Managing Metadata Storage with Purge
The volume of metadata maintained by Navigator Metadata Server can grow quickly and reduce the efficiency of the Solr instance that processes the index, which can affect search results speed and time to display data lineage. In addition, stale metadata may show relationships that no longer exist, or the lineage may take longer to display than necessary as the system processes extraneous details.
Cloudera Navigator's purge function removes metadata for files that have been deleted or for operations that are older than the specified timeframe. The result is faster search and more precise (up-to-date) lineage diagrams.
In addition, clearing metadata before upgrading Cloudera Navigator to a new release can speed-up the upgrade process and reduce the chance of out-of-memory errors.
- After deleting managed metadata properties, as detailed in Purging a Property.
- By using the Cloudera Navigator APIs, as detailed in Using the Purge APIs for Metadata Maintenance Tasks.
- By using the Cloudera Navigator console and scheduling a regular weekly Purge, as detailed below.
Best Practices for Clearing Metadata using Purge
When a purge job runs, any running Navigator tasks—extractions, policy application, or other background tasks—are stopped so that the purge can run immediately. When the purge task completes, the tasks that were stopped are restarted from the beginning. The interruption for the purge task may delay collecting new audits and metadata but does not affect what content is collected.
A purge task won't stop another purge task: if a purge task if already running when a new purge task is triggered, the new purge task will be ignored. For example, if the scheduled metadata purge is running, an administrator won't be able to kick off a purge task for deleting managed metadata properties; if a scheduled metadata purge is still running when the next scheduled purge starts, the new task is ignored.
Based on the purge behavior, consider the following recommendations to make sure that Navigator purge tasks don't conflict with extraction tasks:
- Purge Timing. Because purge tasks stop extraction and other Navigator jobs, it's important to schedule the purge task when it will cause the least disruption: users and processes will be unable to use Cloudera Navigator until the purge process completes.
- First Time Purge Runs. For new installations of Navigator or installations starting with a fresh storage directory, schedule purge jobs after you've seen
the HDFS and Hive HMS extractions shift from bulk extraction to incremental extraction. The first extractions of metadata from HDFS run against every HDFS directory in the cluster and can run for
many hours. Subsequent extractions run incrementally, only extracting metadata for new and changed entities. If the initial extractions are never allowed to complete, the shorter, faster incremental
extractions don't begin. The same is true for HMS extractions.
To avoid a purge task from stopping the initial bulk extraction, avoid scheduling purge tasks until after extraction has shifted to the incremental mode.
Scheduling the Purge Process
Use the Cloudera Navigator console to configure a schedule for a regular weekly purge of deleted and stale metadata from the Navigator Metadata Server and its associated database.
Required Role: Metadata Administrator (or Full Administrator)
- Log in to the Cloudera Navigator console using an account with Full Administrator privileges.
- Go to Administration > Purge Settings tab.
The current Metadata and Lineage purge schedule displays, along with lists of up to five upcoming scheduled purges and a list of up to five most recent completed purges.
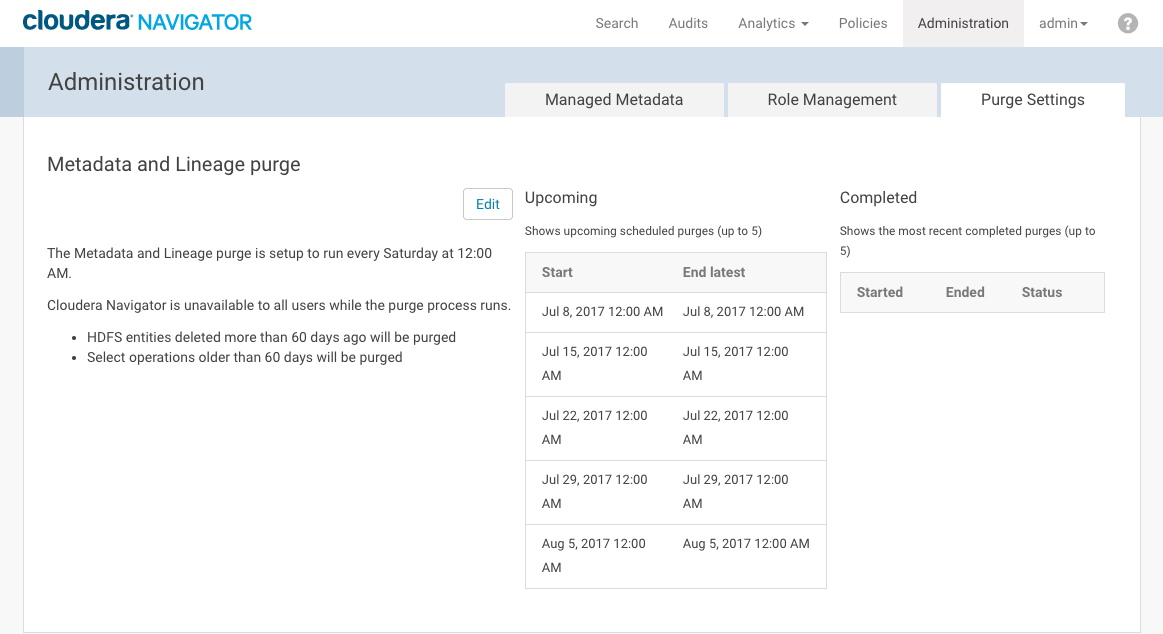
- Click Edit.
