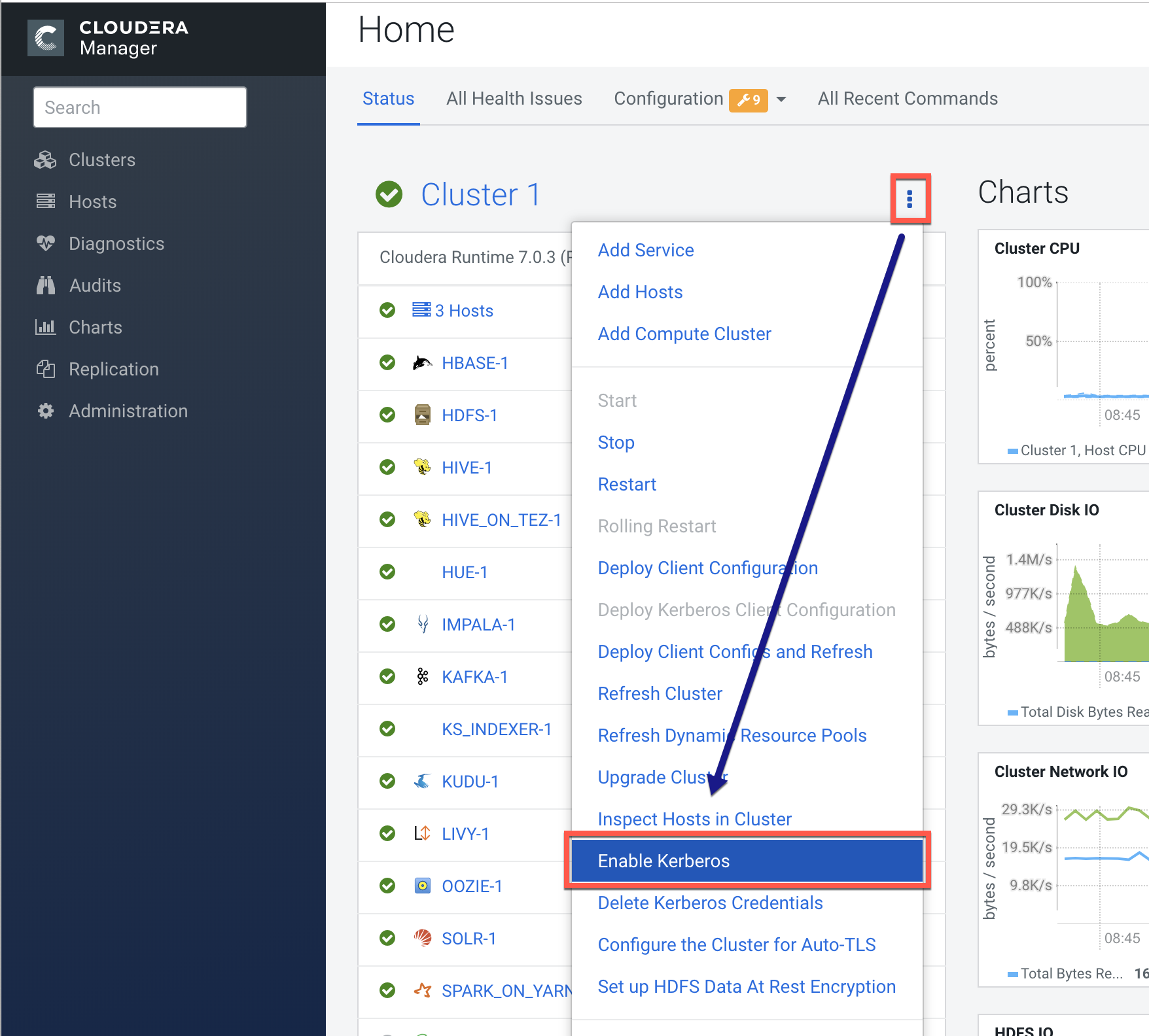
1. Getting Started
- Set up a working KDC in Step 1 of the wizard as described below. Cloudera Manager supports authentication with MIT KDC, Active Directory, and Red Hat Identity Management/FreeIPA.
- Configure the KDC to allow renewable tickets with non-zero ticket lifetimes.
Active Directory allows renewable tickets with non-zero lifetimes by default. You can verify this by checking in Active Directory.
