STRUCT data type
This article describes the specifics of the STRUCT complex data
type.
Syntax for STRUCT
column_name STRUCT < name : type [COMMENT 'comment_string'], ... > type ::= primitive_type | complex_type
A STRUCT has a fixed number of named fields, and each field can be a
different type. A field within a STRUCT can also be another
STRUCT, an ARRAY, or a
MAP
STRUCTs in the Dataset Field interface
In the Dataset Fields interface, a basic
STRUCT data type may look something like the following example.
You can see that each level of a complex data type can be expanded to show component
details, or collapsed for simplicity.
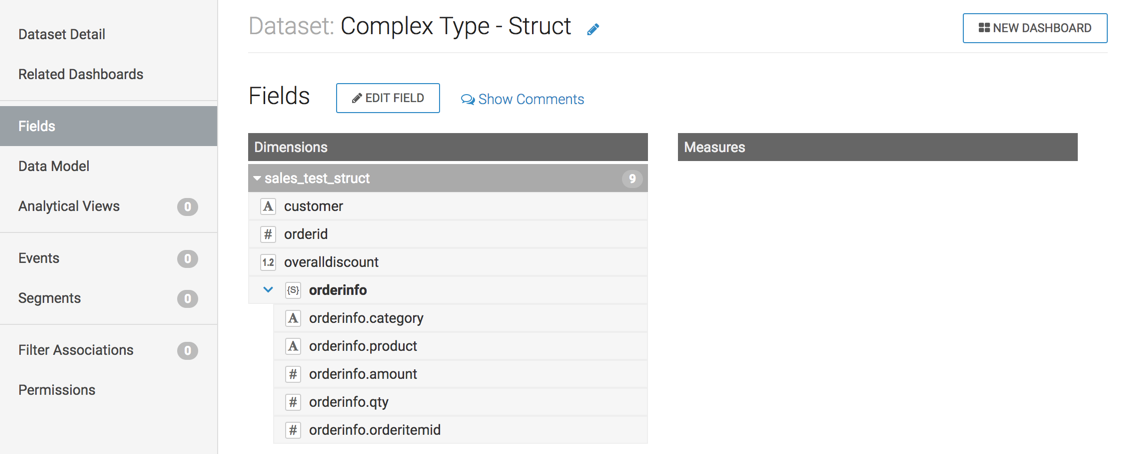
In the example of the dataset Complex Type - Struct, you can see that the
Dimensions
Customer (String, marked with the symbol A), Orderid
(Integer, marked with the symbol #), and overalldiscount
(Real, marked with the symbol 1.2) are primitive types.
However, orderinfo is a Struct data type, marked with the
symbol [S].
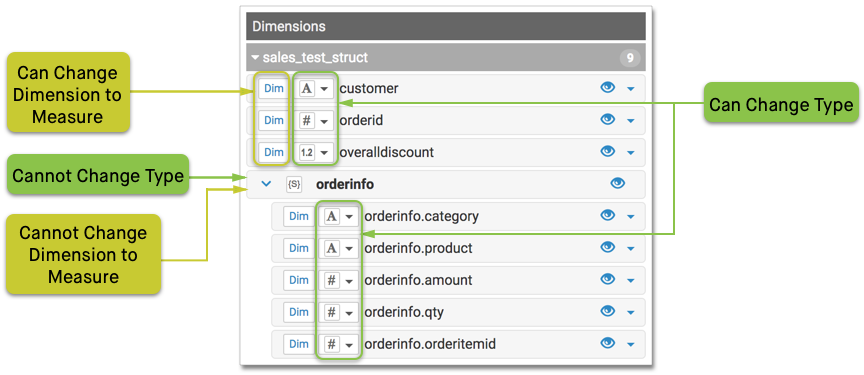
When you click Edit Fields, you can see that while primitive types can be cast as alternate data types (such as Integer into Real), the complex data type STRUCT cannot be changed to another type. However, the primitive components of the array may be cast as other primitive data types. Additionally, unlike other data types, Cloudera Data Visualization uses complex data types only as Dimensions. They or their components cannot be redefined as Measurements of the dataset.
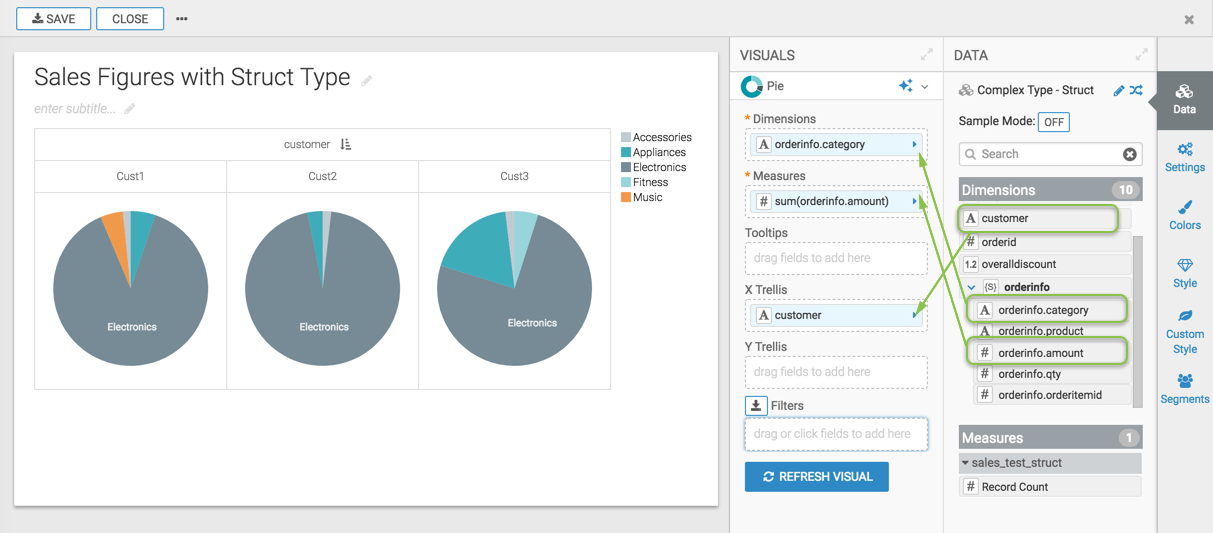
STRUCTs in visuals
When building a visual with complex data, you cannot use the complex type directly as a whole. However, you can add the primitive components of the complex type to the shelves of the visual.
For example, in a Pie visual, you might place Customer Name on the X Trellis shelf, the orderinfo.category component on the Dimensions shelf, and the orderinfo.amount component on the Measures shelf.
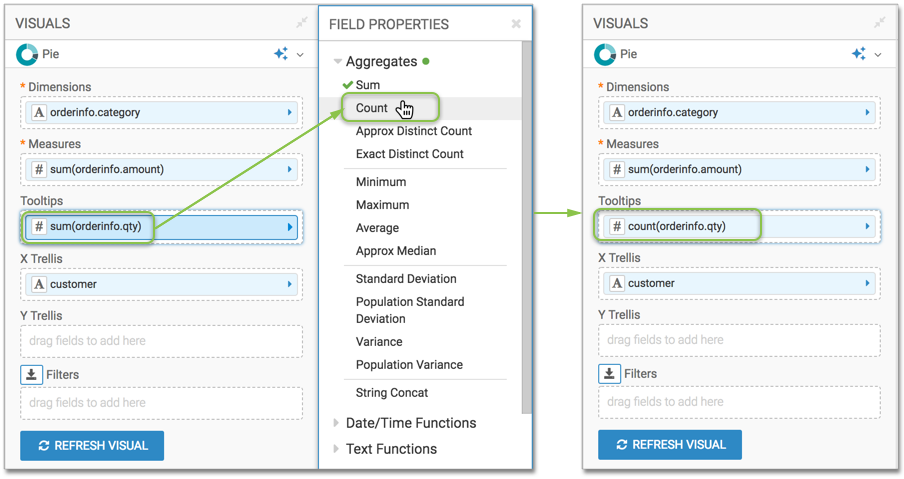
Changing field properties
It is very simple to change field properties for a component of a complex data type.
For example, you can change the orderinfor.qty component on the
Tooltips shelf from the default max()
aggregation to the count() function.
STRUCT in Expression Editor
The expression editor fully supports the use of STRUCTs, both in the
Dataset and Visual interfaces.
This enables advanced data manipulation and customization, leveraging the
capabilities of STRUCT data type in your data visualization
tasks.


