Configure a Resource-based Policy: Hive
How to add a new policy to an existing Hive service.
-
On the Service Manager page, select an existing service under Hive.
 The List of Policies page appears.
The List of Policies page appears.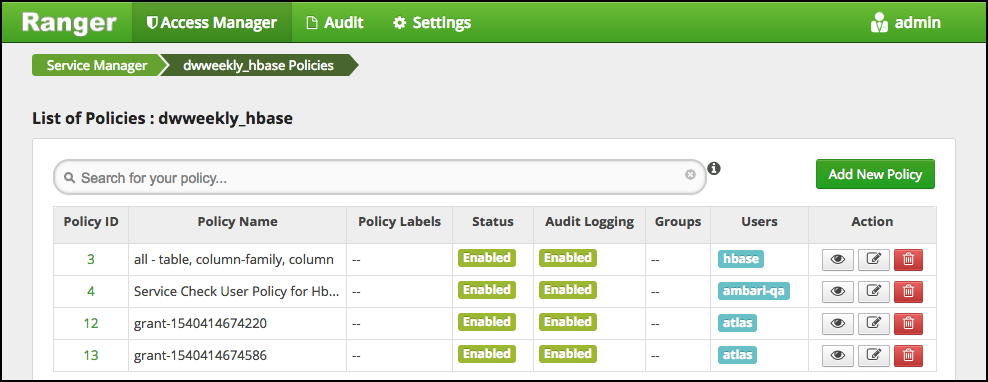
-
Click Add New Policy.
The Create Policy page appears.
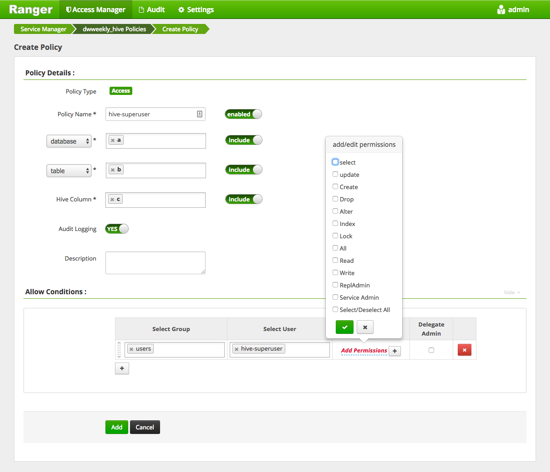
-
Complete the Create Policy page as follows:
Table 1. Policy Details Field Description Policy Name Enter an appropriate policy name. This name cannot be duplicated across the system. This field is mandatory. The policy is enabled by default. Database Type in the applicable database name. The autocomplete feature displays available databases based on the entered text.
Include is selected by default to allow access. Select Exclude to deny access..
Table To continue adding a table-based policy, keep Table selected.
Type in the applicable table name. The autocomplete feature displays available tables based on the entered text.
Include is selected by default to allow access. Select Exclude to deny access.
UDF To continue adding a UDF-based policy, select UDF.
Type in the applicable UDF name. The autocomplete feature displays available tables based on the entered text.
Include is selected by default to allow access. Select Exclude to deny access.
Column Type in the applicable Hive column name. The autocomplete feature displays available columns based on the entered text.
Include is selected by default to allow access. Select Exclude to deny access.
If using the Ranger Hive plugin with HiveServer2 or HiveServer2-LLAP, where column or description permissions include
all, you must set a parameter for Hive columns to display as expected: in Ambari>Hive, under ranger-hive-security.xml, enter: xasecure.hive.describetable.showcolumns.authorization.option=show-all. Failure to set this parameter will result in the error message HiveAccessControlException.URL Specify the cloud storage path (for example
s3a://dev-admin/demo/campaigns.txt) where the end-user permission is needed to read/write the Hive data from/to a cloud storage path.Permissions: READ operation on the URL permits the user to perform HiveServer2 operations which use S3 as data source for Hive tables. WRITE operation on the URL permits the user to perform HiveServer2 operations which write data to the specified S3 location.
This feature is a Technical Preview: it is not ready for production deployment.
URI Hive INSERT OVERWRITE queries require a Ranger URI policy to allow write operations, even if the user has write privilege granted through HDFS policy.
Failure to specify this field will result in the following error:
Error while compiling statement: FAILED: HiveAccessControlException Permission denied: user [jdoe] does not have [WRITE] privilege on [/tmp/*] (state=42000,code=40000)Example value: /tmp/*
Description (Optional) Describe the purpose of the policy.
If using the Ranger Hive plugin with HiveServer2 or HiveServer2-LLAP, where column or description permissions include
all, you must set a parameter for Hive columns to display as expected: in Ambari>Hive, under ranger-hive-security.xml, enter: xasecure.hive.describetable.showcolumns.authorization.option=show-all. Failure to set this parameter will result in the error message HiveAccessControlException.Hive Service Name hiveservice is used only in conjunction with Permissions=Service Admin. Enables a user who has Service Admin permission in Ranger to run the kill query API: kill query <queryID>. Supported value:*. (Required)Audit Logging Specify whether this policy is audited. (De-select to disable auditing). Policy Label Specify a label for this policy. You can search reports and filter policies based on these labels. Table 2. Allow Conditions Label
Description
Select Group Specify a group to which this policy applies. To designate the group as an Administrator for the chosen resource, select the Delegate Admin check box. (Administrators can create child policies based on existing policies).
The public group contains all users, so granting access to the public group grants access to all users.
Select User Specify one or more users to which this policy applies. To designate the group as an Administrator for the chosen resource, select the Delegate Admin check box. (Administrators can create child policies based on existing policies). Permissions Add or edit permissions: Select, Update, Create, Drop, Alter, Index, Lock, All, ReplAdmin, Service Admin, Select/Deselect All.
If using the Ranger Hive plugin with HiveServer2 or HiveServer2-LLAP, where column or description permissions include
all, you must set a parameter for Hive columns to display as expected: in Ambari>Hive, under ranger-hive-security.xml, enter: xasecure.hive.describetable.showcolumns.authorization.option=show-all. Failure to set this parameter will result in the error message HiveAccessControlException.In order to execute repl dump, repl load, or repl status commands, you must set a parameter: in Ambari>Hive, under hive-site.xml, enter: hive.distcp.privileged.doAs=hive.
Service Admin is used in conjunction with Hive Service Name and the kill query API:
kill query <queryID>.Delegate Admin When Delegate Admin is selected, administrative privileges are assigned to the applicable users and groups. Delegated administrators can update and delete policies, and can also create child policies based on the original policy. - You can use the Plus (+) symbol to add additional conditions. Conditions are evaluated in the order listed in the policy. The condition at the top of the list is applied first, then the second, then the third, and so on.
- Click Add.
Provide User Access to Hive Database Tables from the Command Line
Hive provides the means to manage user access to Hive database tables directly from the command line. The most commonly-used commands are:
-
GRANT
Syntax:
grant <permissions> on table <table> to user <user or group>;For example, to create a policy that grants user1 SELECT permission on the table default-hivesmoke22074, the command would be:
grant select on table default.hivesmoke22074 to user user1;The syntax is the same for granting UPDATE, CREATE, DROP, ALTER, INDEX, LOCK, ALL, and ADMIN rights.
-
REVOKE
Syntax:
revoke <permissions> on table <table> from user <user or group>;For example, to revoke the SELECT rights of user1 to the table default.hivesmoke22074, the command would be:
revoke select on table default.hivesmoke22074 from user user1;The syntax is the same for revoking UPDATE, CREATE, DROP, ALTER, INDEX, LOCK, ALL, and ADMIN rights.