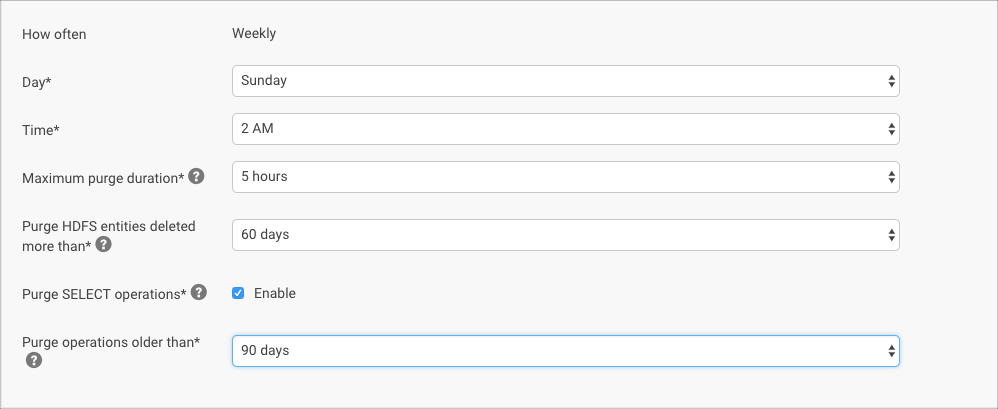
- Set the purge process options.
Option Default Range of selectable values and usage note How often Weekly Not configurable. The purge runs weekly per your specifications for Day and Time. It is enabled by default. Day Saturday Select a day for the purge that will have minimal impact to your user community. Time 12 Midnight Hourly time, from 12 Midnight through 11 PM. Select a time that will have minimal impact on production. Maximum purge duration 12 hours Set the amount of time you want to allow for the purge process to run. If not already complete, the HDFS purge process will not add any new items to purge after your specified duration. Entities purged to that point remain purged. All non-HDFS purge processes will run without limit. If set to 0, the purge is disabled. No other Cloudera Navigator operations, including through the console, can occur during the purge process.
Purge HDFS entities deleted more than* 60 days The number of days after an entity is deleted that elapse until the purge process removes its metadata. For example, a setting of 1 day purges entities deleted before two days ago but retains entities deleted yesterday. Purge SELECT operations* Enabled Hive and Impala SELECT operations older than days specified in Only Purge SELECT operations older than will be purged. Purge operations older than* 60 days Yarn, Sqoop, and Pig operations older than the specified date will be purged. If Purge SELECT Operations is enabled, Hive and Impala SELECT operations older than the specified date will also be purged. - Click Save when finished.
Here is an example of a revised schedule:
What Metadata is Purged?
Purge processes look for metadata that is associated with deleted files and tables and with operation executions that are older than the configured threshold date.
- Hive Metadata
-
- Hive operations
- That don't produce output
- That have all operation executions that were executed earlier than the threshold date
- Hive operation executions
- Associated with Hive operations that don't produce output
- That were executed earlier than the threshold date
- Hive sub-operations
- Associated with Hive operations that were purged
- All relations associated with the purged entities
- Hive operations
- Impala Metadata
-
- Impala operations
- That don't produce output
- That have all operation executions that were executed earlier than the threshold date
- Impala operation executions
- Associated with Impala operations that don't produce output
- That were executed earlier than the threshold date
- Impala sub-operations
- Associated with Impala operations that were purged
- All relations associated with the purged entities
- Impala operations
- Sqoop Metadata
-
- Sqoop import and export operations
- That have all operation executions that were executed earlier than the threshold date and no existing downstream entities
- Sqoop operation executions
- that were executed earlier than the threshold date
- All relations associated with the purged entities
- Sqoop import and export operations
- YARN Metadata
-
- YARN operations
- That have all operation executions that were executed earlier than the threshold date
- YARN operation executions
- That were executed earlier than the threshold date
- All relations associated with the purged entities
- YARN operations
- Pig Metadata
-
- Pig operations
- That have all operation executions that were executed earlier than the threshold date and don't apply to tables connected to existing HDFS files
- Pig operation executions
- That were executed earlier than the threshold date
- Pig tables
- That were created by an operation execution executed earlier than the threshold date and also not connected to an existing HDFS file
- Pig fields
- Fields in purged tables
- All relations associated with the purged entities
- Pig operations
- HDFS Metadata
-
- HDFS directories
- That have been deleted longer than the configured threshold
- AND don't have a logical-physical relation with another entity (such as a Hive table)
- AND don't have children (sub directories or files) that aren't ready to be purged
- AND aren't an endpoint in a data flow relation
- HDFS files
- Deleted file metadata are purged only when the containing directory is purged
- All relations that have both endpoints associated with purged entities
- HDFS directories
Categories: Administrators | Metadata | Navigator | Purge | All Categories