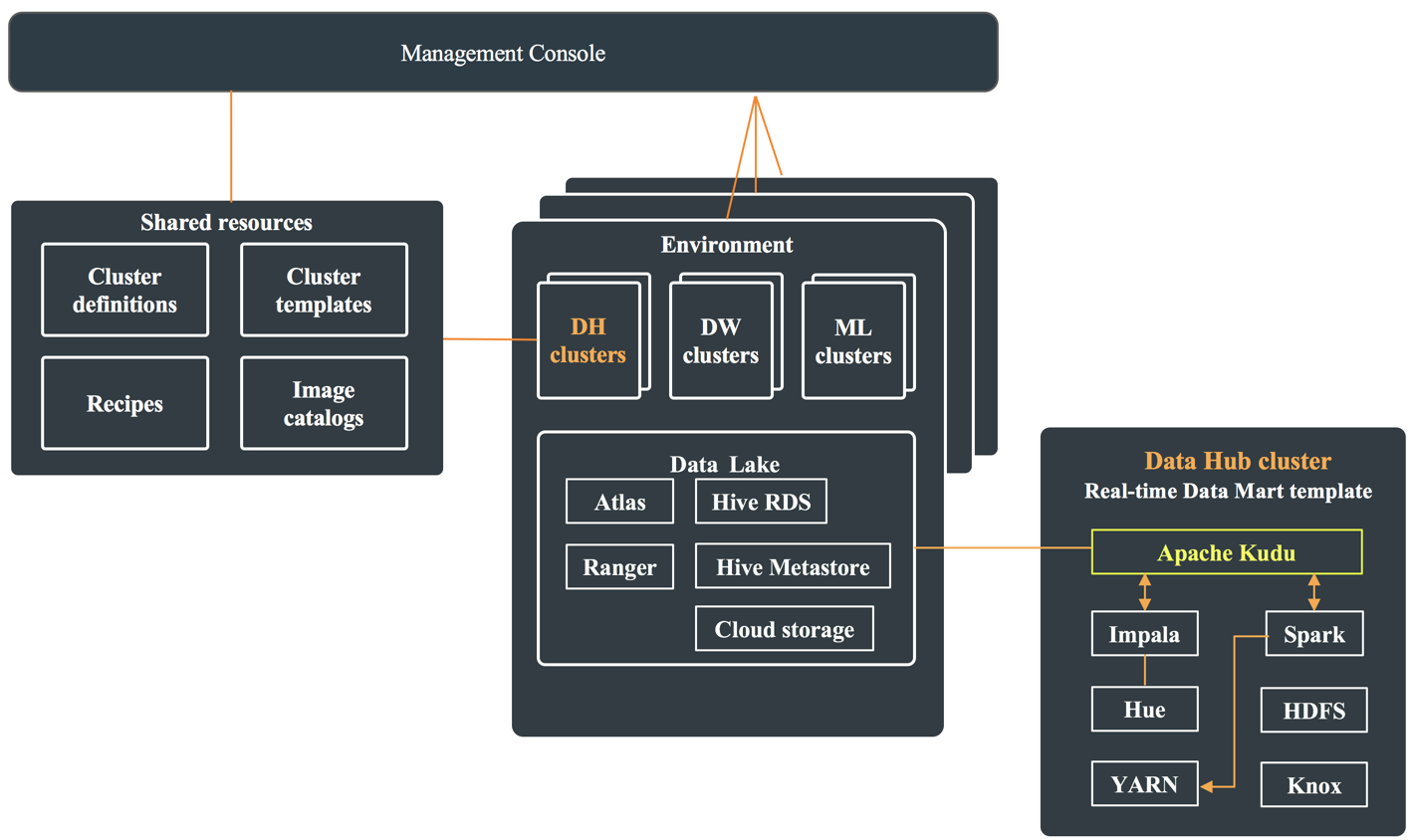
Kudu architecture in a CDP public cloud deployment
In a CDP public cloud deployment, Kudu is available as one of the many Cloudera Runtime services within the Real-time Data Mart template. To use Kudu, you can create a Data Hub cluster by selecting Real-time Data Mart template template in the Management Console.
Each Data Hub cluster that is deployed using the Real-time Data Mart template has an instance of Apache Kudu, Impala, Spark, and Knox. It also contains YARN—which is used to run Spark, Hue—which can be used to issue queries using Impala, and HDFS—because the cluster is managed using Cloudera Manager. These components use the shared resources present within the Data Lake.
Impala is primarily used to execute analytical queries against the data stored in Kudu. It also
manages hierarchical storage between Kudu and the object storage. You can use SQL statements to
move older data in the range partitions from Kudu into the Parquet partitions on object storage,
for example, on Amazon S3 as cold storage. You can then use an Impala UNION ALL
or VIEW statement to query the Kudu and Parquet data together.
Besides ingesting data, Spark is used for backup and disaster recovery (BDR) operations. The Kudu BDR feature is built as a Spark application, and it can take either full or incremental table backups. It then restores a stack of backups into a table.
The following diagram shows Apache Kudu and its dependencies as a part of the Data Hub cluster, and the shared resources they use which are present in the Data Lake: