Cloudera Navigator Metadata Architecture
Cloudera Navigator metadata provides data discovery and data lineage functions. The Cloudera Navigator metadata architecture is illustrated below.
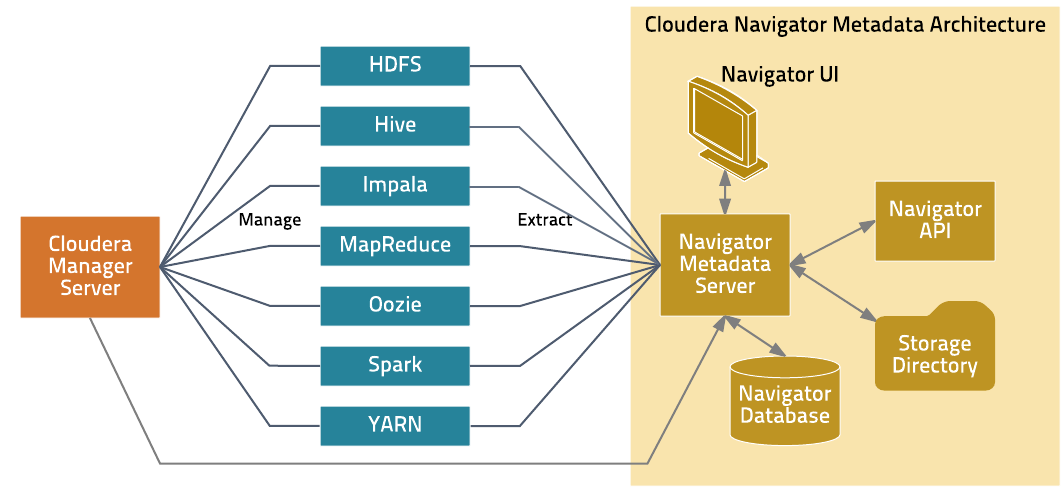
The Navigator Metadata Server performs the following functions:
- Obtains connection information about CDH services from the Cloudera Manager Server
- At periodic intervals, extracts metadata for the entities managed by those services
- Manages and applies metadata extraction policies during metadata extraction
- Indexes and stores entity metadata
- Manages authorization data for Navigator users
- Manages audit report metadata
- Generates metadata and audit analytics
- Implements the Navigator UI and API
The Navigator database stores policies, user authorization and audit report metadata, and analytic data. The storage directory stores the extraction state and extracted metadata.
Continue reading:
The Cloudera Navigator Metadata Server manages metadata about the entities in a CDH cluster and relations between the entities. The metadata schema defines the types of metadata that are available for each entity type it supports.
For example, the following figure shows the entity details of a file entity:
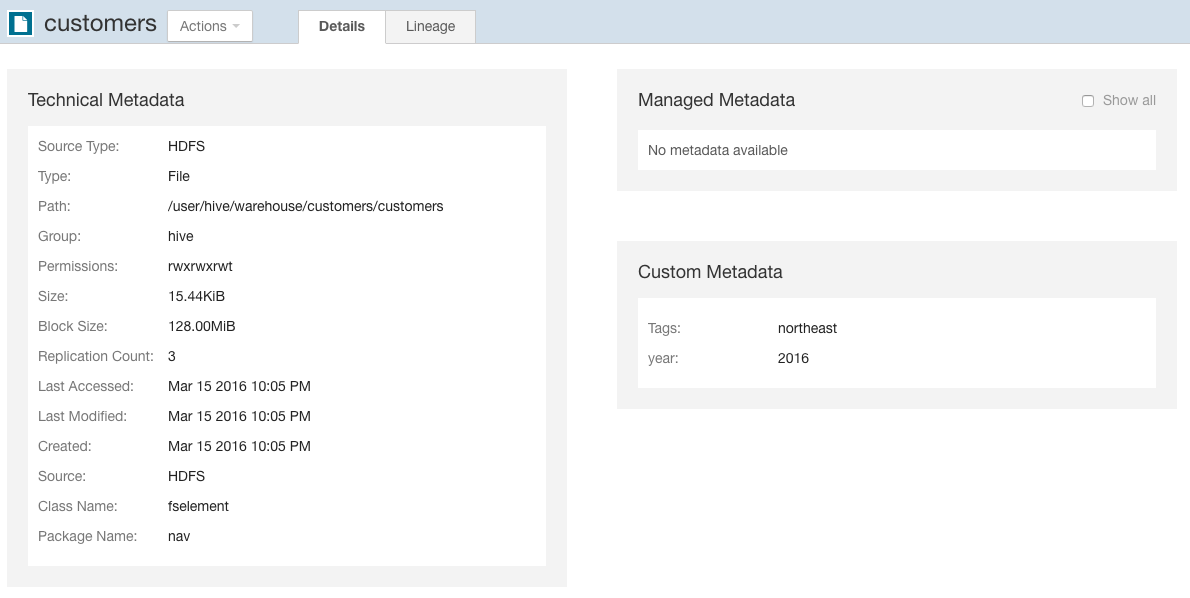
As shown in the Details tab, three classes of metadata are defined for all entities:
- Technical Metadata - Metadata defined when entities are extracted. Such metadata includes:
- The name of an entity
- The service that manages or uses the entity
- Type
- The path to the entity
- Date and time of creation
- Access
- Modification, size, owner, purpose, and relations—parent-child, data flow, and instance of—between entities
- Custom Metadata - Descriptions, key-value pairs, and tags that can be added to entities. You can add and modify custom metadata before and after entities are extracted.
- Managed Metadata - Key-value pairs that can be added to entities. Managed metadata key-value pairs are similar to custom metadata key-value pairs, with additional abilities to define the keys within a namespace and enforce conformance to value constraints (for example, require the value to be a date). You can add and modify managed metadata after entities are extracted.