Detecting block skews
Following are recommendations for detecting block skews, which are slow hosts that impact Impala performance.
By: Manish Maheshwari, Data Architect and Data Scientist at Cloudera, Inc.
The most convenient way to detect a block skew or a “slow-host” issue is to compare the Avg Time to the Max Time in the execution summary section of the query plan:
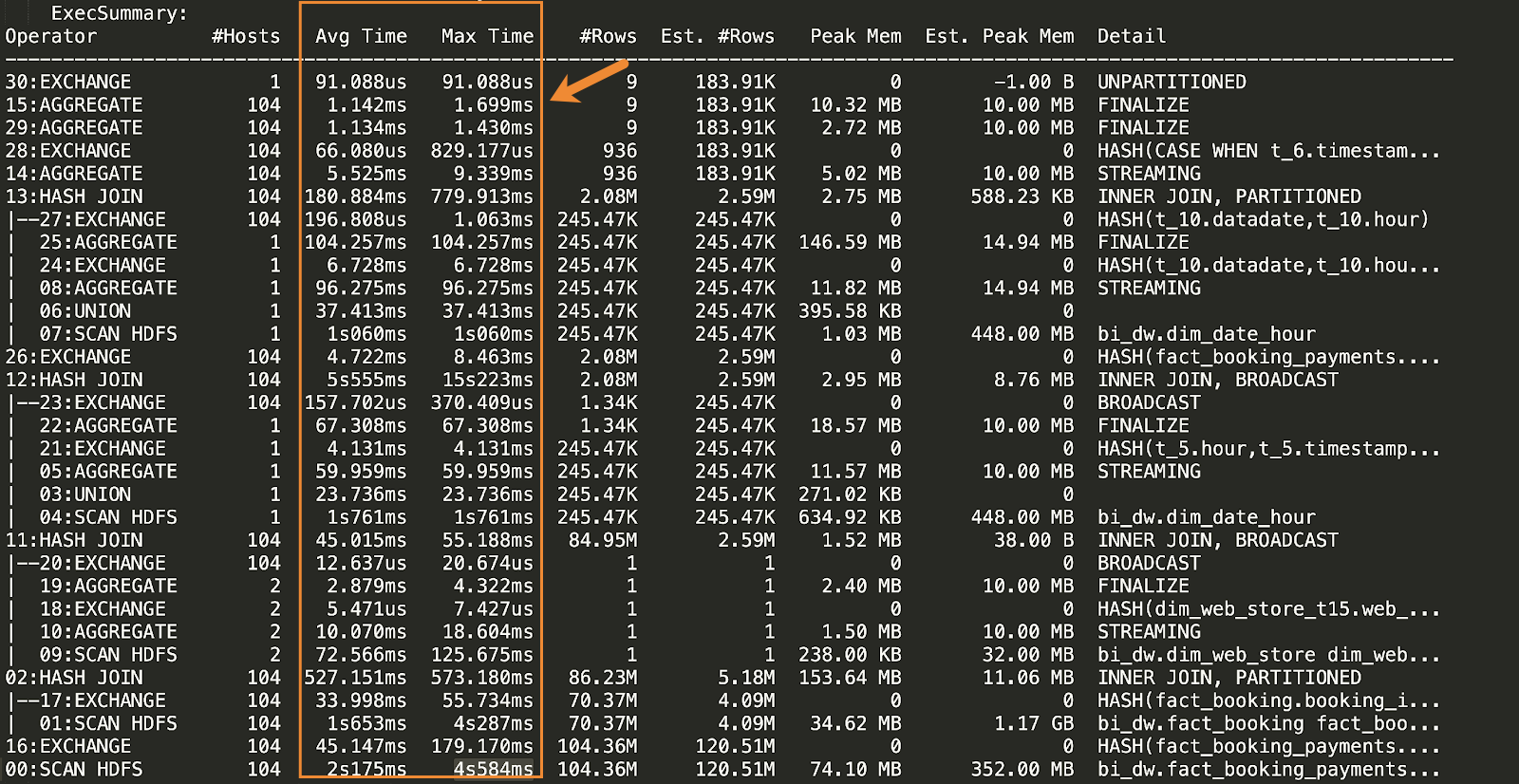
For each phase of the query, there is an Avg Time and a Max Time value, along with #Hosts, which indicates how many hosts are involved in that phase of the query. For all query phases involving more than one host, look for cases where the maximum time is substantially greater than the average time.
Slow hosts can be caused by a variety of reasons. To avoid slow hosts:
- Ensure that all Impala nodes have the same configuration.
- Ensure that other workloads, which are not run by Impala, are evenly
distributed by setting the
yarn.scheduler.fair.assignmultipleproperty tofalsein theyarn-site.xml. - Ensure that HDFS data is balanced by running the HDFS balancer utility
during the off-peak hours and then run the
INVALIDATE METADATAon Impala metadata after you perform the rebalancing to refresh the metadata in the Hive metastore. See HDFS Balancers and INVALIDATE METADATA Statement for more information. - Ensure that the HDFS block sizes are optimal. For example, use 256MB blocks and use snappy compression in a splittable block, which is preferable to GZip.
