Prerequisites for Cloudera Embedded Container Service day two operations
Perform the following steps to get started with Cloudera Embedded Container Service and
the kubectl command line tool.
Getting started
- In Cloudera Manager, confirm that the ECS Cluster is healthy:
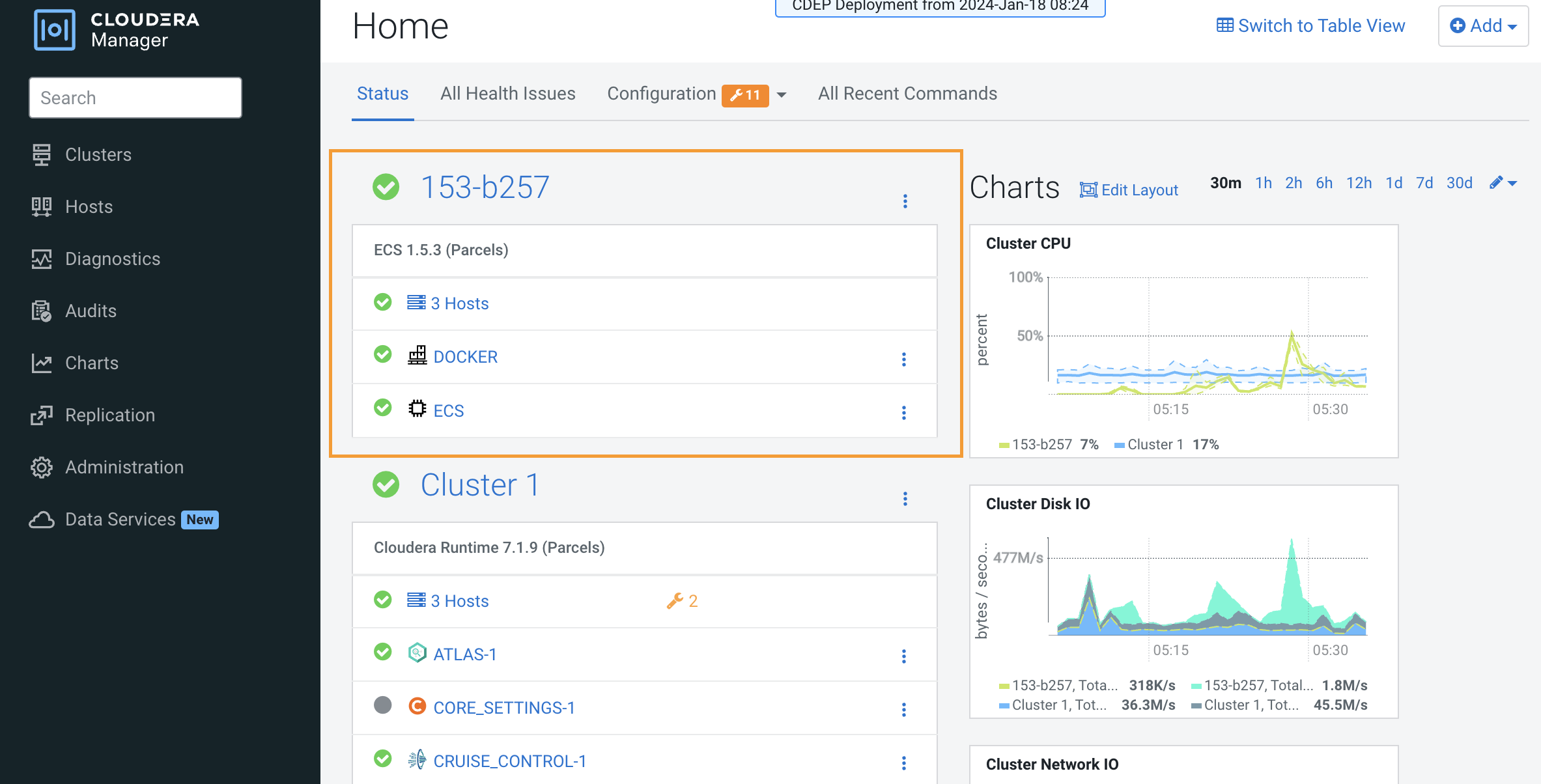
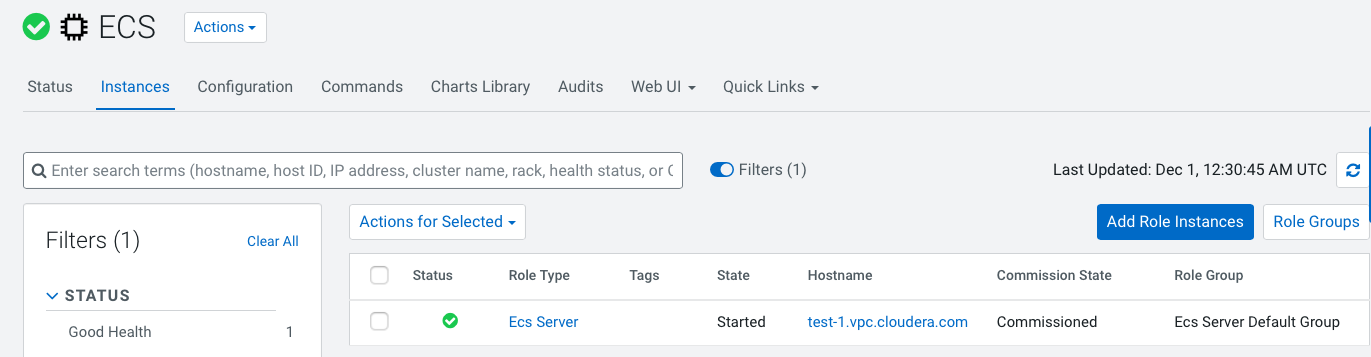
- Identify the ECS server host. Click ECS in the ECS cluster, then
click Instances. The ECS server host is listed in the Hostname column
for the ECS Server role type.
- Open a connection to the ECS server host:
ssh test-1.vpc.cloudera.comEnsure that you are using the root user:
root@test-1 ~]# whoami root
Set up Kubernetes and kubectl
You can use the kubectl command line tool to interact with
Kubernetes.
- Cluster management –
kubectlallows you to manage various aspects of Kubernetes clusters, including deploying applications, inspecting and managing cluster resources, and viewing logs. - Interacting with nodes and pods –
kubectlprovides commands to interact with and manage nodes, pods, and other resources within a Kubernetes cluster. - Deployment and application management – You can use
kubectlto create, update, and delete applications running on Kubernetes, as well as control scaling and rollout of updates. - Debugging and diagnostics –
kubectlincludes various commands for checking the health of resources, diagnosing issues, and accessing logs.
To set up Kubernetes configuration and the kubectl alias, add the
following lines to your bash profile. This eliminates the need to set this up for each
session.
KUBECONFIG=/etc/rancher/rke2/rke2.yaml
alias kubectl=/var/lib/rancher/rke2/bin/kubectl