Installing in air gap environment
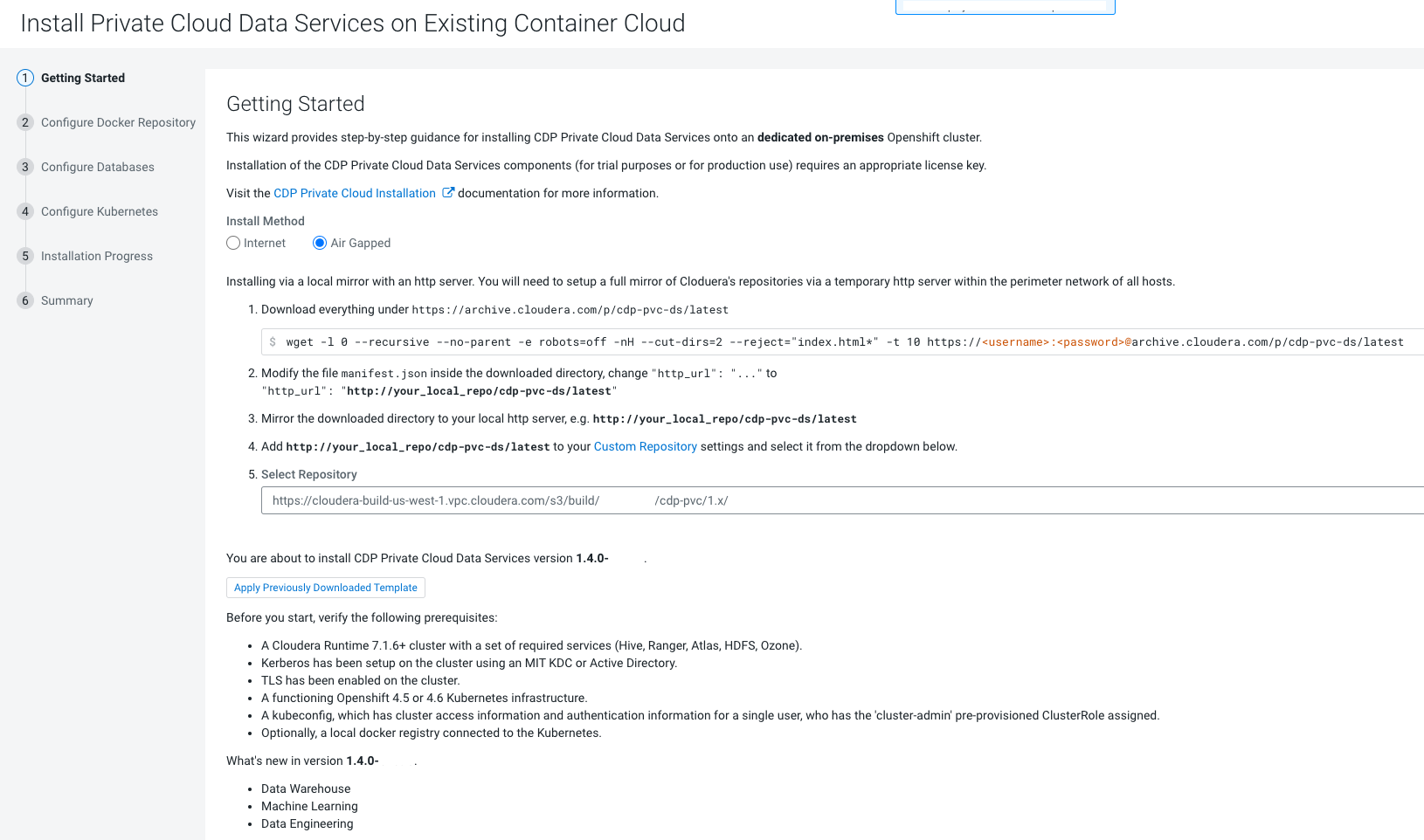
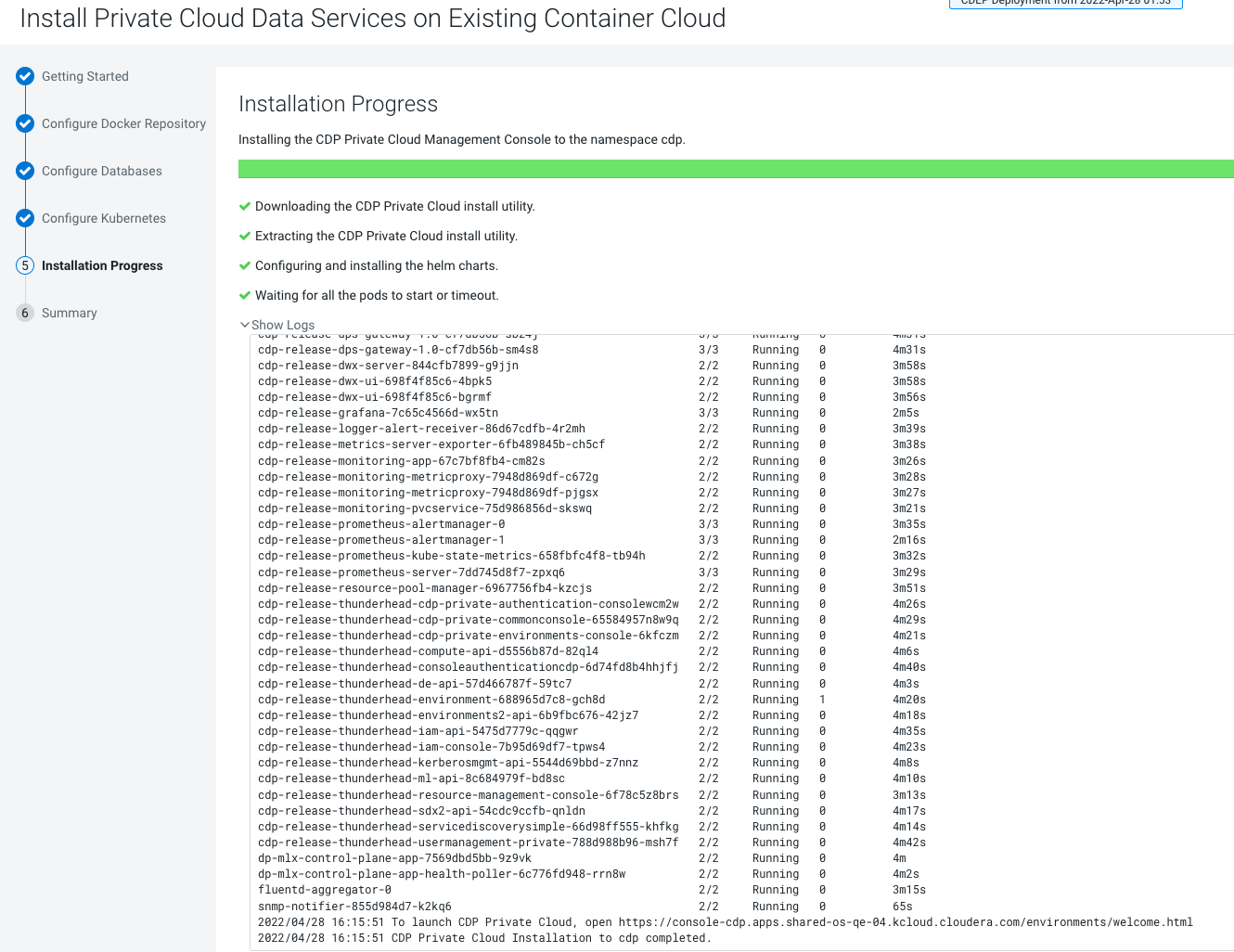
You can launch the Private Cloud installation wizard from Cloudera Manager and follow the steps to install CDP Private Cloud Data Services in an air gap environment where your Cloudera Manager instance or your Kubernetes cluster does not have access to the Internet.
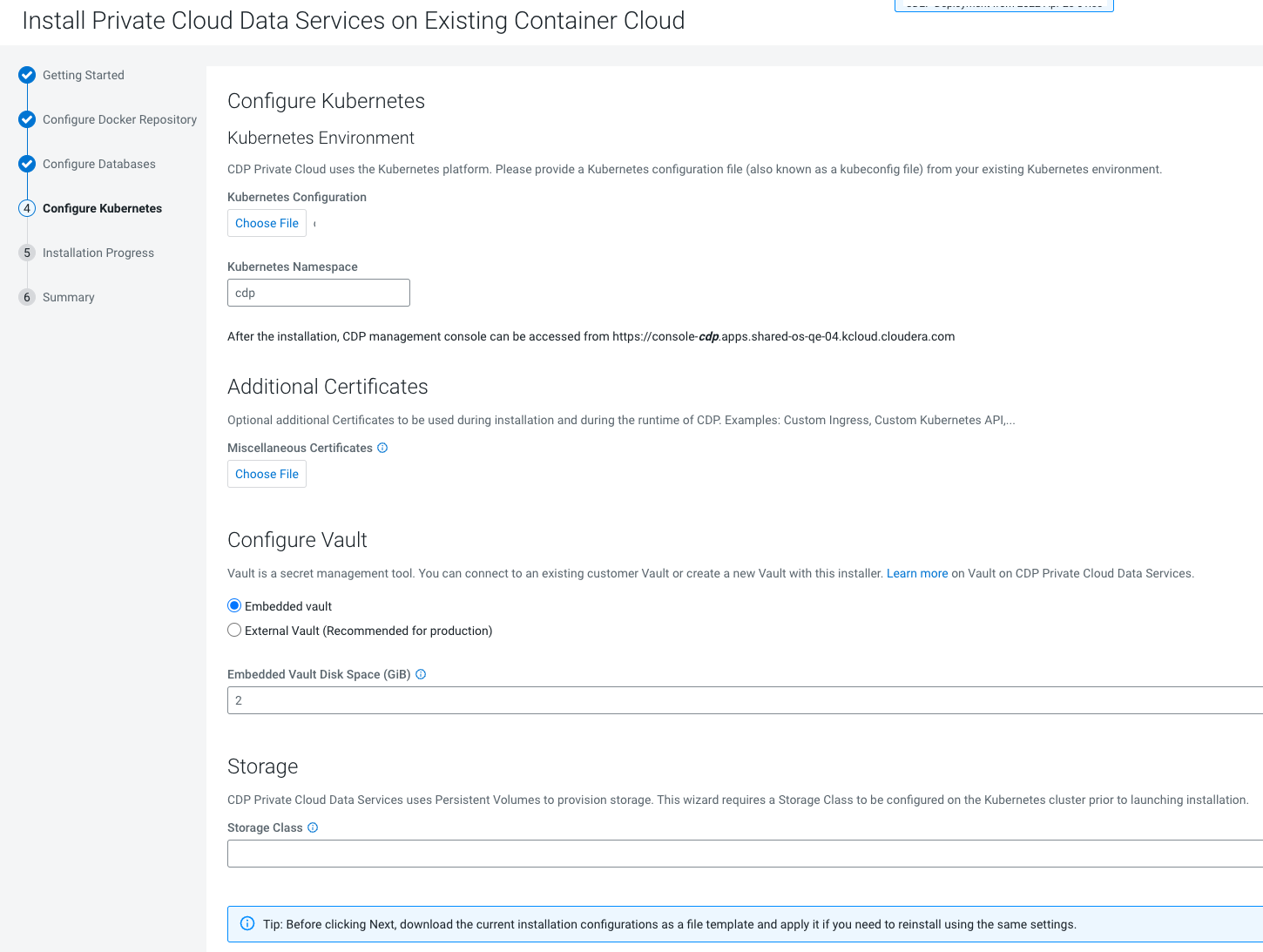
- Ensure that your Kubernetes
kubeconfighas permissions to create Kubernetes namespaces. - You require persistent storage classes defined in your OpenShift cluster. Storage classes can be defined by OpenShift cluster administrators.
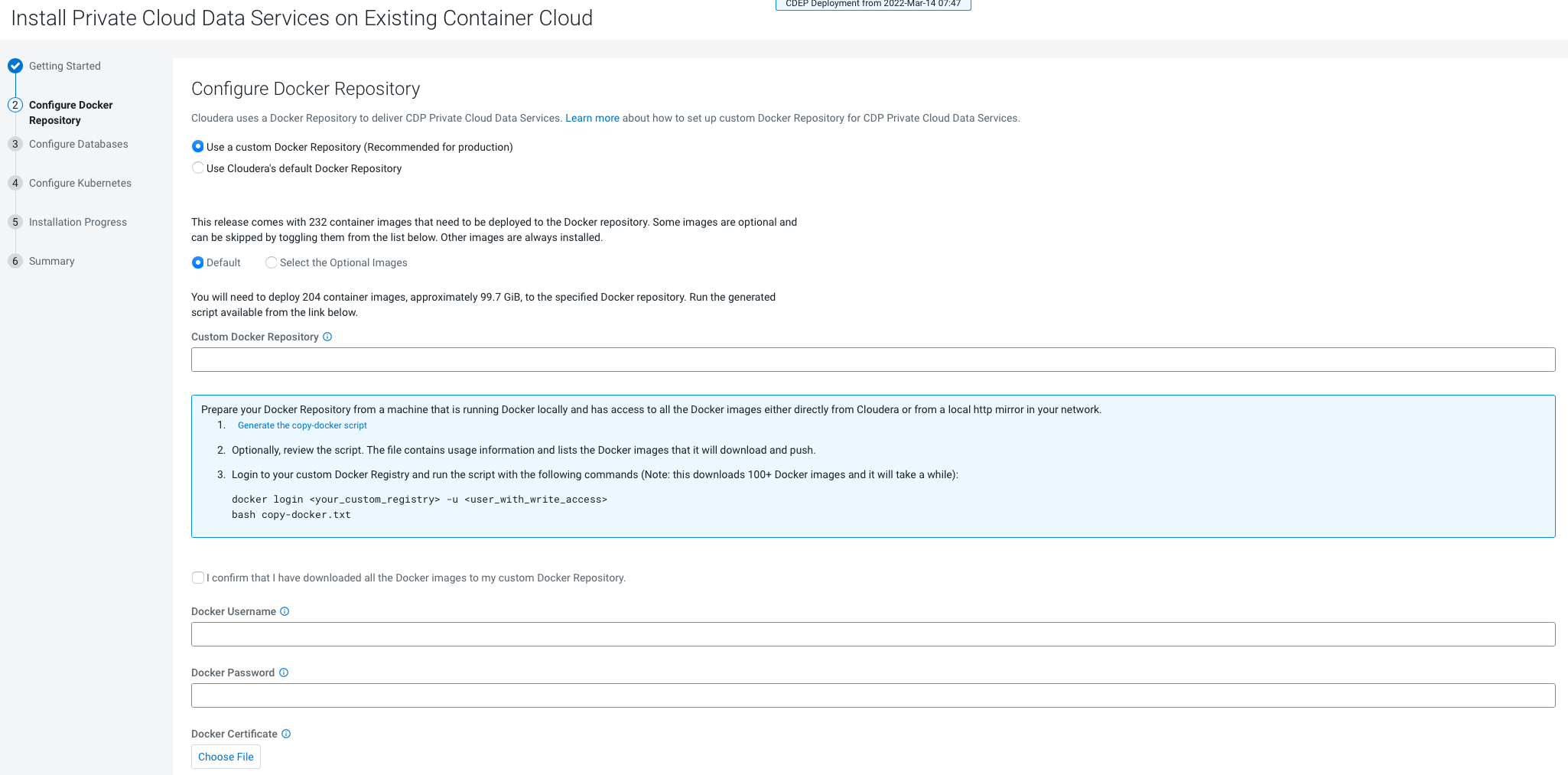
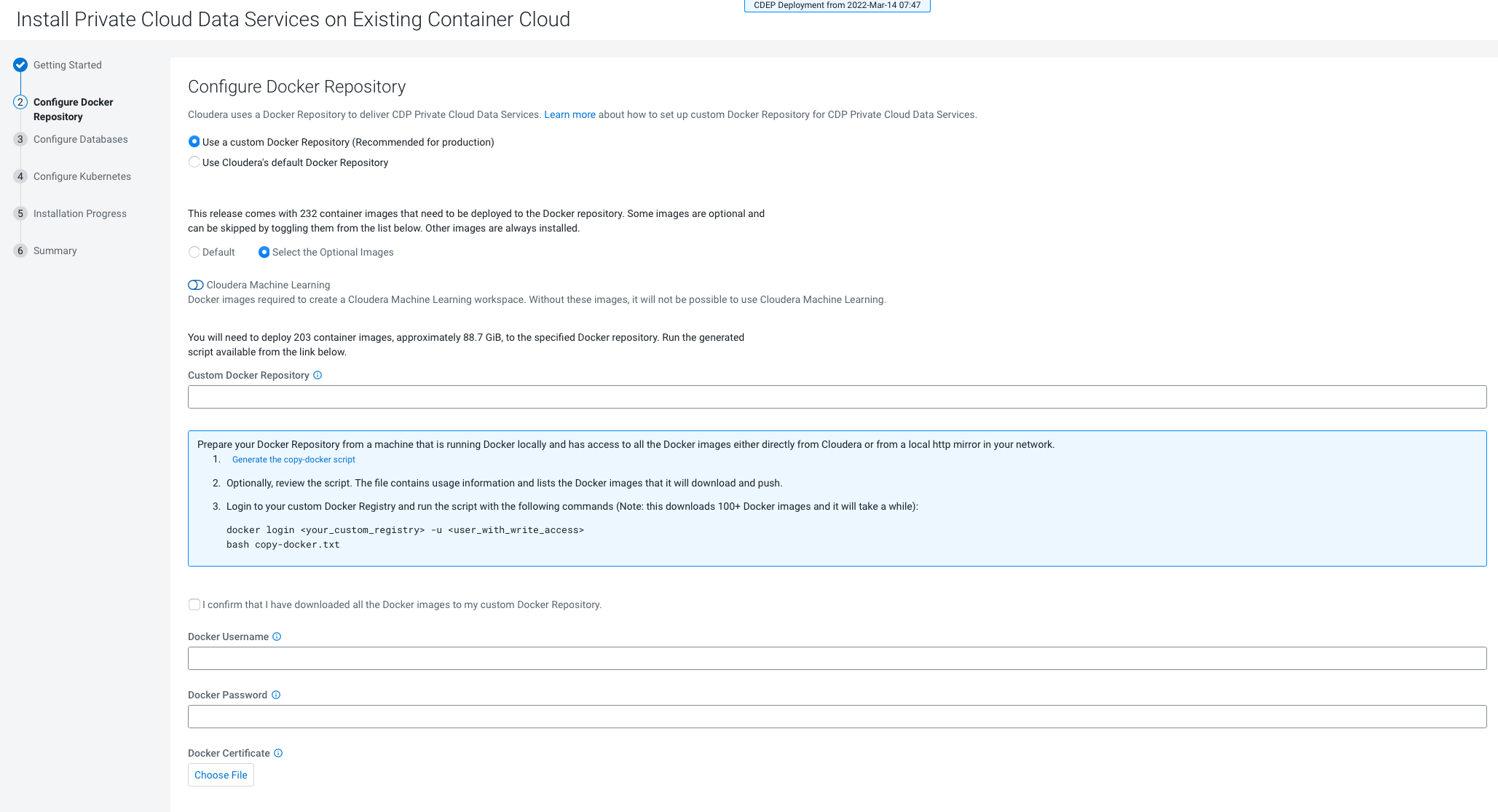
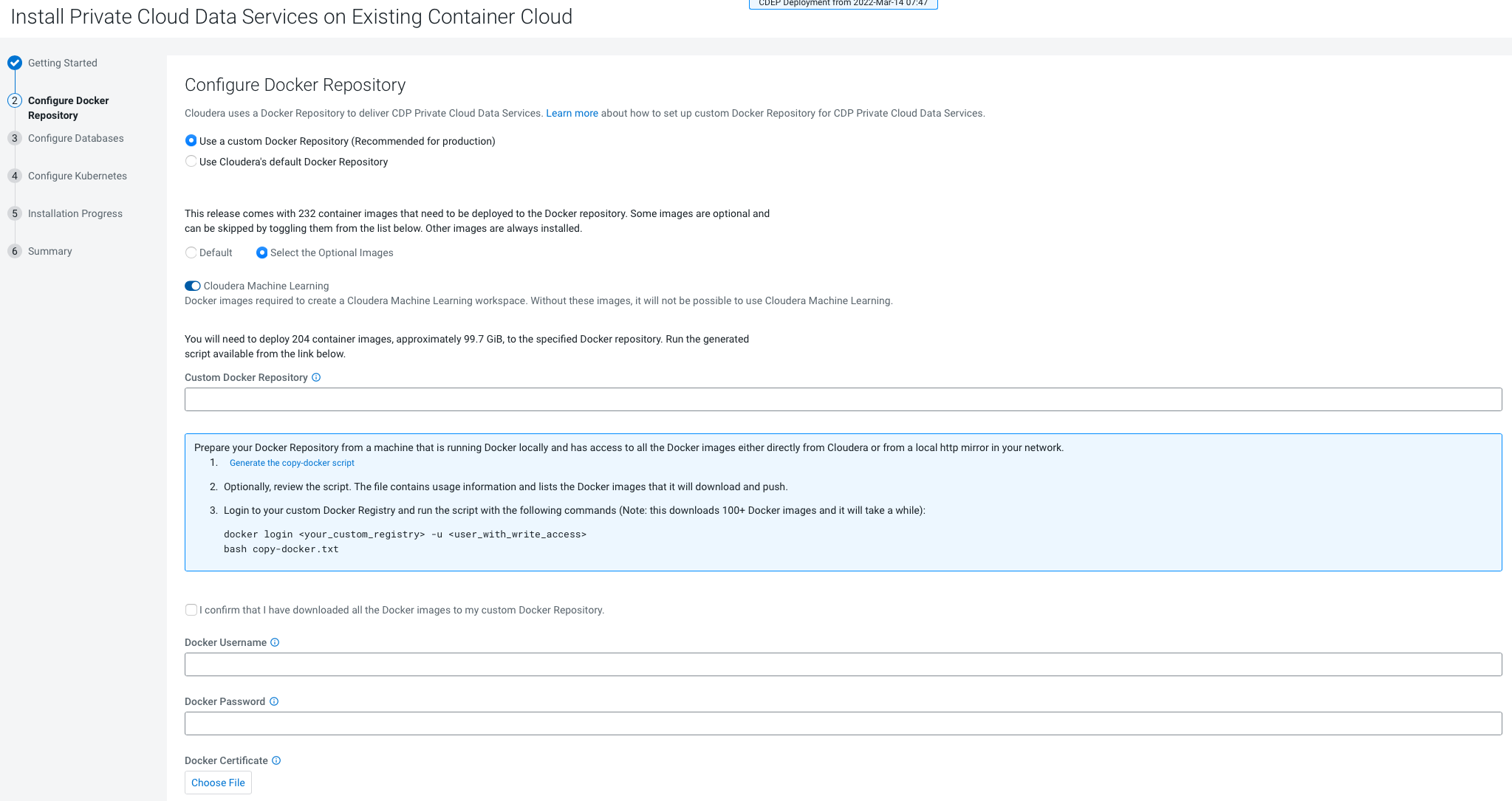
- Only TLS-enabled custom Docker Registry is supported. Ensure that you use a TLS certificate to secure the custom Docker Registry. The TLS certificate can be self-signed, or signed by a private or public trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
- Only TLS 1.2 is supported for authentication with Active Directory/LDAP. You require TLS 1.2 to authenticate the CDP control plane with your LDAP directory service like Active Directory.
