Examples of creating secure external tables
You learn by example how to set up policies to secure HBase-, Kafka- and JDBC-based tables using the Ranger policy properties.
Kafka-based table
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE kafka_table_test (`timestamp` timestamp , `page` string, `newPage` boolean, added int, deleted bigint, delta double)
STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.kafka.KafkaStorageHandler'
TBLPROPERTIES ("kafka.topic" = "test-topic","kafka.bootstrap.servers" = "hostclustername:2181");In this case, the URI for ranger Authentication is
kafka://hostclustername:2181/test-topic/column_names.
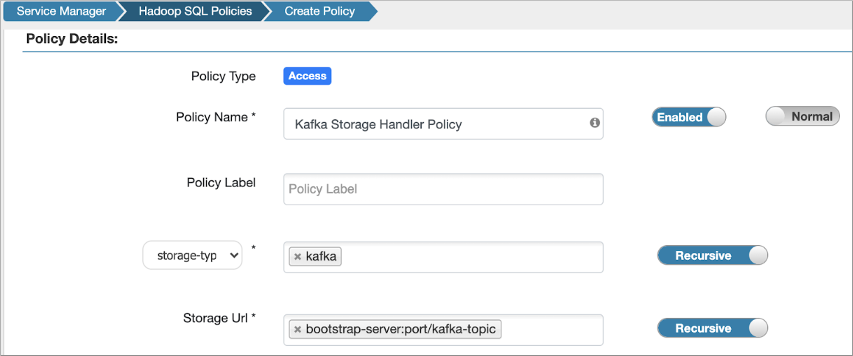
The policy definition sets the kafka storage-type and storage Url format bootstrap-server:port/kafka-topic.
JDBC-based table
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE mytable_jdbc(col1 string, col2 int, col3 double)
STORED BY 'org.apache.hive.storage.jdbc.JdbcStorageHandler'
TBLPROPERTIES ("hive.sql.database.type" = "MYSQL", "hive.sql.jdbc.driver" = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver", "hive.sql.jdbc.url" = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/sample", "hive.sql.dbcp.username" = "hive", "hive.sql.dbcp.password" = "hive", "hive.sql.table" = "MYTABLE");In the query, you need to specify either hive.sql.table or hive.sql.query to tell the
storagehandler how to get data from the JDBC database. In this case, the URI for Ranger
Authentication is jdbc:mysql://localhost/sample/MYTABLE.
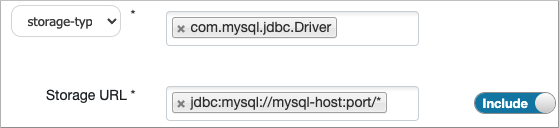
The policy definition sets the com.mysql.jdbc.Driver storage-type and the storage Url format to jdbc:mysql://mysql-host:port/table-name.
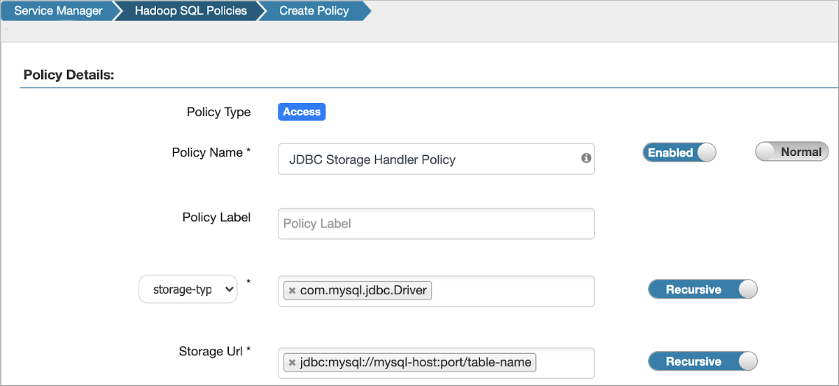
When you create the table, you use the hive.sql.table table property to denote a single table name if your policy defined the Storage Url format using a table name, as shown in the screenshot above.
Alternatively, you can use the wildcard asterisk in the Storage Url format when you define the policy, for example jdbc:mysql://mysql-host:port/* as shown below. In the query, you then use the hive.sql.query table property to denote an arbitrary SQL query: