Using an MLflow Model Artifact in a Model REST API
You can use MLflow to create, deploy, and manage models as REST APIs to serve predictions
- To create an MLflow model add the following information when you run an experiment:
mlflow.log_artifacts ("output") mlflow.sklearn.log_model(lr, "model")For example:
# The data set used in this example is from http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Wine+Quality # P. Cortez, A. Cerdeira, F. Almeida, T. Matos and J. Reis. # Modeling wine preferences by data mining from physicochemical properties. In Decision Support Systems, Elsevier, 47(4):547-553, 2009. import os import warnings import sys import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error, r2_score from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet from urllib.parse import urlparse import mlflow from mlflow.models import infer_signature import mlflow.sklearn import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARN) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) def eval_metrics(actual, pred): rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(actual, pred)) mae = mean_absolute_error(actual, pred) r2 = r2_score(actual, pred) return rmse, mae, r2 if __name__ == "__main__": warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") np.random.seed(40) # Read the wine-quality csv file from the URL csv_url = ( "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mlflow/mlflow/master/tests/datasets/winequality-red.csv" ) try: data = pd.read_csv(csv_url, sep=";") except Exception as e: logger.exception( "Unable to download training & test CSV, check your internet connection. Error: %s", e ) # Split the data into training and test sets. (0.75, 0.25) split. train, test = train_test_split(data) # The predicted column is "quality" which is a scalar from [3, 9] train_x = train.drop(["quality"], axis=1) test_x = test.drop(["quality"], axis=1) train_y = train[["quality"]] test_y = test[["quality"]] alpha = 0.5 l1_ratio = 0.5 with mlflow.start_run(): lr = ElasticNet(alpha=alpha, l1_ratio=l1_ratio, random_state=42) lr.fit(train_x, train_y) predicted_qualities = lr.predict(test_x) (rmse, mae, r2) = eval_metrics(test_y, predicted_qualities) print("Elasticnet model (alpha={:f}, l1_ratio={:f}):".format(alpha, l1_ratio)) print(" RMSE: %s" % rmse) print(" MAE: %s" % mae) print(" R2: %s" % r2) mlflow.log_param("alpha", alpha) mlflow.log_param("l1_ratio", l1_ratio) mlflow.log_metric("rmse", rmse) mlflow.log_metric("r2", r2) mlflow.log_metric("mae", mae) predictions = lr.predict(train_x) signature = infer_signature(train_x, predictions) mlflow.sklearn.log_model(lr, "model", signature=signature, registered_model_name="testmodel")In this example we are training a machine learning model using linear regression to predict wine quality. This script creates the MLflow model artifact and logs it to the model directory:
/home/cdsw/.experiments/<experiment_id>/<run_id>/artifacts/models - To view the model, navigate to the Experiments page and select your experiment name. Cloudera AI displays the Runs page and lists all of your current runs.
- Click the run from step 1 that created the MLflow model. Cloudera AI displays the Runs detail page
- Click Artifacts to display a list of all the logged artifacts for the
run.
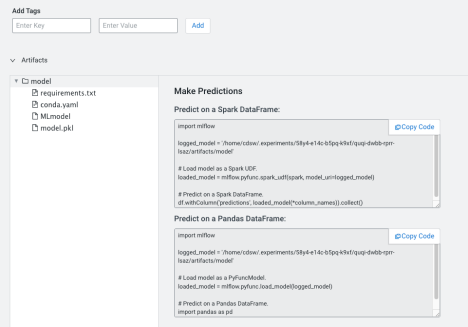
- Click model. Cloudera AI displays the MLflow information you use to create predictions for your experiment.
