Creating Webhook tables
You can configure the webhook table to perform an HTTP action per message (default) or to create code that controls the frequency (for instance, every N messages). When developing webhook sinks, it is recommended to check your webhook before pointing at your true destination.
-
Navigate to the Streaming SQL Console.
- Go to your cluster in Cloudera Manager.
- Select SQL Stream Builder from the list of services.
- Click SQLStreamBuilder Console.
The Streaming SQL Console opens in a new window. -
Click Create Job or select a previous job on the
Getting Started page.
You are redirected to the Console page.
-
Select Add table > Webhook.
The Webhook Table window appears.
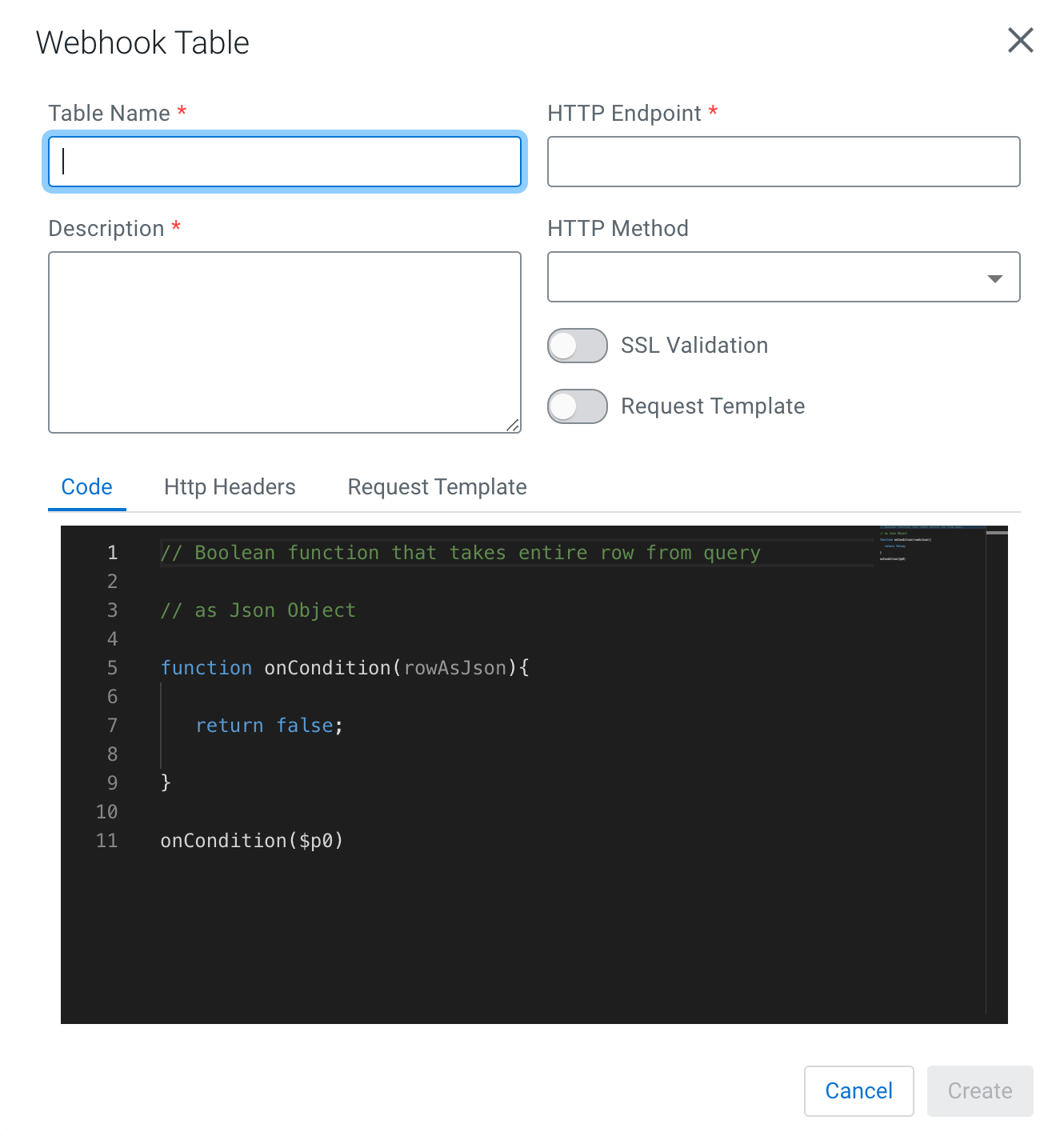
- Provide a name to the Table.
-
Enter an HTTP endpoint. The endpoint must start with
http://orhttps://. - Add a Description about the webhook sink.
- Select POST or PUT in the HTTP Method select box.
- Choose to Disable SSL Validation, if needed.
-
Enable Request Template, if needed.
-
If you selected Yes, then the template defined
in the Request Template tab is used for output.
This is useful if the service you are posting requires a particular data output format. The data format must be a valid JSON format, and use
"${columnname}"to represent fields. For example, a template for use with Pagerduty looks like this:{ "incident":{ "type":"incident", "title":"${icao} is too high!", "body":{ "type":"incident_body", "details":"Airplane with id ${icao} has reached an altitude of ${altitude} meters." } } }
-
If you selected Yes, then the template defined
in the Request Template tab is used for output.
-
In the Code editor, you can specify a code block that controls how the webhook
displays the data.
For a webhook that is called for each message the following code is used:
// Boolean function that takes entire row from query as Json Object function onCondition(rowAsJson) {return true; // return false here for no-op, or plug in custom logic} onCondition($p0) -
Add HTTP headers using the HTTP Headers tab, if
needed.
Headers are
name:valueheader elements. For instance,Content-Type:application/json, etc. - Click Create.

