MAP data type
This article describes the specifics of the MAP complex data type.
Syntax for MAP
column_name MAP < primitive_type, type > type ::= primitive_type | complex_type
MAP data types represent sets of key-value pairs. These collections
have an arbitrary number of elements, where each element is the same type. A
MAP type is like a miniature table; the table equivalent of a
scalar (primitive) values that has two columns:
- KEY
A scalar type, such as
BIGINT,STRING,TIMESTAMP, which enables you to define non-continuous sequences or categories with arbitrary names. The keys in a map column may represent a numeric sequence of events during a manufacturing process, orTIMESTAMPvalues that correspond to sensor observations.Access as
map_name.key. - VALUE
The second part of a key-value pair in a map. May be a scalar, or another complex type (an
ARRAY, aSTRUCT, or anotherMAP).Access as
map_name.value.If a map contains a
STRUCT, access asmap_name.value.field_name, or asmap_name.field_name.
MAPs in the Dataset Field Interface
In the Dataset Fields interface, an example of a basic
MAP data type may look something like the following image.
Notice that each level of a complex data type may be expanded to show component
details, or collapsed.
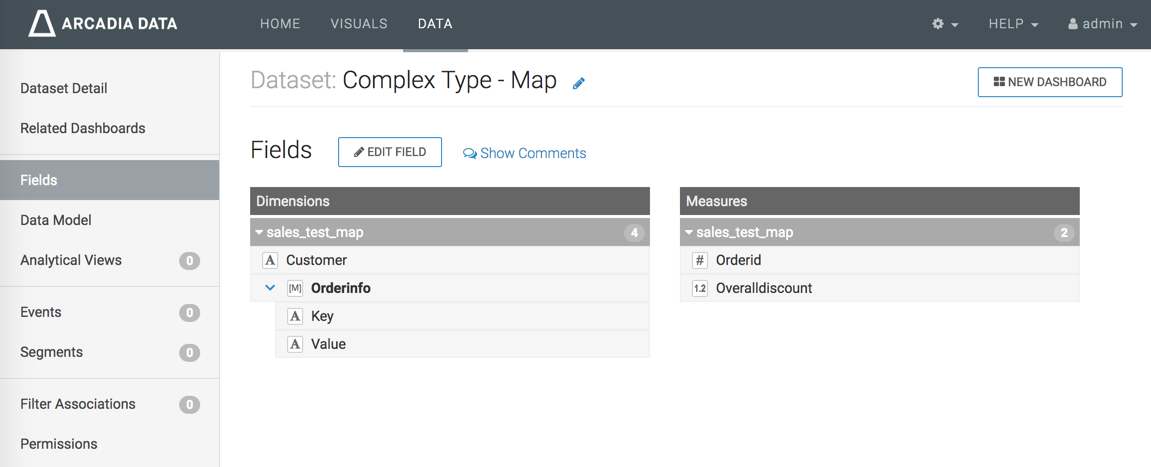
In the example of the dataset Complex Type - Map, you can see that the
Dimension
Customer (a String, symbolized by A), and
Measures
Orderid (an Integer, symbolized by #) and
Overalldiscount (a Real, symbolized by 1.2) are
primitive types. However, the Dimension
Orderinfo is a Map data type, symbolized by [M].
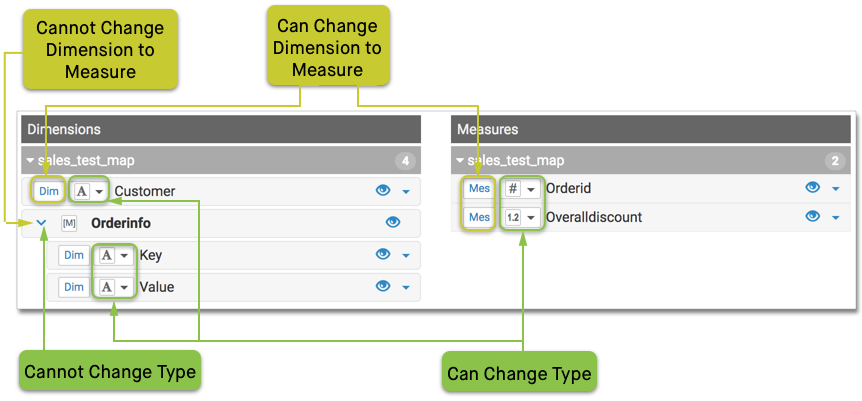
When we click Edit Fields, we can see that while primitive types can be cast as alternate data types (such as Integer into Real), the complex data type Array cannot be changed to another type. However, the primitive components of the array may be cast as other primitive data types. Additionally, unlike other data types, uses complex datatypes only as Dimensions; they or their components cannot be re-defined as Measurements of the dataset.
MAPs in Visuals
When building a visual with complex data, you cannot use the complex type directly, as a whole. However, you can add the primitive components of the complex type to the shelves of the visual.
Changing Field Properties
It is very simple to change field properties for a component of a complex data type. You can change the aggregation function of a component, its type, the display options, and so on, just like a standalone primitive type field.
MAPs in Expression Editor
The expression editor supports the full use of MAPs, both in Dataset and Visual interfaces.


