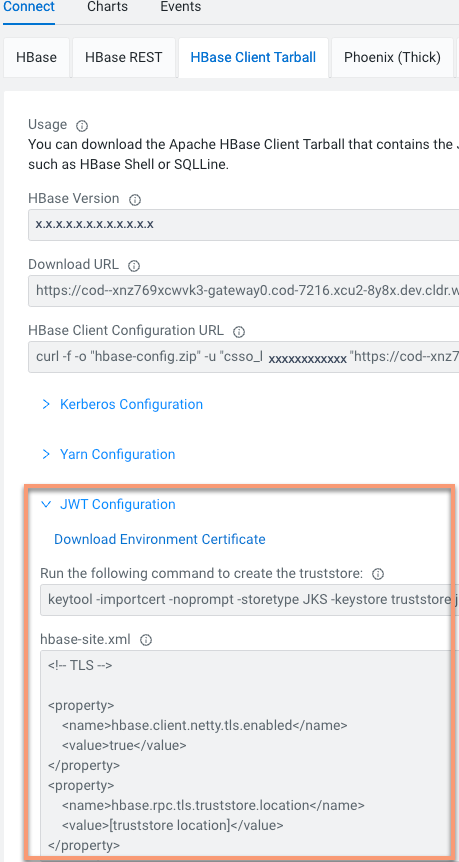
Configuring JWT authentication for HBase client
JWT (JSON Web Token)-based authentication uses an unique identifier and is a standard way of securely transmitting signed information between two parties. Learn how to configure JWT-based authentication for your HBase client.
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is used as the payload of a JSON Web Signature (JWS) structure or as the plaintext of a JSON Web Encryption (JWE) structure, enabling the claims to be digitally signed or integrity protected with a Message Authentication Code (MAC) and/or encrypted. The structure of JWT allows you to verify whether the content is tampered.
To disable JWT authentication for HBase clients, you can use the
--disable-jwt-auth option while creating an operational
database using CDP CLI. Ensure that the COD_JWT_AUTH entitlement is
enabled for the HBase client.
For example,
cdp opdb create-database --environment-name myEnvironment --database-name myDatabase --disable-jwt-auth
- CDP CLI must have been configured to access Cloudera environments.
- Ensure that you have
COD_JWT_AUTHentitlement enabled for your HBase client.
Validate that JWT is correctly set up. Use the following list command to validate that you are able to run commands on HBase.
bin/hbase shell
hbase> listAfter successful authentication, you can see the list of available tables in the database.