sc1, gp2 or io1 volume type # ebsVolumeSizeGiB: 500 # ebsIops: 500 # Number of IOPS, only valid and required for io1 volume type # # EBS Volume Encryption # # Encryption can be enabled on the additional EBS volumes. An optional CMK can # be specified for volume encryption. Not setting a CMK means the default CMK # for EBS will be used. The encryption here does not apply to the root volume. # # See http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/EBSEncryption.html # # enableEbsEncryption: false # ebsKmsKeyId: "arn:aws:kms:REPLACE-ME" # full ARN of the KMS CMK # # EBS Optimized # # Specify whether to enable EBS Optimized I/O. This optimization isn't available # with all instance types. Some instance types are EBS Optimized by default # regardless of this flag. Additional usage charges may apply when using an # EBS-optimized instance. # # See http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/EBSOptimized.html # # ebsOptimized : false
EBS Volume Encryption
- enableEbsEncryption: Labeled Enable EBS Encryption in the web UI. Set to true or false. If this value is set to true, the data on EBS volumes created with this instance template will be encrypted.
- ebsKmsKeyId: Labeled EBS KMS Key ID in the web UI. The key used to encrypt data in the EBS volumes. KMS includes a
default master key for each service that supports encryption, including EBS. If you leave this field empty, Cloudera Director configures the EBS volumes to use the KMS default master key for EBS.
Alternatively, you can import a custom master key from your own key management infrastructure into KMS and specify it here to be used for the EBS service. To specify a custom master key, enter the
full Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the custom master key that you have stored in
KMS: arn:aws:kms:your_key_name. For example:
arn:aws:kms:us-west-1:635144601417:key/39b8cdf2-923e-721b-9c6c-652a7e517d72
For more information about EBS encryption, see Amazon EBS Encryption in the AWS documentation. For more information about KMS, see AWS Key Management Service Details in the AWS documentation.
Creating an Encrypted Root Volume
Configuring Device Names for EBS Volumes and Instance Store Volumes
When requesting EC2 instances in Cloudera Director with additional EBS volumes or requesting an instance that contains instance store volumes, Cloudera Director will automatically assign device names to the volumes. For more information about device names in EC2, see Device Naming on Linux Instances in the AWS documentation. You can configure the way the device names are assigned to the volumes. This might be necessary to ensure that the device names used by Cloudera Director doesn't overlap with any additional volumes associated with an AMI.
ephemeralDeviceMappings {
deviceNamePrefix: /dev/sd
rangeStart: b
}ebsDeviceMappings {
deviceNamePrefix: /dev/sd
rangeStart: f
}Note that Cloudera Director does not attach both instance store volumes and EBS volumes at the same time. If you specify EBS volumes, instance store volumes will not be attached.