Sentry High Availability
High availability for Sentry provides automatic failover in the event that your primary Sentry host goes down or is unavailable.
Architecture
With Sentry high availability enabled, there is a leader Sentry Server that gets the current Hive metadata from the Hive metastore and permissions from HiveServer2, and writes that information to the Sentry database. The other Sentry Server then asks the Sentry database for the updated information; the Sentry Servers do not communicate with each other directly. The Sentry Server leader is determined randomly by the ZooKeeper service and is not configurable by the administrator. If the Sentry Server leader goes down, the other Sentry Server becomes the leader. Load balancing between the Sentry services is achieved by each client randomly selecting a Sentry service to connect to.
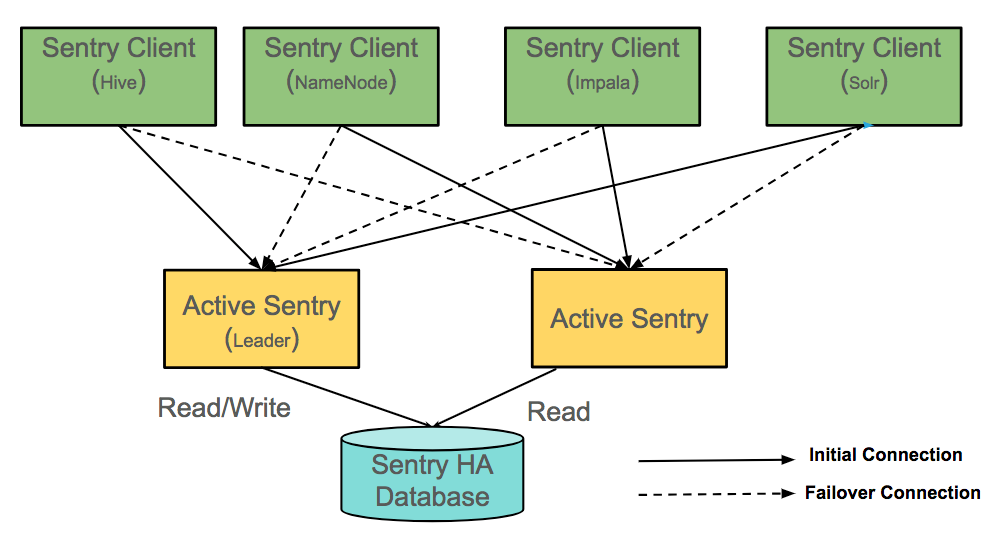
The image below illustrates how the Sentry Servers interact with the clients and the Sentry database when both Sentry Servers are available. The clients can connect to both Sentry Servers. The leader Sentry Server reads from and writes to the Sentry database, and the other Sentry Server reads from the Sentry database.
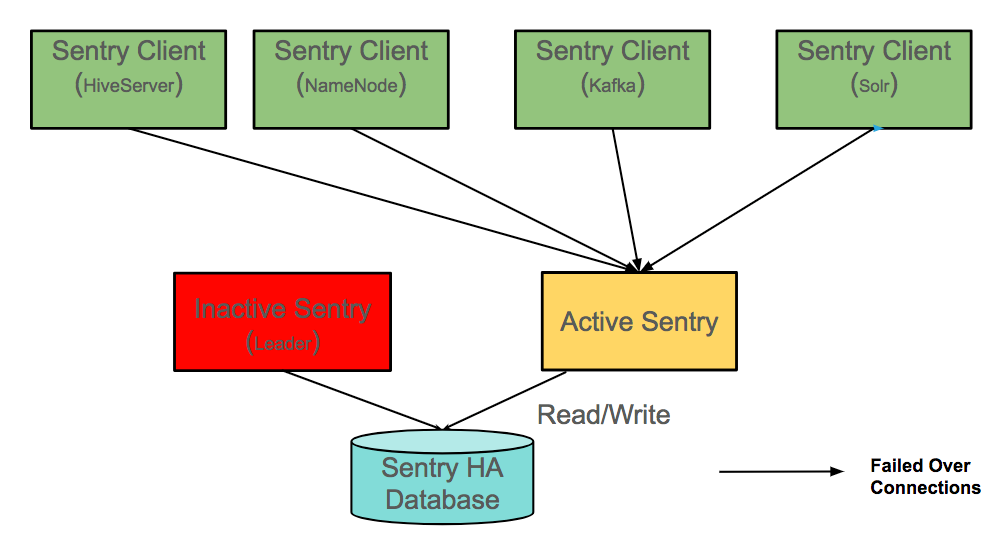
When one of the Sentry Servers is unavailable, as in the following image, the clients connect to the Sentry Server that is available. As the image illustrates, if the leader Sentry Server is unavailable, the other Sentry Server can write to the Sentry database.
