Data Engineering clusters
Learn about the default Data Engineering clusters, including cluster definition and template names, included services, and compatible Cloudera Runtime version.
Data Engineering provides a complete data processing solution, powered by Apache Spark and Apache Hive. Spark and Hive enable fast, scalable, fault-tolerant data engineering and analytics over petabytes of data.
Data Engineering cluster definition
This Data Engineering template includes a standalone deployment of Spark and Hive, as well as Apache Oozie for job scheduling and orchestration, Apache Livy for remote job submission, and Hue and Apache Zeppelin for job authoring and interactive analysis.
- Cluster definition names
-
- Data Engineering for AWS
- Data Engineering for Azure
- Data Engineering for Google Cloud
- Data Engineering HA - Spark3 for AWS
- Data Engineering HA - Spark3 for Azure
- Data Engineering HA - Spark3 for Google Cloud
- Data Engineering Spark3 for AWS
- Data Engineering Spark3 for Azure
- Data Engineering Spark3 for Google Cloud
- Data Engineering - Spark3 (ARM) for AWS
- Data Engineering HA - Spark3 (ARM) for AWS
- Cluster template name
-
- Data Engineering: Apache Spark3, Apache Hive, Apache Oozie
- Data Engineering: HA: Apache Spark3, Apache Hive, Apache Oozie
- Included services
-
- HDFS
- Hive
- Hue
- Livy
- Spark 3
- Yarn
- Zeppelin is no longer supported starting with Cloudera Runtime version 7.3.1.
- ZooKeeper
- Oozie is supported for Spark 3 as of Cloudera Runtime version 7.2.18.
- Hive Warehouse Connector is supported as of Cloudera Runtime version 7.2.16.
- Compatible Cloudera Runtime version
-
- 7.2.15
- 7.2.16
- 7.2.17
- 7.2.18
- 7.3.1
Topology of the Data Engineering cluster
Topology is a set of host groups that are defined in the cluster template and cluster definition used by Data Engineering. Data Engineering uses the following topology:
| Host group | Description | Node configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Master Node count: 1 |
The master host group runs the components for managing the cluster resources including Cloudera Manager, Name Node, Resource Manager, as well as other master components such HiveServer2, HMS, Hue etc. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Worker Node count: 3 |
The worker host group runs the components that are used for executing processing tasks (such as NodeManager) and handling storing data in HDFS such as DataNode. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Compute Node count: 0+ |
The compute host group can optionally be used for running data processing tasks (such as NodeManager). By default the number of compute nodes is set to 1 for proper configurations of YARN containers. This node group can be scaled down to 0 when there are no compute needs. Additionally, if load-based auto-scaling is enabled with minimum count set to 0, the compute nodegroup will be resized to 0 automatically. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Gateway Node count: 0+ |
The gateway host group can optionally be used for connecting to the cluster endpoints like Oozie, Beeline etc. This nodegroup does not run any critical services. This nodegroup resides in the same subnet as the rest of the nodegroups. If additional software binaries are required they could be installed using recipes. | m5.2xlarge; gp2 - 100 GB |
| Host group | Description | Node configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Master Node count: 1 |
The master host group runs the components for managing the cluster resources including Cloudera Manager, Name Node, Resource Manager, as well as other master components such HiveServer2, HMS, Hue etc. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Worker Node count: 3 |
The worker host group runs the components that are used for executing processing tasks (such as NodeManager) and handling storing data in HDFS such as DataNode. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Compute Node count: 0+ |
The compute host group can optionally be used for running data processing tasks (such as NodeManager). By default the number of compute nodes is set to 1 for proper configurations of YARN containers. This node group can be scaled down to 0 when there are no compute needs. Additionally, if load-based auto-scaling is enabled with minimum count set to 0, the compute nodegroup will be resized to 0 automatically. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Gateway Node count: 0+ |
The gateway host group can optionally be used for connecting to the cluster endpoints like Oozie, Beeline etc. This nodegroup does not run any critical services. This nodegroup resides in the same subnet as the rest of the nodegroups. If additional software binaries are required they could be installed using recipes. | Standard_D8_v3; StandardSSD_LRS - 100 GB |
| Host group | Description | Node configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Master Node count: 1 |
The master host group runs the components for managing the cluster resources including Cloudera Manager, Name Node, Resource Manager, as well as other master components such HiveServer2, HMS, Hue etc. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Worker Node count: 3 |
The worker host group runs the components that are used for executing processing tasks (such as NodeManager) and handling storing data in HDFS such as DataNode. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Compute Node count: 0+ |
The compute host group can optionally be used for running data processing tasks (such as NodeManager). By default the number of compute nodes is set to 1 for proper configurations of YARN containers. This node group can be scaled down to 0 when there are no compute needs. Additionally, if load-based auto-scaling is enabled with minimum count set to 0, the compute nodegroup will be resized to 0 automatically. | For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions lower
than 7.2.14:
For clusters created with Cloudera Runtime versions
7.2.14 or higher versions:
|
| Gateway Node count: 0+ |
The gateway host group can optionally be used for connecting to the cluster endpoints like Oozie, Beeline etc. This nodegroup does not run any critical services. This nodegroup resides in the same subnet as the rest of the nodegroups. If additional software binaries are required they could be installed using recipes. | e2-standard-8; pd-ssd - 100 GB |
Configurations
| Host group | Service configuration |
|---|---|
| Master | Cloudera Manager, HDFS, Hive (on Tez), HMS, Yarn RM, Oozie, Hue, DAS, Zookeeper, Livy, Zeppelin and Sqoop |
| Gateway | Configurations for the services on the master node |
| Worker | Data Node and YARN NodeManager |
| Compute | YARN NodeManager |
Note the following:
- There is a Hive Metastore Service (HMS) running in the cluster that talks to the same database instance as the Data Lake in the environment.
- If you use CLI to create the cluster, you can optionally pass an argument to create an external database for the cluster use such as Cloudera Manager, Oozie, Hue, and DAS. This database is by default embedded in the master node external volume. If you specify the external database to be of type HA or NON_HA, the database will be provisioned in the cloud provider. For all these types of databases the lifecycle is still associated with the cluster, so upon deletion of the cluster, the database will also be deleted.
- The HDFS in this cluster is for storing the intermediary processing data. For resiliency, store the data in the cloud object stores.
- For high availability requirements choose the Data Engineering High Availability cluster shape.
- Architecture of the Data Engineering HA for AWS cluster
-
The Data Engineering HA for AWS cluster shape provides failure resilience for several of the Data Engineering HA services, including Knox, Oozie, HDFS, HS2, Hue, Livy, YARN, and HMS.
Services that do not yet run in HA mode include Cloudera Manager, DAS, and Zeppelin.
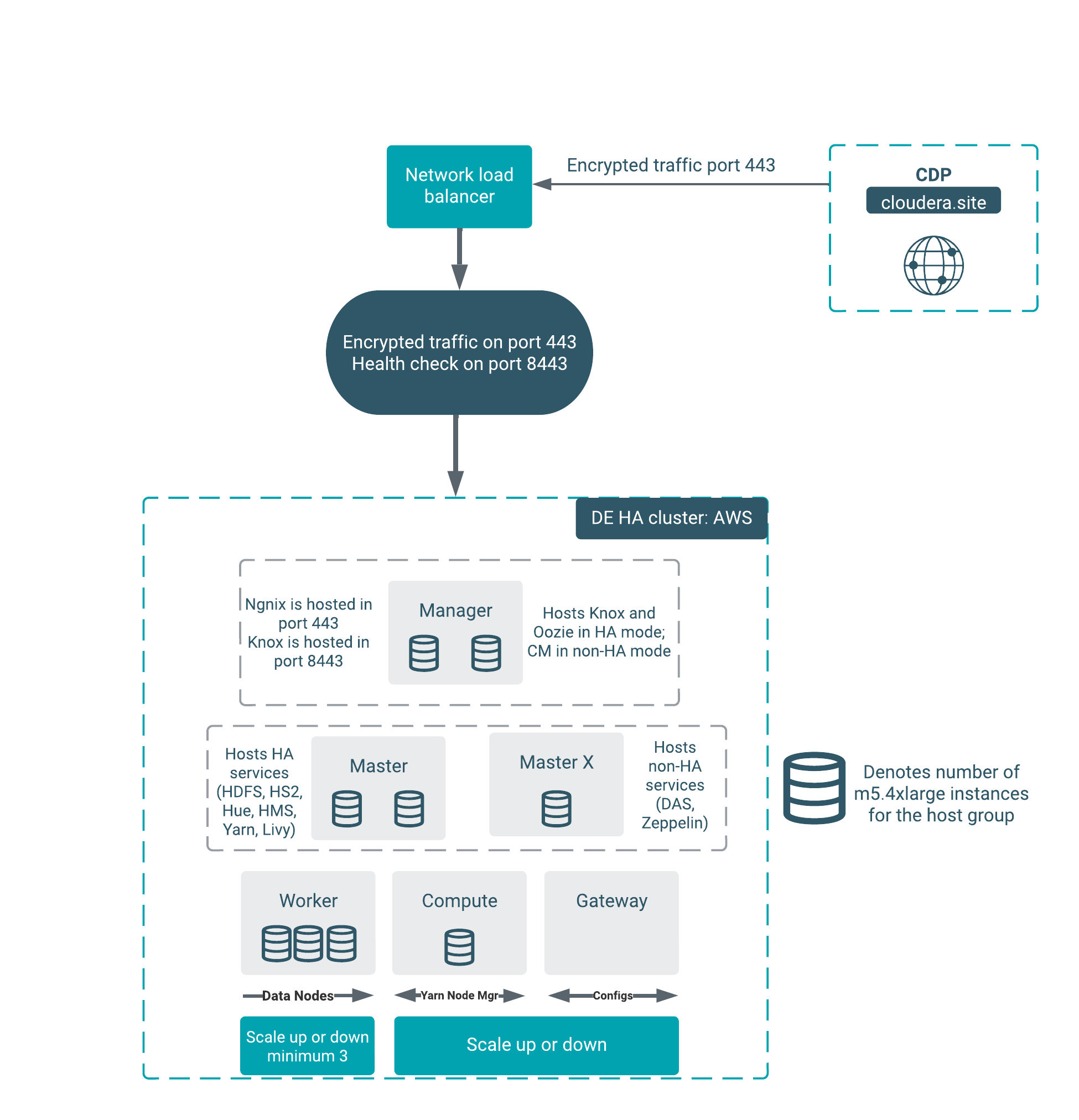
The architecture outlined in the diagram above handles the failure of one node in all of the host groups except for the “masterx” group. See the table below for additional details about the component interactions in failure mode:
Component
Failure
User experience