For MIT KDC, make sure you have the following lines in thekdc.conf.max_life = 1d max_renewable_life = 7d
- If you are using Active Directory, make sure LDAP over TLS/SSL (LDAPS) is enabled for the Domain Controllers.
- Host names must be in lowercase. If you use uppercase letters in any host name, the cluster services will not start after enabling Kerberos.
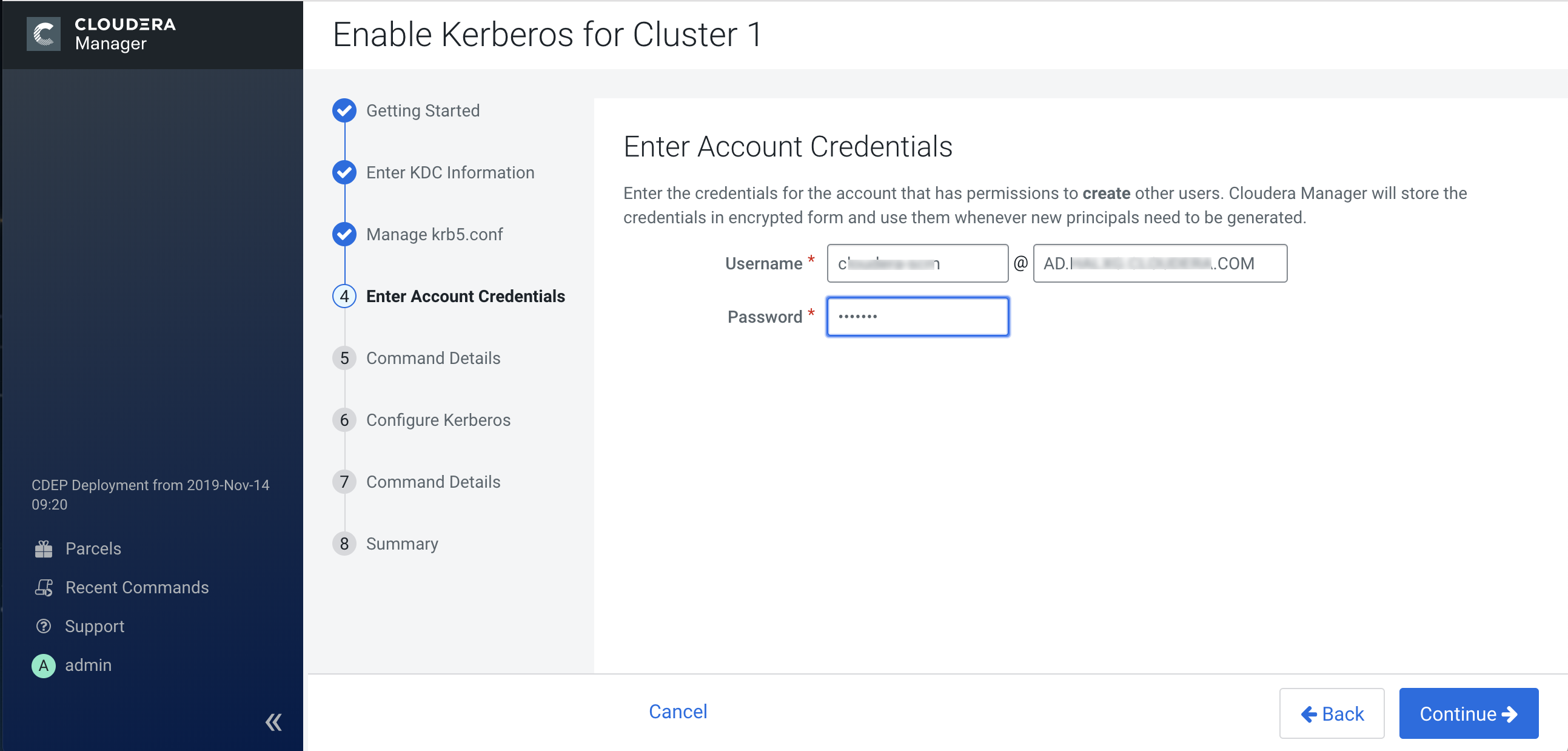
- Create an account for Cloudera Manager that has the permissions to create other
accounts in the KDC. This should have been completed as part of
Step 3: Create the Kerberos Principal for Cloudera Manager Server
.