Sentry and Hive Metastore High Availability
You can also use Sentry high availability with Hive metastore high availability. When all the Sentry Servers and Hive metastores are available, the Sentry leader pulls Hive metadata from the Hive metastore master. If one or more is unavailable, the available Sentry Server that is available pulls metadata from the Hive metastore that is available.
For more information about Hive metastore high availability, see Configuring Apache Hive Metastore High Availability in CDH.
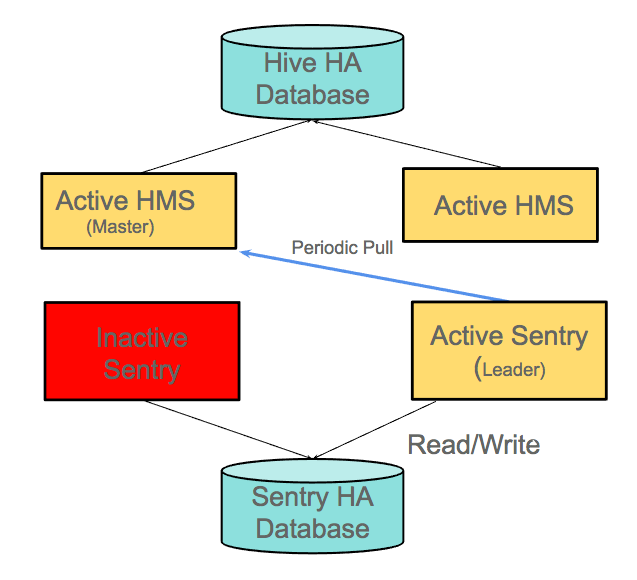
In the image below, one of the Sentry Servers is unavailable. The Sentry Server that is available pulls metadata from the Hive metastore leader.
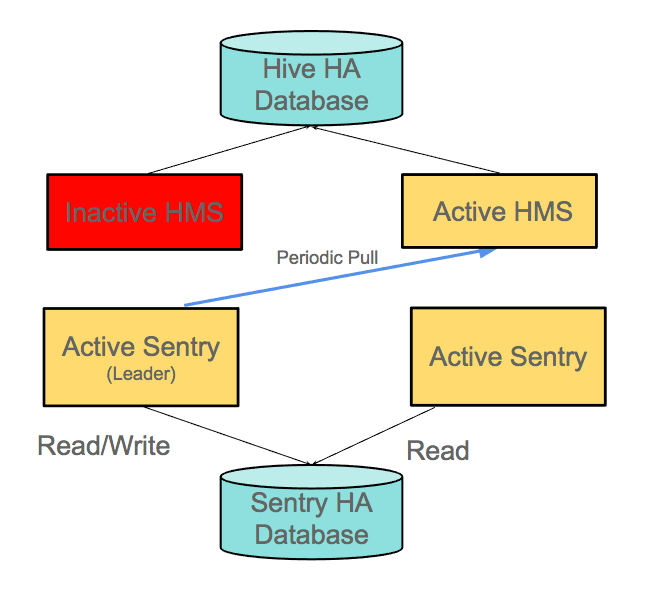
When one of the Hive metastores is unavailable, the Sentry leader pulls metadata from the metastore that is available, as the following figure illustrates:
Prerequisites
Verify the following prerequisites before you enable high availability for Sentry:
- You must have CDH version 5.13.0 or higher installed.
