Transitioning HDP 3.1.5 cluster to CDP Private Cloud Base 7.1.x cluster using the AM2CM tool
Use the AM2CM tool to transition from Ambari-managed HDP cluster to Cloudera Manager-managed CDP cluster.
Transition from HDP to CDP
The latest and supported version of the AM2CM tool is AM2CM 2.8.1.0. The AM2CM tool 2.0.2 and higher supports the transition from HDP to CDP Private Cloud Base 7.1.6 and 7.1.7. However, HDP to CDP 7.1.8 is supported by only from AM2CM 2.3.0 and higher. For more information, see Software download matrix
Transitioning the cluster from HDP to CDP Private Cloud Base using the AM2CM tool
Transition the HDP cluster managed by Ambari to Cloudera Private Cloud Base cluster managed by Cloudera Manager using the AM2CM tool. Here we have taken the AM2CM 2.8.1.0 tool as an example.
- Log in to the Ambari server.
-
In the new tab, enter the URL:
http://<ambari_ip>:<port>/api/v1/clusters/<cluster-name>?format=blueprint_with_hosts - Download the Ambari blueprint and save it in JSON format.
- Download the AM2CM tool from Software download matrix.
-
Extract the am2cm-tool-2.8.1.0-1.tar file to
am2cm-tool-2.8.1.0-1folder. -
Set the
JAVA_HOMEvariable. For example,$ export JAVA_HOME= [path to your installed JDK] - The kafka-broker-ids.ini file generated must be manually copied to $am2cm-tool-2.8.1.0-1/conf/ path before running the tool. For more information, see Extract Kafka Broker ID.
-
Navigate to the
am2cm-tool-2.8.1.0-1/conf/
user-settings.inifile and update Parcels, Cluster name, passwords, and JDBC URL information.# Cluster details cluster.name=<Cluster-Name> cluster.displayname=<Cluster-Name> ambari.cluster.name=<Ambari-cluster-Name cm.rolegroups.enable = false # Hive JDBC settings SERVICE_HIVE_hive_metastore_database_password=<DB-Password> SERVICE_HIVE_hive_jdbc_url_override=<JDBC_URL> # Oozie JDBC settings SERVICE_OOZIE_oozie_database_password=<DB-Password> SERVICE_OOZIE_oozie_service_JPAService_jdbc_url=<JDBC_URL> # Ranger JDBC settings SERVICE_RANGER_ranger_database_password=<Ranger-DB-Password> SERVICE_RANGER_rangeradmin_user_password=<Rangeradmin-user-Password> SERVICE_RANGER_rangerusersync_user_password=<Rangerusersync-user-Password> SERVICE_RANGER_rangertagsync_user_password=<Rangertagsync-user-Password> SERVICE_RANGER_rangerkeyadmin_user_password=<Rangerkeyadmin-user-Password> SERVICE_RANGER_KMS_ranger_kms_master_key_password=<Rangerksmmaster-key-Password> SERVICE_RANGER_KMS_ranger_kms_database_password=<Rangerkms-database-Password> #Knox Settings SERVICE_KNOX_gateway_master_secret=admin -
Generate the Cloudera Manager Deployment template.
# cd am2cm-2.8.1.0-1 # chmod +x ./am2cm.sh # ./am2cm.sh -bp /PATH/TO/Amb_blueprint.json -dt /PATH/TO/cm_deployment_template.json -sv <hdp_version> -tv <cdp_version> Where -sv <hdp_version> -tv <cdp_version> can be selected from the below list: -sv hdp3 -tv 7.1.6 -sv hdp3 -tv 7.1.7 -sv hdp3 -tv 7.1.8 - Check for errors in the console or in the am2cm-tool-2.8.1.0-1/cm_migration.log logs.
- Stop HDP services from Ambari.
- In Ambari UI, disable Auto Start Settings. For more information, see Disable service auto start settings from Ambari Web
-
Import the template into Cloudera Manager using the Cloudera Manager API
through browser or CLI.
- Using browser: If you are using browser, you must authenticate to
the Swagger UI using the Cloudera Manager full admin credentials.
- Copy the URL in the browser and enter.
http://<CM_HOST>:7180/static/apidocs/ui/index.html#!/ClouderaManagerResource/updateDeployment2 - Navigate to Cloudera ManagerResource
- Copy the template in body.
- Click Tryit out!
- Copy the URL in the browser and enter.