Knox One of the Knox services is down External users will still be able to access all of the UIs, APIs, and JDBC. Cloudera Manager The first node in manager host group is down The cluster operations (such as repair, scaling, and upgrade) will not work. Cloudera Manager The second node in the manager host group is down No impact. HMS One of the HMS services is down No impact. Hue One of the Hue services is down in master host group No impact. HS2 One of the HS2 services is down in the master host group External users will still be able to access the Hive service via JDBC. But if Hue was accessing that particular service it will not failover to the other host. The quick fix for Hue is to restart Hue to be able to use Hive functionality. YARN One of the YARN services is down No impact. HDFS One of the HDFS services is down No impact. Nginx Nginx in one of the manager hosts is down Fifty percent of the UI, API, and JDBC calls will be affected. If the entire manager node is down, there is no impact. This is caused by the process of forwarding and health checking that is done by the network load-balancer. Oozie One of the Oozie servers is down in the manager host group. No impact for AWS as of Cloudera Runtime version 7.2.11.
If you create a custom template for DE HA, follow these two rules:
- Oozie must be in single hostgroup.
- Oozie and Hue must not be in the same hostgroup.
- Architecture of the Data Engineering HA for Azure cluster
-
The Data Engineering HA for Azure cluster shape provides failure resilience for several of the Data Engineering HA services, including Knox, Oozie, HDFS, HS2, Hue, Livy, YARN, and HMS.
Services that do not yet run in HA mode include Cloudera Manager, DAS, and Zeppelin.
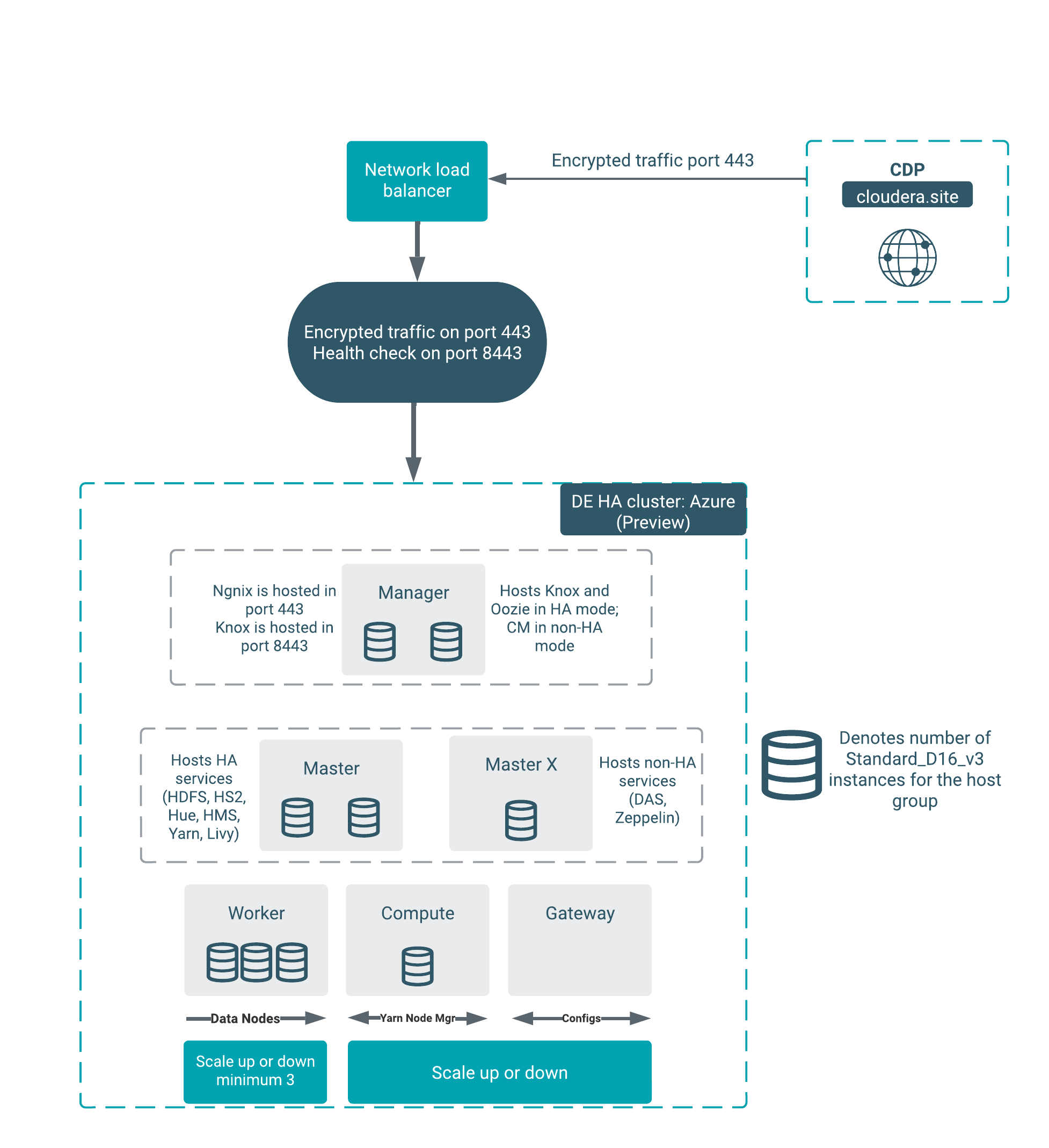
Component
Failure
User experience
Knox One of the Knox services is down External users will still be able to access all of the UIs, APIs, and JDBC. Cloudera Manager The first node in manager host group is down The cluster operations (such as repair, scaling, and upgrade) will not work. Cloudera Manager The second node in the manager host group is down No impact. HMS One of the HMS services is down No impact. Hue One of the Hue services is down in master host group No impact. HS2 One of the HS2 services is down in the master host group External users will still be able to access the Hive service via JDBC. But if Hue was accessing that particular service it will not failover to the other host. The quick fix for Hue is to restart Hue to be able to use Hive functionality. YARN One of the YARN services is down No impact. HDFS One of the HDFS services is down No impact. Nginx Nginx in one of the manager hosts is down Fifty percent of the UI, API, and JDBC calls will be affected. If the entire manager node is down, there is no impact. This is caused by the process of forwarding and health checking that is done by the network load-balancer. Oozie One of the Oozie servers is down in the manager host group. No impact for Azure as of Cloudera Runtime version 7.2.11.
If you create a custom template for DE HA, follow these two rules:
- Oozie must be in single hostgroup.
- Oozie and Hue must not be in the same hostgroup.
Custom templates
Any custom DE HA template that you create must be forked from the default templates of the
corresponding version. You must create a custom cluster definition for this with the JSON
parameter “enableLoadBalancers”: true , using the
create-aws/azure/gcp-cluster CLI command parameter
--request-template. Support for pre-existing custom cluster definitions
will be added in a future release. As with the template, the custom cluster definition must
be forked from the default cluster definition. You are allowed to modify the instance types
and disks in the custom cluster definition. You must not change the placement of the
services like Cloudera Manager, Oozie, and Hue. Currently the custom template is fully
supported only via CLI.
The simplest way to change the DE HA definition is to create a custom cluster definition. In the Create Data Hub UI when you click Advanced Options, the default definition is not used fully, which will cause issues in the HA setup.
