Defining Managed Metadata
Minimum Required Role:: Metadata Administrator (also provided by Full Administrator)
Managed metadata allows you to add typed metadata to classes of entities. You can add namespaces and properties.
A namespace is a container for properties. There are four reserved namespaces: nav for Navigator metadata classes (for example, fselement and user-defined custom fields), up (custom metadata), tp (technical properties) and xt (partner applications). The combination of namespace and property name must be unique.
A property can be one of the following types: boolean, date, integer, long, float, double, text, and enum (of string). For text properties, you can specify optional maximum length and regular expression validation criteria. A property can be single-valued or assume multiple values.
Once you have created properties and assigned property values to specific entities, you can create search filters for property values.
Creating Custom Properties Using the Metadata UI
- Do one of the following:
- Enter the URL of the Navigator UI in a browser: http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/, where Navigator_Metadata_Server_host is the name of the host on which you are running the Navigator Metadata Server role and port is the port configured for the role. The default port of the Navigator Metadata Server is 7187. To change the port, follow the instructions in Configuring the Navigator Metadata Server Port.
- Do one of the following:
- Select .
- Navigate from the Navigator Metadata Server role:
- Do one of the following:
- Select .
- On the tab, in Cloudera Management Service table, click the Cloudera Management Service link.
- Click the Instances tab.
- Click the Navigator Metadata Server role.
- Click the Cloudera Navigator link.
- Do one of the following:
- Log in to Cloudera Navigator with the credentials of a user having one of the following user roles:
- Cloudera Manager Full Administrator
- Cloudera Manager Navigator Administrator
- Cloudera Navigator Full Administrator
- Cloudera Navigator Metadata Administrator
- Click the Administration link in the upper right. The Managed Metadata tab displays the list of namespaces and the properties defined in the namespaces.
- Click the Create... button.
- In the Class field, click
 or type
the beginning of a Navigator entity classname.
or type
the beginning of a Navigator entity classname. - Select the class of entities to which the property applies. To clear the field, hover over the field and click the
 that displays at the right of the field.
that displays at the right of the field. - Click the Namespace field. If the Namespace drop-down list is empty, click Create Namespace....
- Specify a namespace name and optional description.
- Click Continue.
- In the Namespaces drop-down list, select a namespace.
- Specify an optional description.
- Fill in the name of the property.
The name can contain letters, numbers, underscores, and hyphens and can be up to 50 characters long.
- Select the Multivalued checkbox if the property can have more than one value. For example, an emailFrom property should accept only one value, but an emailTo property could accept more than one value.
- In the Type drop-down list, select the property type and specify constraints on the value.
- Boolean - Boolean: true or false.
- Date - Date and time.
- Enumeration - A set of values. In the Enumeration field, type valid enumeration values and press Enter or Tab.
- Number - A number. In the Number Type field, select the type of the number: Integer, Long, Float, Double.
- Text - A string.
- Maximum Length - The maximum length of the string.
- Regular Expression - A regular expression that determines whether a string is a valid value.
- Click Continue to Review. The Review and Save screen displays.
- Click Create to commit the change or Back to Edit Property to continue editing the property.
Example Properties
The following figure shows two properties contained in the namespace MailAnnotation that apply to entities of the fselement class (that is, HDFS files and directories). The emailFrom property is of type TEXT and can be assigned a single value. The emailTo property is also of type TEXT but can have multiple values.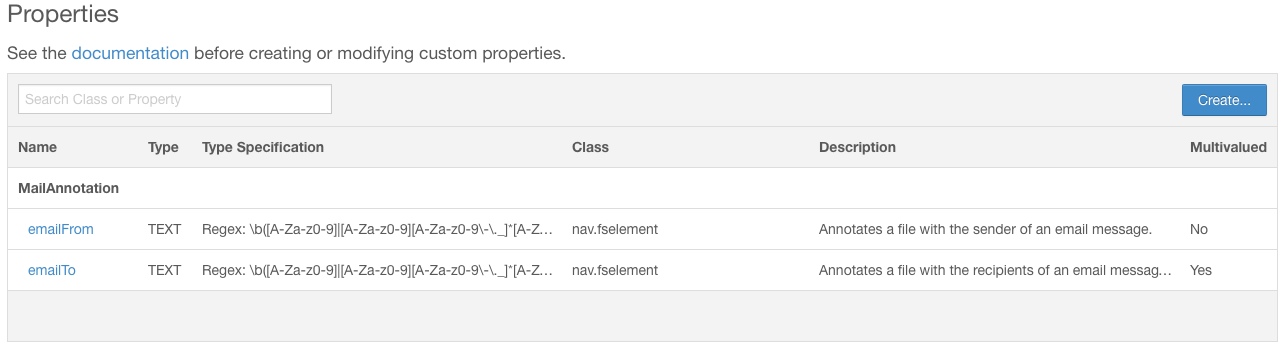
Editing Custom Properties Using the Metadata UI
The only changes you can make to a custom property are to add classes to which the property applies and enumeration values.
