Setting up dedicated coordinators
Setting up dedicated coordinators helps improve performance on large clusters or for large Impala workloads.
By: Manish Maheshwari, Data Architect and Data Scientist at Cloudera, Inc.
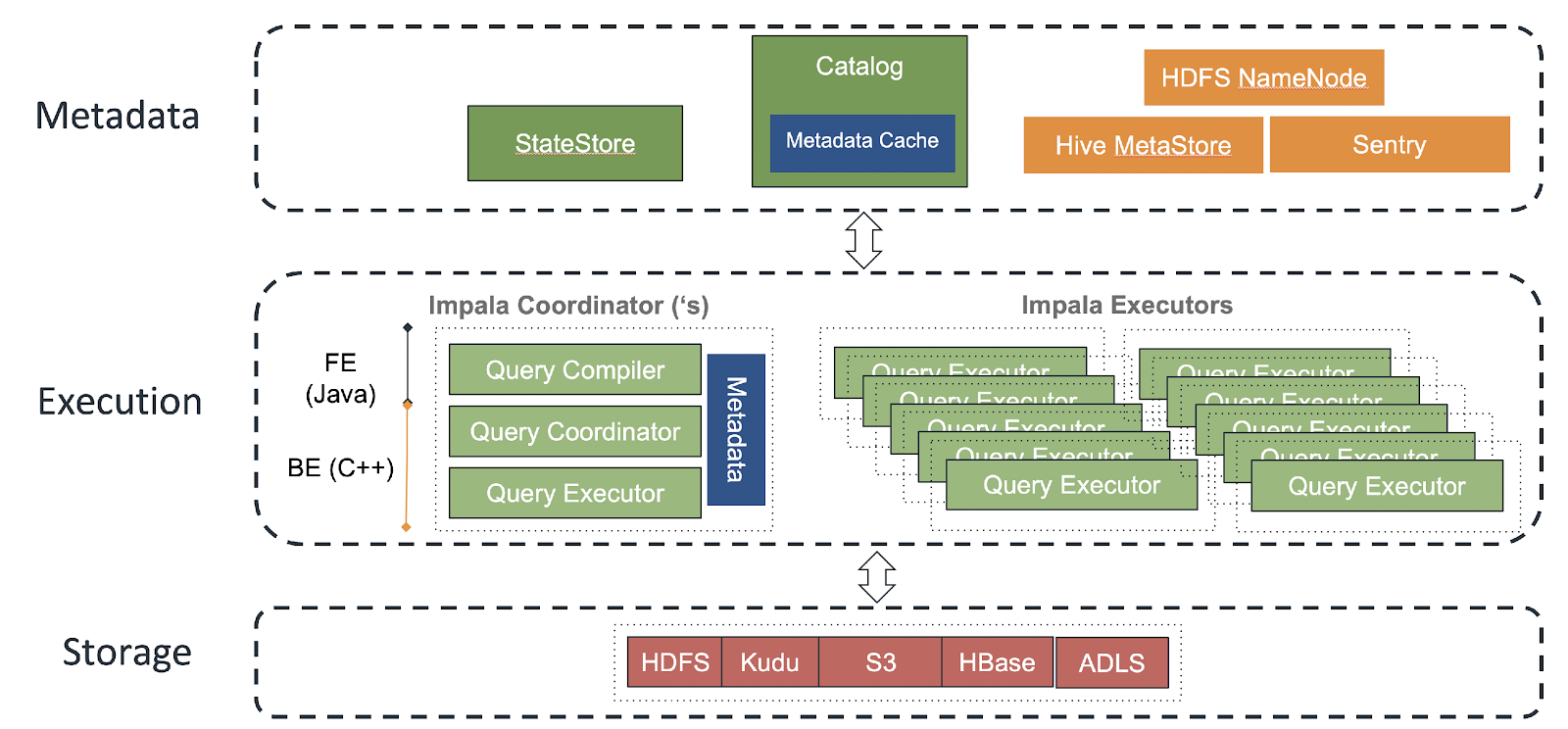
Impala can build execution plans and execute queries rapidly because it
caches block and file metadata for HDFS tables on the Catalog Server and
the query coordinator. When a new table is queried, the coordinator node
requests the metadata from the catalog service daemon (catalogd),
which in turn talks to the Hive Metastore (HMS) and the Namenode to
retrieve the information:
Problem with typical coordinator setup:
On large clusters or for large Impala workloads, the typical coordinator setup can become problematic for the following reasons:
- Each coordinator caches metadata for all table partitions and data files. This requires coordinators to be configured with a large JVM heap size.
