Security Requirements
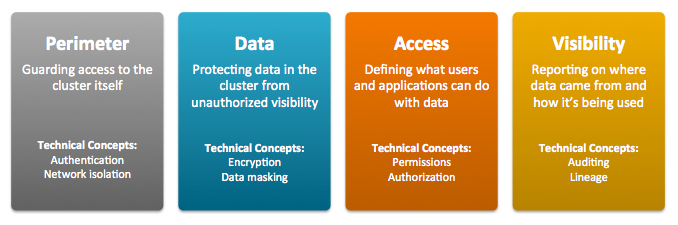
- Perimeter Access to the cluster must be protected from a variety of threats coming from internal and external networks and from a variety of actors. Network isolation can be provided by proper configuration of firewalls, routers, subnets, and the proper use of public and private IP addresses, for example. Authentication mechanisms ensure that people, processes, and applications properly identify themselves to the cluster and prove they are who they say they are, before gaining access to the cluster.
- Data Data in the cluster must always be protected from unauthorized exposure. Similarly, communications between the nodes in the cluster must be protected. Encryption mechanisms ensure that even if network packets are intercepted or hard-disk drives are physically removed from the system by bad actors, the contents are not usable.
- Access Access to any specific service or item of data within the cluster must be specifically granted. Authorization mechanisms ensure that once users have authenticated themselves to the cluster, they can only see the data and use the processes to which they have been granted specific permission.
- Visibility Visibility means that the history of data changes is transparent and capable of meeting data governance policies. Auditing mechanisms ensure that all actions on data and its lineage—source, changes over time, and so on—are documented as they occur.
Securing the cluster to meet specific organizational goals involves using security features inherent to the Hadoop ecosystem as well as using external security infrastructure. The various security mechanisms can be applied in a range of levels.