- You must have Cloudera Manager version 5.13.0 or higher installed.
- The Sentry service must be installed and running. See Before You Install Sentry and Installing and Upgrading the Sentry Service for information about how to install the Sentry service.
- The ZooKeeper service must be enabled. To view the ZooKeeper service that the Sentry service depends on, open the Sentry service in Cloudera Manager, click the Configuration tab and enter ZooKeeper in the Search box. The ZooKeeper Service property is displayed.
- The Sentry service must be backed by a relational database, not a flat file.
- If you want to use a rolling restart to restart the cluster, you must have HDFS high availability enabled. For information about configuring HDFS high availability, see HDFS High Availability.
Enable Sentry High Availability
You can enable high availability for Sentry using a rolling restart or with a manual cluster restart. A rolling restart allows you to restart the cluster without completely bringing down the cluster, but you must have HDFS high availability enabled.
The following sections describe the steps to enable high availability with and without a rolling restart. You can also view the how-to article, How to Enable Sentry High Availability, for steps to enable high availability with images to guide you through the process, or you can watch the following video:
Enabling with a Rolling Restart
You can perform a rolling restart through Cloudera Manager if you want to enable Sentry high availability without bringing down the cluster. You must have HDFS high availability enabled and you must perform a cluster-level rolling restart. Note that while you can use a rolling restart to enable Sentry high availability without stopping the cluster, the restart will stop the Sentry service.
For information about configuring HDFS high availability, see HDFS High Availability.
For more information about using Cloudera Manager to perform a rolling restart, see Rolling Restart.
Complete the following steps to enable Sentry high availability with a rolling restart:
- In Cloudera Manager, open the Sentry service.
- Open the Instances tab and click Add Role Instances.
- In the Add Role Instances wizard, click the Select a host button for the Sentry Server. You do not have to edit the Gateway host.
-
A pop-up window opens that allows you to pick an alternate host for the Sentry service. Click the hostname of the host that you want to use for high availability. The host that the Sentry service is currently running on is already selected and grayed out. You can select one alternate host for the Sentry service.
You can search for a host or you can filter the list by entering a range of hosts in the Search field. You can search for hosts with the following information:
- Range of hostnames. Use the following range definitions:
Range Definition Matching Hosts 10.1.1.[1-4] 10.1.1.1, 10.1.1.2, 10.1.1.3, 10.1.1.4 host[1-3].company.com host1.company.com, host2.company.com, host3.company.com host[07-10].company.com host07.company.com, host08.company.com, host09.company.com, host10.company.com - IP addresses
- Rack name
- Range of hostnames. Use the following range definitions:
- After you have selected the alternate host, click OK to close the window. The hostname appears below the Sentry Server.
- Click Continue. The wizard closes and the Sentry hosts are listed.
- Go to the Cloudera Manager home page and click the All Recent Commands tab. Verify that the Generate Missing Credentials command has successfully completed before you proceed with the rolling restart.
- Click the Status tab to return to the Cloudera Manager home page.
- Click the down arrow next to the cluster name to open the menu and click Deploy Client Configuration.
- A window opens asking if you are sure you want to run the Deploy Client Configuration command. Click Deploy Client Configuration.
- When the steps are successfully completed, click Close to close the window.
- Click the down arrow next to the cluster name again to open the menu and click Rolling Restart. For detailed information about the rolling restart, see Rolling Restart.
-
In the Rolling Restart window that opens, select the services that have stale configurations, including the Sentry service. Every service that is dependent on Sentry will have a stale configuration. In the Roles to Include parameter, select All Roles.
Note that the services that do not support rolling restart will simply be restarted and will be unavailable during their restart, including the Sentry service.
