You can create a materialized view of a query to calculate and store results of an
expensive operation, such as particular join, that you repeatedly execute. When you issue
queries specified by that materialized view, the optimizer rewrites the query based on it.
This action saves reprocessing. Query performance improves.
In this task, you create and populate example tables. You create a materialized view
of a join of the tables. Subsequently, when you run a query to join the tables, the
query plan takes advantage of the precomputed join to accelerate processing. This
task is over-simplified and is intended to show the syntax and output of a
materialized view, not to demonstrate accelerated processing that results in a
real-world task, which would process a large amount of data.
-
In Data Analytics Studio (DAS), the Hive shell, or other Hive UI, create two
tables:
CREATE TABLE emps (
empid INT,
deptno INT,
name VARCHAR(256),
salary FLOAT,
hire_date TIMESTAMP);
CREATE TABLE depts (
deptno INT,
deptname VARCHAR(256),
locationid INT);
-
Insert some data into the tables for example purposes:
INSERT INTO TABLE emps VALUES (10001,101,'jane doe',250000,'2018-01-10');
INSERT INTO TABLE emps VALUES (10002,100,'somporn klailee',210000,'2017-12-25');
INSERT INTO TABLE emps VALUES (10003,200,'jeiranan thongnopneua',175000,'2018-05-05');
INSERT INTO TABLE depts VALUES (100,'HR',10);
INSERT INTO TABLE depts VALUES (101,'Eng',11);
INSERT INTO TABLE depts VALUES (200,'Sup',20);
-
Create a materialized view to join the tables:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW mv1
AS SELECT empid, deptname, hire_date
FROM emps JOIN depts
ON (emps.deptno = depts.deptno)
WHERE hire_date >= '2017-01-01';
-
Execute a query that takes advantage of the precomputation performed by the
materialized view:
SELECT empid, deptname
FROM emps
JOIN depts
ON (emps.deptno = depts.deptno)
WHERE hire_date >= '2017-01-01'
AND hire_date <= '2019-01-01';
Output is:
+--------+-----------+
| empid | deptname |
+--------+-----------+
| 10003 | Sup |
| 10002 | HR |
| 10001 | Eng |
+--------+-----------+
-
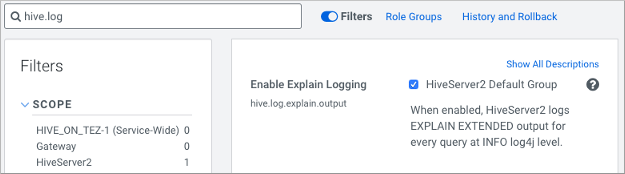
In Cloudera Manager, enable explain logging: Navigate to , search for
hive.log.explain.output, check
HiveServer2 Default Group, and click Save Changes.
-
Verify that the query rewrite used the materialized view by running an extended
EXPLAIN statement:
EXPLAIN EXTENDED SELECT empid, deptname
FROM emps
JOIN depts
ON (emps.deptno = depts.deptno)
WHERE hire_date >= '2017-01-01'
AND hire_date <= '2019-01-01';
The output shows the alias
default.mv1 for the
materialized view in the TableScan section of the plan.
OPTIMIZED SQL: SELECT `empid`, `deptname`
FROM `default`.`mv1`
WHERE TIMESTAMP '2019-01-01 00:00:00.000000000' >= `hire_date`
STAGE DEPENDENCIES:
Stage-0 is a root stage
STAGE PLANS:
Stage: Stage-0
Fetch Operator
limit: -1
Processor Tree:
TableScan
alias: default.mv1
filterExpr: (hire_date <= TIMESTAMP'2019-01-01
00:00:00') (type: boolean) |
GatherStats: false
Filter Operator
isSamplingPred: false
predicate: (hire_date <= TIMESTAMP'2019-01-01
00:00:00') (type: boolean)
Select Operator
expressions: empid (type: int), deptname (type: varchar(256))
outputColumnNames: _col0, _col1
ListSink