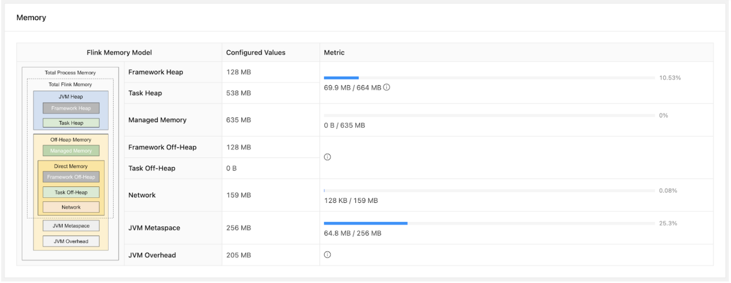
Configuring Flink application resources
Generally, Flink automatically identifies the required resources for an application based on the parallelism settings. However, you can adjust the configurations based on your requirements by specifying the number of task managers and their memory allocation for individual Flink applications or for the entire Flink deployment.
- Number of Task Slots
- The number of task slots controls how many parallel pipeline/operator instances can be
executed in a single TaskManager. Together with the parallelism setting, you can ultimately
define how many TaskManagers will be allocated for the job. For example, if you set the job
parallelism to 12 and the
taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlotsto 4, there will be 3 TaskManager containers for the job as the value of parallelism will be divided with the number of task slots. - TaskManager Process Memory Size
- The
taskmanager.memory.process.sizeoption controls the total memory size of the TaskManager containers. For applications that store data on heap or use large state sizes, it is recommended towe should increase the process size accordingly. You can set the number of task slots in Cloudera Manager under the Configuration tab.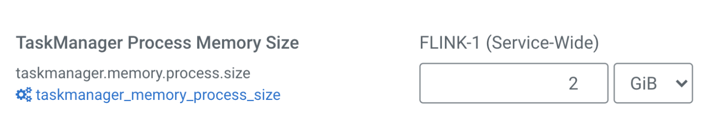
Network buffers for throughput and latency
Flink uses network buffers to transfer data from one operator to another. These buffers are filled up with data during the specified time for the timeout. In case of high data rates, the set time is usually never reached. For cases when the data rate is high, the throughput can be further increased with setting the buffer timeout to an intentionally higher value due to the characteristics of the TCP channel. However, this in turn increases the latency of the pipeline.
Yarn Related Configurations
Flink on YARN jobs are configured to tolerate a maximum number of failed containers before they terminate. You can configure the YARN maximum failed containers setting in proportion to the total parallelism and the expected lifetime of the job.
High Availability is enabled by default in CSA. This eliminates the JobManager as a single point of failure. You can also tune the application resilience by setting the YARN maximum application attempts, which determines how many times the application will retry in case of failures.
Furthermore, you can use a YARN queue with preemption disabled to avoid long running jobs being affected when the cluster reaches its capacity limit.
Reference values for the configurations
| Configuration | Parameter | Recommended value |
|---|---|---|
| TM container memory | -ytm / taskmanager.heap.size |
TM Heap + Heap-cutoff |
| Managed Memory Fraction | taskmanager.memory.managed.fraction |
0.4 - 0.9 |
| Max parallelism | pipeline.max-parallelism |
120,720,1260,5040 |
| Buffer timeout | execution.buffer-timeout |
1-100 |
| YARN queue | -yqu |
A queue with no preemption |
| YARN max failed containers | yarn.maximum-failed-containers |
3*num_containers |
| YARN max AM failures | yarn.application-attempts |
3-5 |