- The extra work required for the coordinator interferes with its capacity to perform query execution work due to network and CPU overhead for queries containing a large number of query fragments.
-
Having a large number of hosts acting as coordinators can cause unnecessary network overhead because each of those hosts receives metadata from the Statestore daemon (
statestored) for metadata updates>: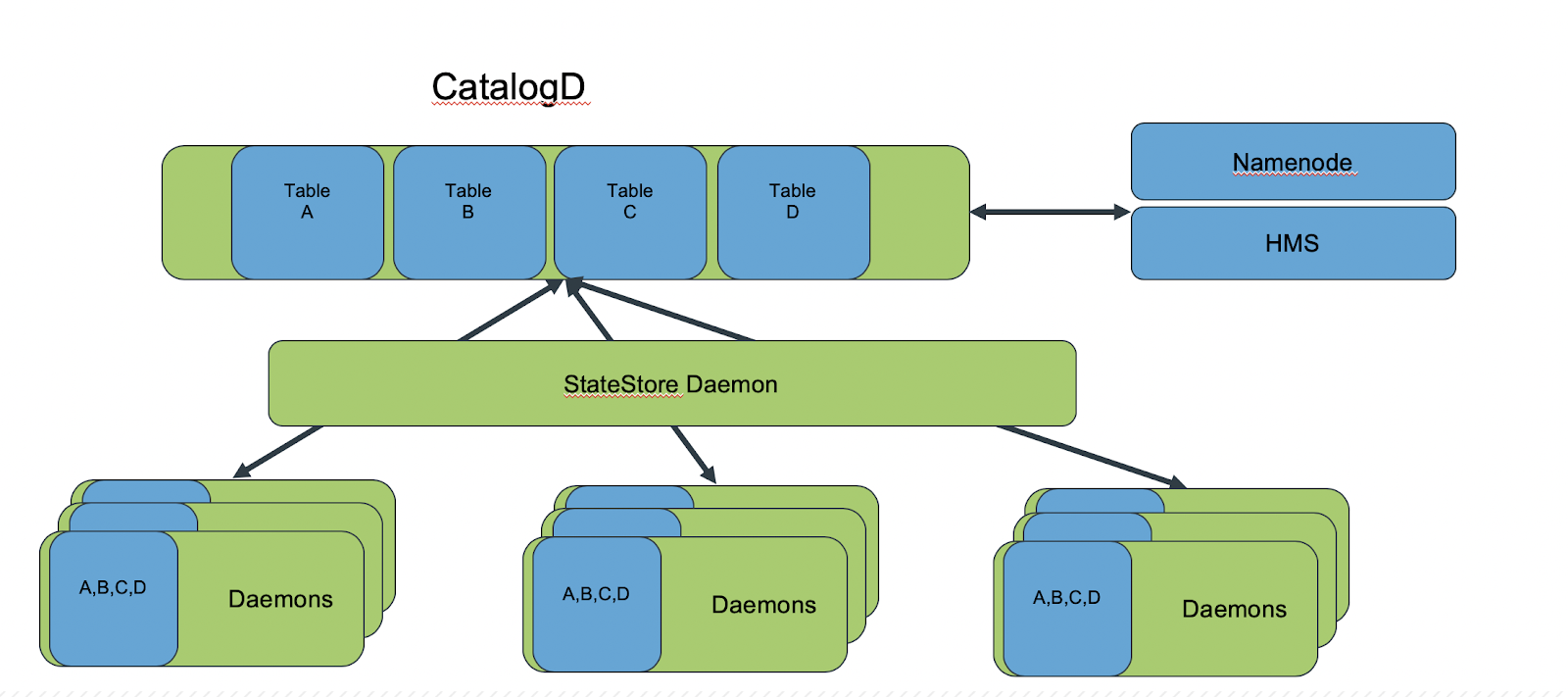
- Depending on the size of the Hive Metastore and the partitions, files, and blocks of the tables being queried, the in-memory catalog can become very large. This can cause pressure on the Impala daemons’ memory.
- The soft limits imposed by the admission control feature are more likely to be exceeded when there is a large number of heavily loaded hosts acting as coordinators, which causes admission control limits to be exceeded.
Dedicated coordinator setup solution:
To solve this coordinator setup problem, separate roles for coordinators and executors as shown below:
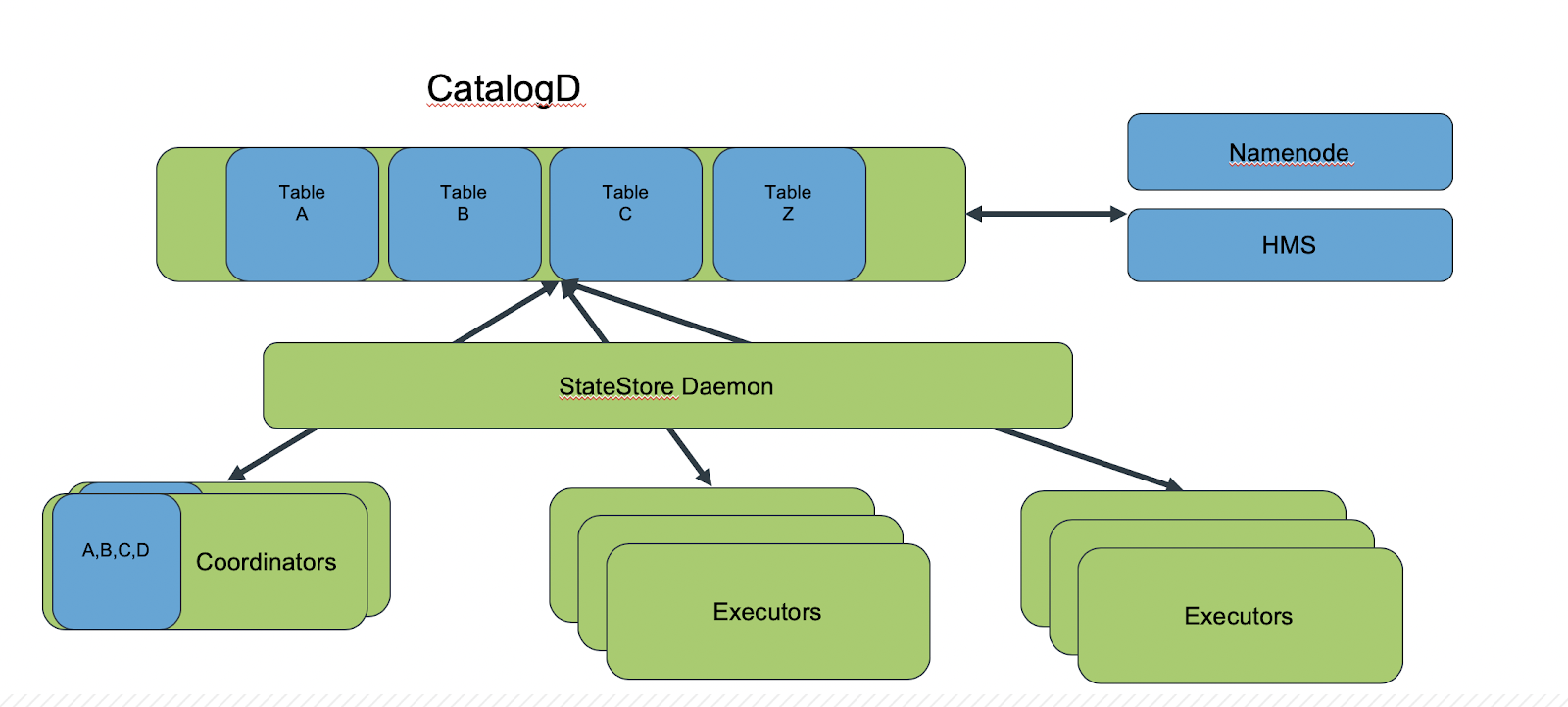
How the dedicated coordinator setup works
- Run coordinator roles on edge nodes and gateway nodes. Run executors on the data nodes.
- Only coordinator nodes cache the metadata. They perform the task of query coordination and a few other tasks like final sorts for the queries. The executor roles read from HDFS, join tables, and some related tasks.
- With this configuration, the executor daemons cannot be connected through Impala shell or JDBC connections.
- Configure coordinator daemons with large enough JVM heap size to hold the metadata in memory. Configure For Impala daemons that are assigned a dedicated role as an executor only, configure those with the default JVM heap size. See Impala Properties for the suggested default JVM heap size to set for Impala daemons.
Benefits of setting up dedicated coordinators
- Reduces memory usage on executor nodes.
- Avoids coordinator CPU bottlenecks caused by query execution tasks.
- Reduces the likelihood that admission control limits are exceeded.
- Reduces network utilization on the Statestore daemon by limiting metadata broadcast to only the coordinator nodes.
- Improves reliability and performance by reducing workload stress on coordinators.