- Click Rolling Restart to begin the restart.
- A pop-up window opens that lists the rolling restart steps and the status of each step. When the rolling restart is complete, click Close to close the pop-up.
- Verify that none of the services have stale configurations. If one or more services has a stale configuration after the rolling restart, Sentry high availability might not be configured properly.
- To verify the statuses of the Sentry hosts, open the Sentry service and click the Instances tab.
Enabling with a Cluster Restart
Complete the following steps to enable high availability for Sentry in Cloudera Manager with a cluster restart:
- In Cloudera Manager, open the Sentry service.
-
In the Actions drop-down menu, click Enable High Availability.
The wizard walks you through the steps to enable high availability.
- Click Select a Host in the Sentry Server Hosts field. You do not have to edit the Gateway host.
-
A pop-up window opens that allows you to pick an alternate host for the Sentry service. Click the hostname of the host that you want to use for high availability. The host that the Sentry service is currently running on is already selected and grayed out. You can select one alternate host for the Sentry service.
You can search for a host or you can filter the list by entering a range of hosts in the Search field. You can search for hosts with the following information:
Click the hostname to select the host and click OK to close the window.- Range of hostnames. Use the following range definitions:
Range Definition Matching Hosts 10.1.1.[1-4] 10.1.1.1, 10.1.1.2, 10.1.1.3, 10.1.1.4 host[1-3].company.com host1.company.com, host2.company.com, host3.company.com host[07-10].company.com host07.company.com, host08.company.com, host09.company.com, host10.company.com - IP addresses
- Rack name
- Range of hostnames. Use the following range definitions:
- The two Sentry server hosts are listed in the Sentry Server Hosts field. Click Continue.
- You can see the status of the of the new Sentry Server and the cluster restart. When the steps have successfully completed, click Finish to close the wizard.
- From the Sentry service page, you can view the status of your hosts by clicking the Instances tab.
Disable Sentry High Availability
You can also disable high availability for Sentry with a rolling restart or with a manual cluster restart. As with enabling high availability, the rolling restart allows you to restart the cluster with minimal downtime, but you must have HDFS high availability enabled.
Complete the steps below to disable high availability for Sentry:
Disabling with a Rolling Restart
You can use a rolling restart to disable Sentry high availability without bringing down the cluster. Although you do not have to stop the cluster, the rolling restart does stop the Sentry service.
- In Cloudera Manager, open the Sentry service.
- Click the Instances tab.
- Select the instance that you no longer want to be a host for the Sentry service.
- Click .
- In the pop-up window that appears, click Stop.
- The pop-up window shows the status of the command. When it is complete, click Close to close the pop-up.
- With the host still selected, click .
- In the pop-up window that appears, click Delete.
- The pop-up closes and the host is removed from the list of Sentry hosts.
- Navigate to the Cloudera Manager home page.
- Click the down arrow next to the cluster name to open the menu and click Rolling Restart. For detailed information about the rolling restart, see Rolling Restart.
- Select the services that you want to restart, including the Sentry service, and click Rolling Restart. Note that the services that do not support rolling restart will simply be restarted and will be unavailable during their restart, including the Sentry service.
- A pop-up window opens that lists the rolling restart steps and the status of each step. When the rolling restart is complete, click Close to close the pop-up.
- To verify the status of the Sentry host, open the Sentry service and click the Instances tab.
Disabling with a Cluster Restart
Complete the following steps to disable high availability for Sentry in Cloudera Manager with a cluster restart:
- In Cloudera Manager, open the Sentry service.
- In the Actions drop-down menu, click Disable High Availability.
The wizard walks you through the steps to disable high availability.
- Select the host that you want the Sentry service to run on after you disable high availability. Click the hostname and click Continue.
- You can see the status of the Sentry server and cluster restart. When the steps have successfully completed, click Finish to close the wizard.
- When the wizard closes, Cloudera Manager takes you back to the Sentry service page. You can view the status of your host by clicking the Instances tab.