Join query performance tuning
Join queries are tuned by using the join order and using the appropriate type of join.
By: Manish Maheshwari, Data Architect and Data Scientist at Cloudera, Inc.
Join order
- Make sure that table and column statistics are collected on join columns. This allows Impala to create the most optimal join plan. See Manually Setting Table and Column Statistics with ALTER TABLE for more information.
- If table or column statistics are not available, join the largest table first. If table or column statistics are not available for some tables in a join, Impala reorders the tables. Impala places tables with statistics on the left side of the join order in descending order of cost, based on overall size and cardinality. Tables without statistics are treated as “zero-size,” which means they are always placed on the right side of the join order.
- If you want to override the default Impala behaviour, use the
STRAIGHT_JOINtechnique explained in Overriding Join Reordering with STRAIGHT_JOIN.
Join types
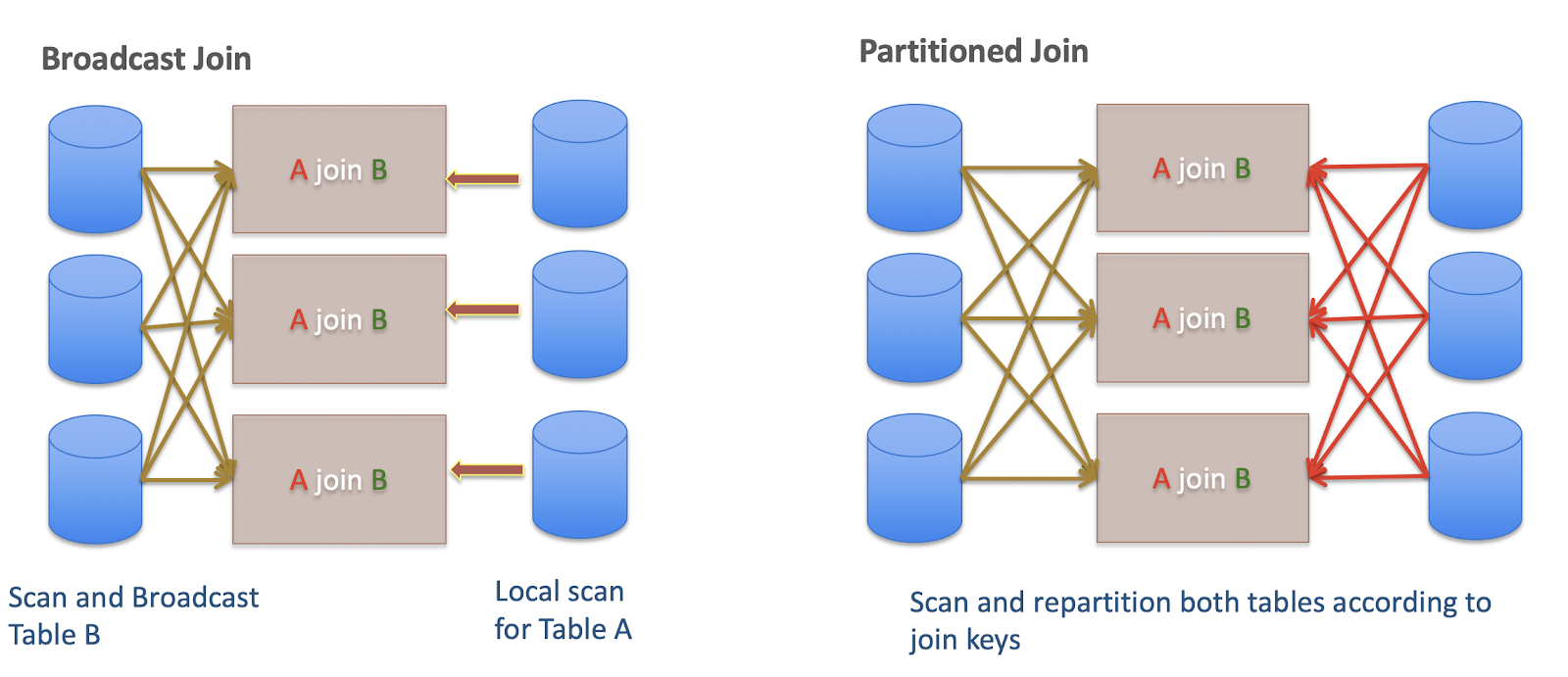
- Broadcast joins are the default join type. In this join type the right-hand table is considered to be smaller than the left-hand table, and its contents are sent to all the other nodes involved in the query.
- Partitioned joins are more suitable for large tables of roughly equal size. With this technique, portions of each table are sent to other appropriate nodes where those subsets of rows can be processed in parallel.
- The choice of broadcast or partitioned joins also depends on statistics being available for all tables in the join.
-
Join types can be set manually using the following query options:
SET DEFAULT_JOIN_DISTRIBUTION_MODE=shuffle;SET DEFAULT_JOIN_DISTRIBUTION_MODE=broadcast;
See DEFAULT_JOIN_DISTRIBUTION_MODE Query Option for more information.
The following diagram illustrates the broadcast and partitioned join types: