Set ACLs for Impala
To allow Impala to write to the Hive Warehouse Directory you must set ACLs for Impala.
- The data files for managed tables are located in warehouse location specified by
the Cloudera Manager configuration setting,
Hive Warehouse Directory. - The data files for external tables are located in warehouse location specified
by the Cloudera Manager configuration setting,
Hive Warehouse External Directory.
During the upgrade from CDH to CDP, the ACL settings are taken care automatically for the default warehouse directories. If you decide to change the default warehouse directories after upgrading to CDP then you must run the commands shown in Step 3.
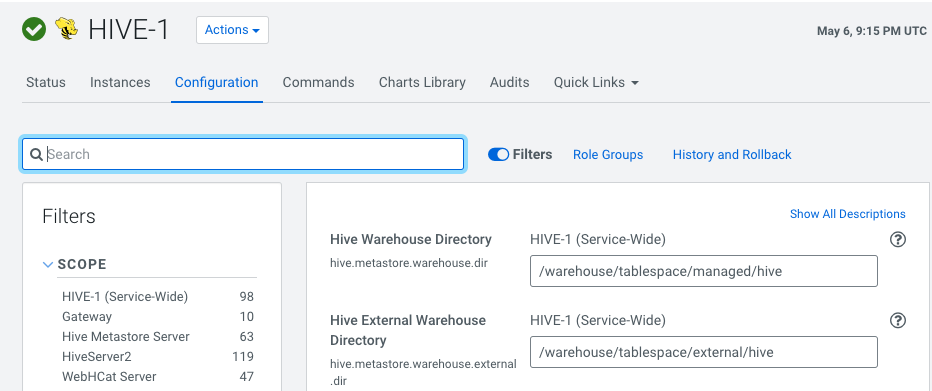
After upgrading, the
(hive.metastore.warehouse.dir) is set to
/warehouse/tablespace/managed/hive where the Impala managed tables are
located.
You can change the location of the warehouse using the Hive Metastore Action menu in Cloudera Manager.
Complete the initial configurations in the free-form fields on the
Hive/Impala Configuration pages in Cloudera
Manager to allow Impala to write to the Hive Warehouse Directory.
-
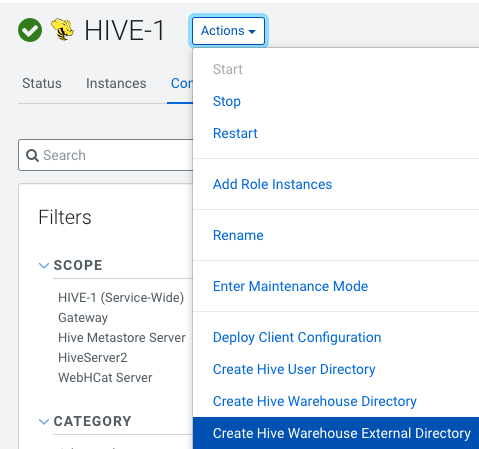
Create Hive Directories using the
Hive Configurationpage -
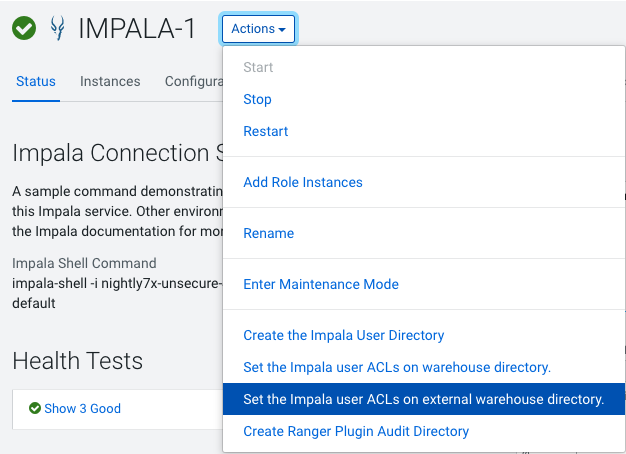
Set Up Impala User ACLs using the
Impala Configurationpage -
Cloudera Manager sets the ACL for the user "Impala" however before starting the Impala service, verify permissions and ACLs set on the
individual database directories using the sub-commands
getfaclandsetfacl.