- Do one of the following:
- Enter the URL of the Navigator UI in a browser: http://Navigator_Metadata_Server_host:port/, where Navigator_Metadata_Server_host is the name of the host on which you are running the Navigator Metadata Server role and port is the port configured for the role. The default port of the Navigator Metadata Server is 7187. To change the port, follow the instructions in Configuring the Navigator Metadata Server Port.
- Do one of the following:
- Select .
- Navigate from the Navigator Metadata Server role:
- Do one of the following:
- Select .
- On the tab, in Cloudera Management Service table, click the Cloudera Management Service link.
- Click the Instances tab.
- Click the Navigator Metadata Server role.
- Click the Cloudera Navigator link.
- Do one of the following:
- Log in to Cloudera Navigator with the credentials of a user having one of the following user roles:
- Cloudera Manager Full Administrator
- Cloudera Manager Navigator Administrator
- Cloudera Navigator Full Administrator
- Cloudera Navigator Metadata Administrator
- Click the Administration link in the upper right. The Managed Metadata tab displays the list of namespaces and the properties defined in the namespaces.
- In the Properties table, click a property link. The Edit propertyname dialog box displays.
- In the Additional Class field, click
 or type the beginning of a Navigator entity classname.
or type the beginning of a Navigator entity classname. - Select the class of entities to which the property applies. To clear the field, hover over the field and click the
 that displays at the right of the field.
that displays at the right of the field. - In the Additional Enumeration Values field, type valid enumeration values and press Enter or Tab.
- Click Continue to Review. The Review and Save screen displays.
- Click Update to commit the change or Back to Edit Property to continue editing the property.
Navigator Built-in Classes
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| hdfs_dataset | Logical dataset backed by a path in HDFS. |
| hdfs_dataset_field | Field in an HDFS dataset. |
| fselement | DFS file or directory. |
| hv_column | Column in a Hive table. |
| hv_database | Hive database. |
| hv_partition | Partition of a Hive table. |
| hv_query | Hive query template. |
| hv_query_exec | Instance of a Hive query. |
| hv_query_part | Component of a Hive query that maps specific input columns to output columns. |
| hv_table | A Hive table. |
| hv_view | View on one or more Hive tables. |
| impala_query | Impala query template. |
| impala_query_exec | Instance of an Impala query. |
| impala_query_part | Component of an Impala query that maps specific input columns to output columns. |
| mrjobinstance | Instance of a MapReduce, YARN, or Spark job. |
| mrjobspec | Template for a MapReduce, YARN, or Spark job. |
| oozie_workflow | Template for an Oozie workflow. |
| oozie_wf_instance | Instance of an Oozie workflow. |
| sq_export_sub_oper | Sqoop export component that connects specific columns. |
| sq_qry_import | Sqoop import job with query options. |
| sq_import_sub_oper | Sqoop import component that connects specific columns. |
| sq_oper_exec | Instance of a Sqoop job. |
| sq_tbl_import | Sqoop table import operation template. |
| sq_tbl_export | Sqoop table export operation template. |
| pig_field | Field for a relation in Pig; similar to a column in a Hive table. |
| pig_operation | Template for a Pig transformation. |
| pig_op_exec | Instance of a Pig transformation. |
| pig_relation | Pig relation; similar to a Hive table. |
| userexpression | User-specified sub-operation of a MapReduce or YARN job; used for specifying custom column-level lineage. |
Defining Metadata with the Navigator API and Navigator SDK
In addition to defining metadata using features provided by the Navigator Metadata UI, you can also define metadata using the Navigator API and Navigator SDK.
For information on the Navigator API, see Cloudera Navigator Data Management API.
For information on the SDK, see the Navigator SDK documentation.