Schema Registry metadata collection
Integrating Schema Registry with Atlas will enable you to persist and view the schemas in Atlas.
Atlas serves as a metadata catalogue that shows relationships between entities. Additionally, when Kafka is also integrated with Atlas you can connect Kafka topics and schemas.
As an example, an ETL job which reads encoded data from Hadoop, performs some operations on it and writes it into Kafka. In order to read the encoded data, the ETL job needs access to Schema Registry to obtain the schema. To write the data into Kafka, it needs to be encoded again, perhaps with a different schema. A relationship graph for this example is detailed in the following diagram.
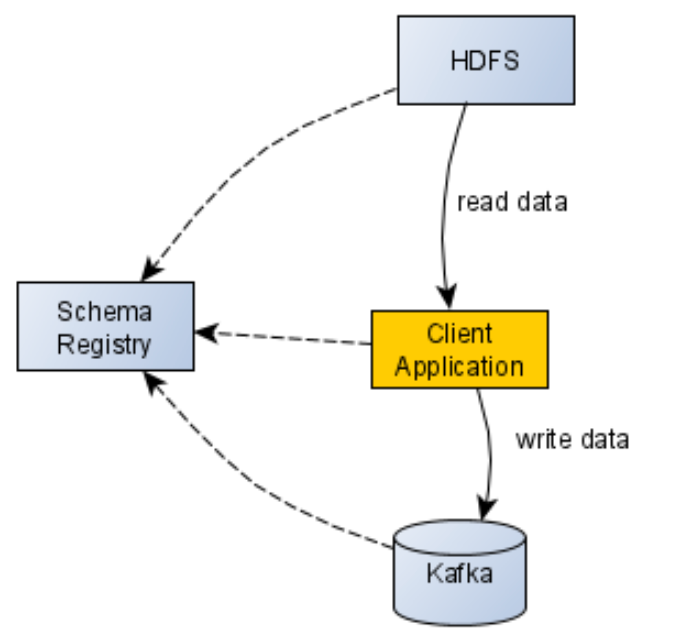
In a real-world environment, however, we can have many components communicating with each other and it might become hard to track the relations and data flows.
Atlas in its core is a metadata catalog which uses a graph database to store entities and its relationships, which lets users track the data flows as discussed earlier in this section. The graph would be built automatically for the end-user. The corresponding services (Hadoop, Schema Registry, Kafka, Hive (HiveServer2 and HMS), Impala, Spark, HBase, Sqoop, Storm, NiFi) send updates to Atlas and build the graph on the go.
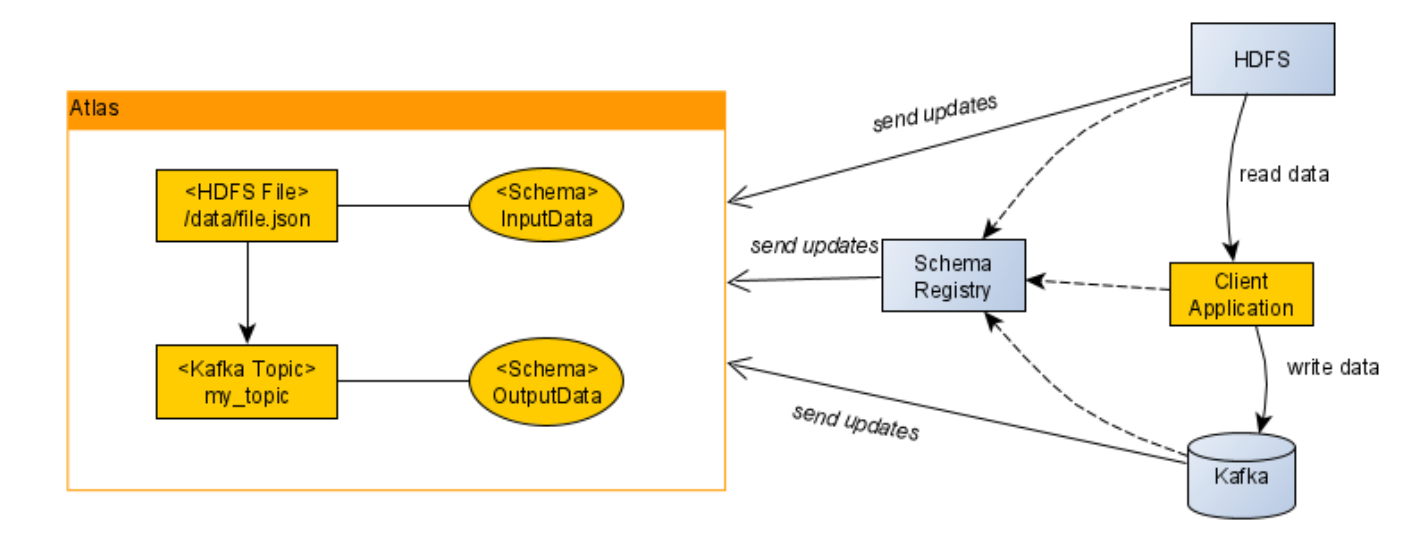
- When Kafka topic is created:

- When Schema data is created in Atlas: