Custom Runtime Addons with CML
Custom ML Runtimes enable you to create runtimes with your own choice of libraries and applications, but it is also possible to further customize existing ML runtimes with additional configuration files or binaries such as connection drivers, without the effort of creating a new custom ML runtime.
How this feature works
Package your dependencies into a tarball file, following the specified format. A site administrator can then register the custom runtime addon by uploading the tarball via an API call on the command line.
After a custom runtime addon has been registered, the site administrator can enable or disable addons in the UI.
When an addon is enabled, it is mounted to all newly started runtime-based workloads, in read-only mode.
Creating the Custom Runtime Addon
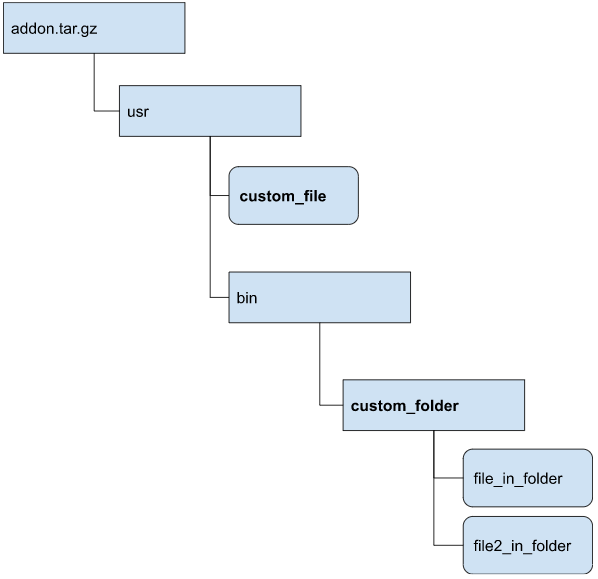
- You must create a structure of files and folders that follows the pattern shown here, and
package it as a tar.gz archive. For example, to mount a folder called
custom_folder, with all of its content under
/usr/bin/custom_folder, and custom_file at
/usr/custom_file, the internal structure of the tarball should look like
this:
- Next, you create a json file that describes the custom runtime addon to register in CML. The
json file should follow this structure:
{ "name" : "name-of-the-addon", "spec" : {"paths" : ["/usr/custom_file", "/usr/bin/custom_folder"]} } - Finally, the json file and tar.gz file are uploaded by a Site administrator. Use the
following curl command, with these substitutions:
metadata.json: the name of the json fileaddon.tar.gz: the name of the tar.gz file
curl '<cml_cluster>/api/v2/runtimeaddons/custom' -F metadata=@metadata.json -F tarball=@addon.tar.gz -H 'Authorization: Bearer <APIv2 key>'
After the runtime add-on has been uploaded, it will be enabled and mounted to all newly started Runtime-based workloads.
Requirements
- Name of the addon must contain only lowercase letters, numbers, underscores and hyphens. Also, it must be no longer than 35 characters. When added to CML, the addon will be prefixed with the term "custom-addon-".
- There should be at least one path mentioned in the uploaded json file.
- Paths in the metadata file should not end with a forward slash (
/) character. - Requested paths will be symlinked in the workloads’s filesystem by the "cdsw" user, therefore these locations must not exist in the workload’s file system and "cdsw" user must have write access to these locations.
Limitations
- Injecting Python or R libraries into workloads via Custom Runtime Addons is not supported. To accomplish this, create a Custom Runtime instead. For more information, see (link).
- Misconfigured Custom Runtime Addons can break user workloads (e.g. if metadata refers to paths that do not exist in the uploaded tarball archive).
- It is not possible to add Custom Runtime Addons through the UI.
- Custom Runtime Addons can not be updated or removed, only disabled.
- Custom Runtime Addons are mounted to workloads in read only mode.
Troubleshooting
When a Custom Runtime Addon tries to mount in a file or folder that falls into one of the below categories, workloads might fail to come up. In that case, CML UI will show the error messages “Failed setting up runtime addons”, also “Engine exited with status 33”. The exact error message can help determine what scenario causes the issue.
Possible root causes CML not being able to mount in files or folders from Custom Runtime Addons:
- The file or folder does not exist in the uploaded tarball or is not located under the proper path within the tarball archive.
- Solution: Adjust paths in the tarball/metadata file according to the Requirements.
- The file or folder a Custom Runtime Addon tries to mount exists already in the filesystem. Either the file/folder exists on the Runtime image or is mounted in by another Runtime Addon.
- Solution: Due to a limitation, Custom Runtime Addons can not overwrite existing files. Customers should change the path of the mounted files.
- cdsw user has no write access in the pod’s file system to create symlinks to mounted files.
- Solution: Change the path of the mounted files to a location that is writable by the cdsw user. Alternatively, create a Custom Runtime image with adjusted permissions and use that in all workload