- Using
CLI:
curl --user admin:admin -k -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d @cm_deployment_template.json 'http://<CM_HOST>:7180/api/v41/cm/deployment?deleteCurrentDeployment=false'
- Using browser: If you are using browser, you must authenticate to
the Swagger UI using the Cloudera Manager full admin credentials.
-
In Cloudera Manager Parcel screen, download Cloudera
Runtime and distribute the parcel. Cloudera Manager deploys the parcel to
the cluster hosts. The default is 10 concurrent hosts. You can adjust this
to a maximum of 50 by increasing the setting in the Other Parcel
Configurations screen, but must be configured before the
template is applied.

-
Enable Cloudera Manager TLS (Optional) if you want:
- Certificate management: Creating certificates, keystores, and truststores.
- Certificate distribution or configuration:
- Copying keystores & truststores to servers.
- Configuring services to reference these keystores & truststores.
- Configuring related TLS properties for service.
- Ensure that you compare Manual TLS and Auto TLS and then proceed. For more information, see Comparing manual TLS and Auto-TLS
- If you select the Manual TLS option, you must manually configure TLS. For more information, see Manually configure TLS Encryption for Cloudera Manager.
- If you select the Auto TLS option 1, Cloudera Manager handles it
independent of any company certificate authority. This is basically
creating a private certificate authority that only Cloudera Manager
knows about.
- If you want TLS but you do not have any of the external certificate management infrastructures then you will probably want this.
- The benefit is you get full automation for the cluster side (management & certificate distribution and configuration) but requires client configuration to trust the private certificate authority. For more information, see Auto TLS 1
- If you select Auto TLS option 2a, Cloudera Manager handles certificate
management based on a company certificate authority. Cloudera Manager
generates certificates on your behalf using the certificate authority
and performs distribution and configuration for you.
- If you want TLS and are willing to extend trust from an external certificate authority to Cloudera Manager and allow Cloudera Manager to generate certificates will want this.
- The benefit is you get full automation for the cluster side (management & certificate distribution and configuration) but requires extending trust to Cloudera Manager. Clients need not require any additional configuration because they would already trust the global company certificate authority. For more information, see Auto TLS 2
- If you select AutoTLS option 2b, you are only doing certificate
distribution and configuration because you are doing certificate
management outside of Cloudera Manager and manually loading those
certificates into Cloudera Manager's certificate repository.
- If you want TLS but are unwilling to extend trust from an external certificate authority to Cloudera Manager will want this.
- The benefit is you get partially automated for the cluster side (certificate distribution and configuration only). Per-host or per-service certificate management done outside of Cloudera Manager and certificates manually uploaded into Cloudera Manager by an admin. For more information, see Auto TLS 2
-
After the parcels are deployed on Cloudera Manager, activate the Cloudera
Runtime 7.1.x parcels.
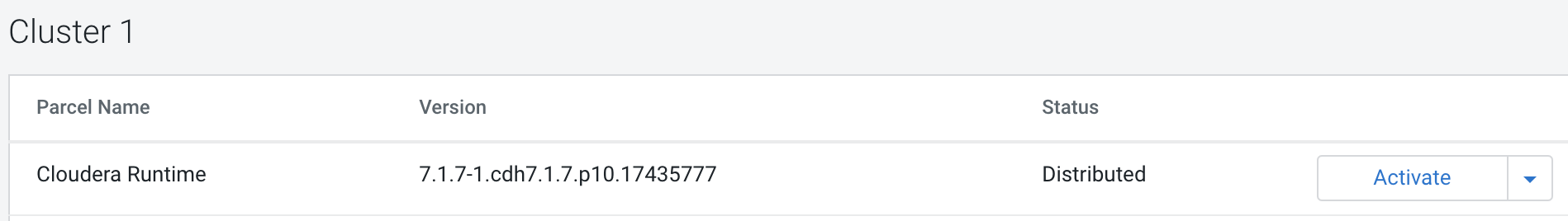
-
LZO package configuration: If HDP is configured with LZO packages then follow
the steps given below.
- Go to the Parcels/Parcel Repository & Network Settings page on Cloudera Manager user interface and add Remote Parcel Repository URLs.URL
- In the Parcels screen - Download, Distribute, and Activate “GPLEXTRAS”. If the HDP intermediate bits or Ambari 7.1.x.x has used LZO packages, then enable or add the packages to Cloudera Manager. For more information, see the Configuring Data Compression documentation.
