Working with data profiling
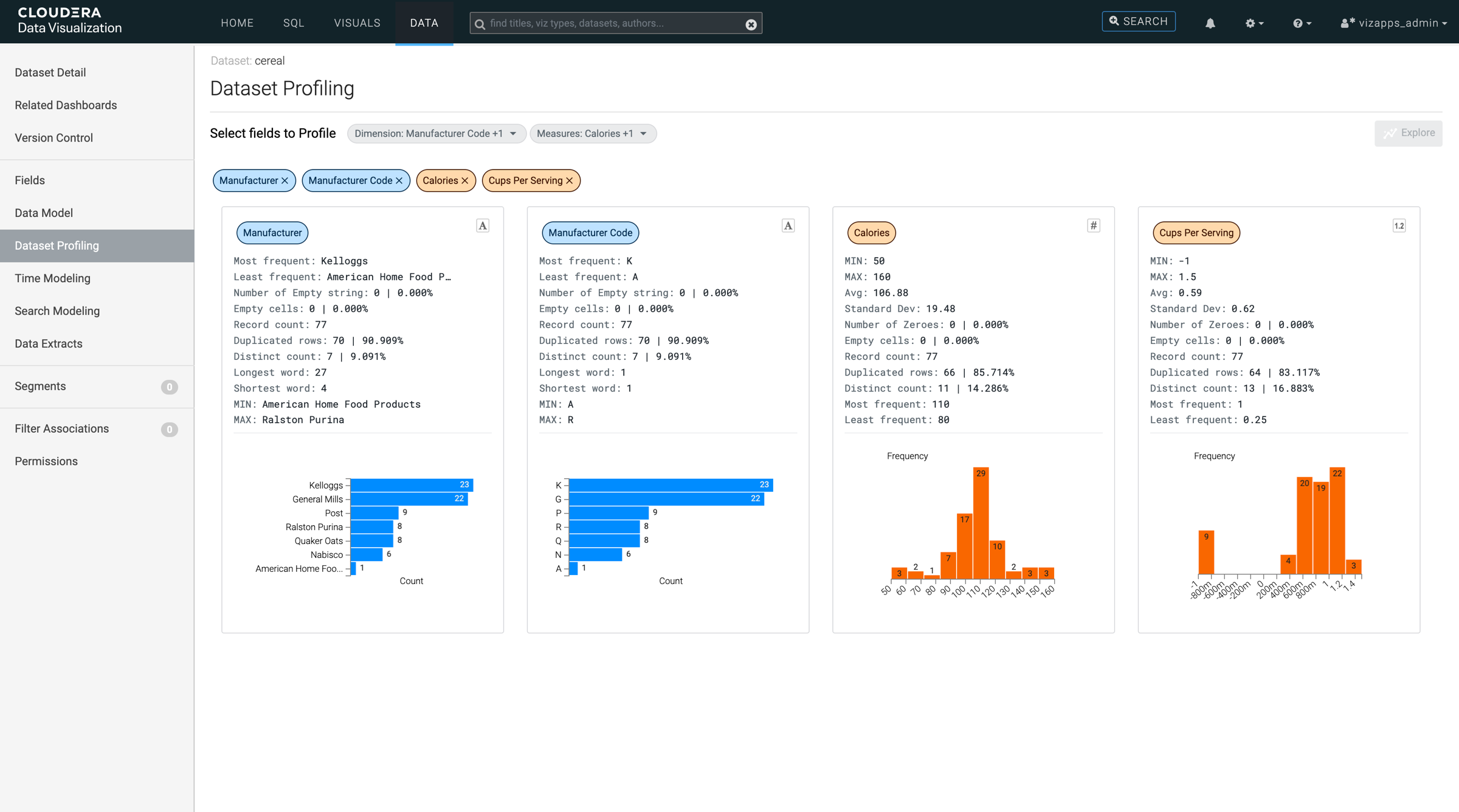
Learn how you can profile your datasets. Dataset profiling provides a high-level overview of your data, offering insights into structure, content, and quality. This feature allows you to quickly assess the suitability of your data for analysis, and helps you identify the appropriate visualizations and any necessary data transformations.
With dataset profiling, you can access detailed statistics for dimension or measure in your dataset, including data type distributions, missing values, and unique values, as well as more in-depth information such as column distribution charts and statistics. These insights help you better understand the quality and characteristics of your data, ensuring it is suitable for the intended analysis or visualization.
-
You need to enable the data profiling feature in . For more information, see Managing data related site settings.