- OCP network configurations that restrict pod communication are not supported. For example, multi-tenancy isolation with network policy is not supported.
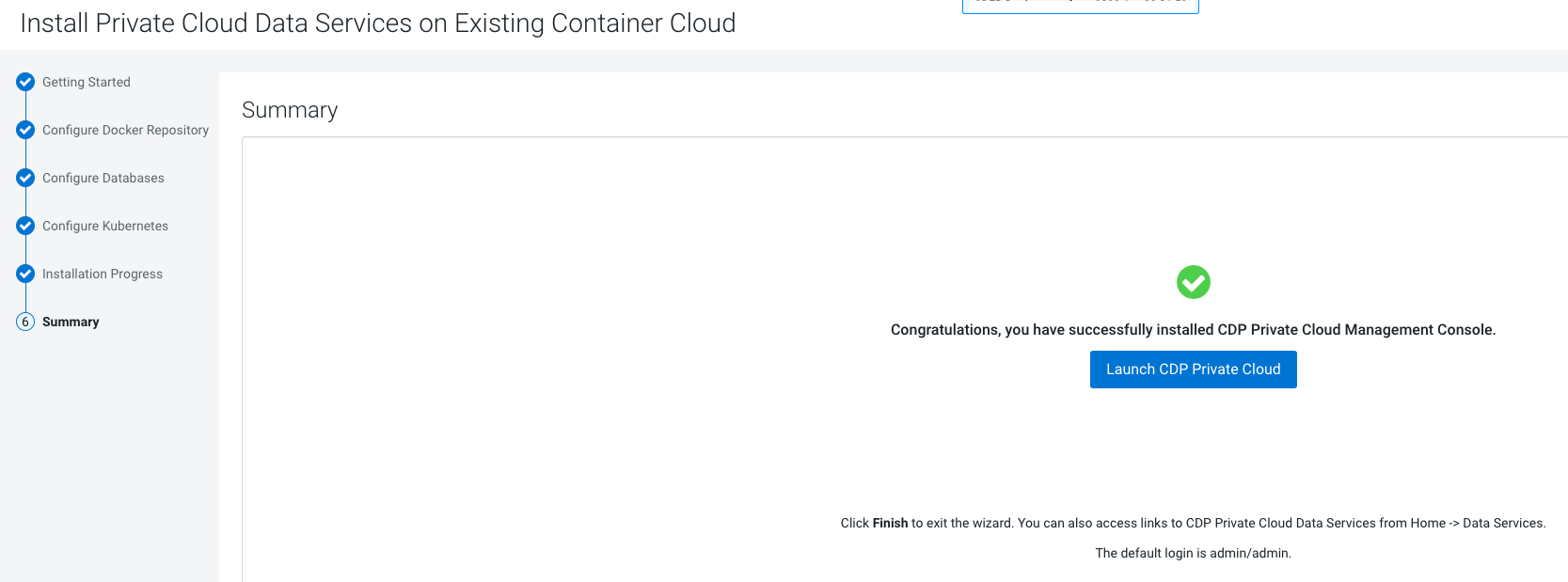
- Click Launch CDP to launch your CDP Private Cloud Data Services.
- Log in using the default user name and password
admin/admin. - In the Welcome to CDP Private Cloud page, click Change Password to change the Local Administrator Account password.
- Set up external authentication using the URL of the LDAP server and a CA certificate of your secure LDAP. Follow the instructions on the Welcome to CDP Private Cloud page to complete this step.
- Click Test Connection to ensure that you can connect to the configured LDAP server.
- Register a CDP Private Cloud Data Services environment.
- Create your first Virtual Warehouse in the CDW Data Services and/or Provision an ML Workspace in the CML Data Services.