Rotating database certificates
AWS requires the rotation of the SSL/TLS certificates used for secure communication between Cloudera on cloud Data Lakes and certain Data Hubs and the external AWS RDS database instances that they rely on. Cloudera on cloud provides multiple options to perform the required RDS certificate rotation.
Cloudera on cloud Data Lakes and certain Cloudera Data Hub clusters rely on Amazon Web Services (AWS) Relational Database Service (RDS) database instances that are provisioned by Cloudera during the creation of the respective resources. Similarly to other compute resources, these database instances are created in the cloud accounts of customers. The deployed Cloudera resources use a secure connection to communicate with the database using the SSL/TLS certificates issued by AWS.
SSL/TLS certificates used by Amazon RDS instances created before December 2022 are potentially using certificates that will expire in 2024. Amazon RDS instances with an expiring certificate require that a certification rotation is performed. This will replace the soon expiring certificate with a newer one. If the RDS certification rotation is not performed by 22nd August, 2024, Amazon will perform the rotation for each RDS instance and as a result, the affected Cloudera clusters will not be able to connect to the external database instances.
The actions you need to take depend on whether you have SSL enforcement enabled or disabled on the Data Lake or Cloudera Data Hub cluster as shown in the Database tab of the Data Lake or Data Hub details page. This setting controls whether the database server mandates the use of an encrypted connection. It is recommended to check SSL enforcement setting on the Data Lake of your environment and separately for each Cloudera Data Hub cluster.
It is strongly recommended that, when SSL enforcement is enabled, you do not perform the RDS certificate rotation directly using AWS tools, as this can lead to a service degradation or an outage of Cloudera services using the respective database. Instead, follow the instructions below so that the new certificates can be properly installed by Cloudera before changing them on the database instances. Once you have performed the required steps in Cloudera, there are no additional actions needed in the AWS console. During the database certificate rotation, Cloudera will automatically make the changes required and rotate the certificate of the attached AWS RDS database.
- Sign in to the Cloudera web interface.
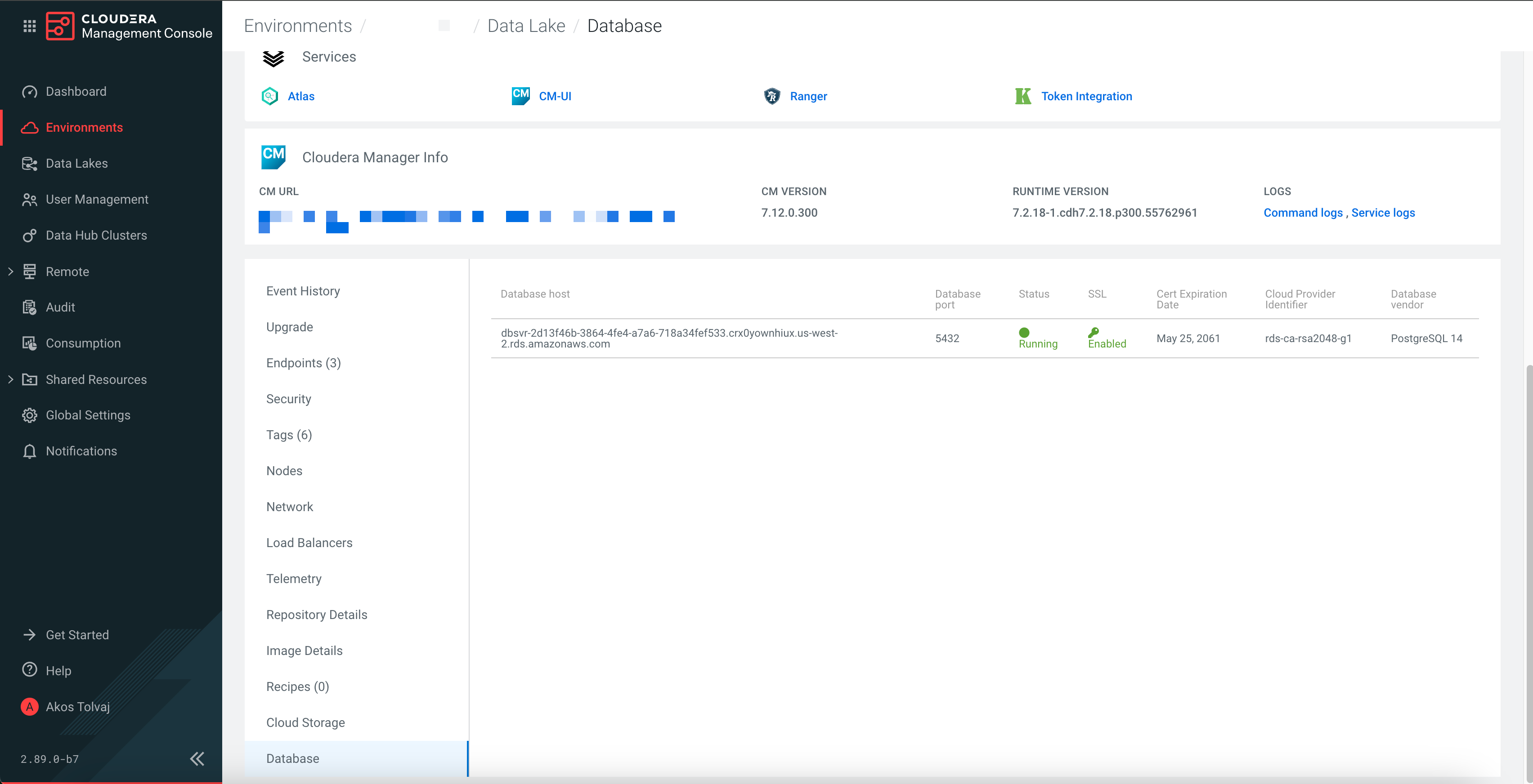
- Navigate to .
- Select the environment by clicking the environment name.
- Click the Data Lake tab.
- Scroll to the bottom of the page and select Database.
- Sign in to the Cloudera web interface.
- Navigate to .
- Select the environment by clicking the environment name.
- Click the Data Hub tab.
- Select a Cloudera Data Hub cluster.
- Scroll to the bottom of the Data Hub details page and select Database.
If the value for SSL is Enabled, it means SSL enforcement is enabled on your Data Lake or Cloudera Data Hub cluster, and you must perform certificate rotation as described in Rotating database certificates when SSL enforcement is enabled. If the value is Disabled, no action is required on that particular Data Lake or Cloudera Data Hub cluster. For further information, see Rotating database certificates when SSL enforcement is disabled.
